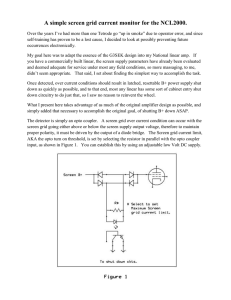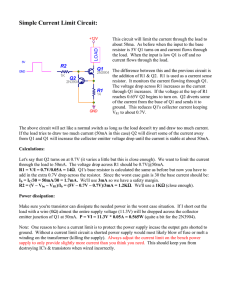
Simple Current Limit Circuit using Transistors
... Let's say that Q2 turns on at 0.7V (it varies a little but this is close enough). We want to limit the current through the load to 50mA. The voltage drop across R1 should be 0.7V@50mA. R1 = V/I = 0.7V/0.05A = 14Ω. Q1's base resistor is calculated the same as before but now you have to add in the ext ...
... Let's say that Q2 turns on at 0.7V (it varies a little but this is close enough). We want to limit the current through the load to 50mA. The voltage drop across R1 should be 0.7V@50mA. R1 = V/I = 0.7V/0.05A = 14Ω. Q1's base resistor is calculated the same as before but now you have to add in the ext ...
Bourns® Rectifier Diodes
... Reverse Leakage Current (IR) is the diode's reverse leakage current, and low IR rectifier diodes have less power dissipation in the reverse direction for power reduction. Junction Capacitance (CJ) is the junction capacitance, and Reverse Recovery Time (Trr) is the turn-off delay from the forward dir ...
... Reverse Leakage Current (IR) is the diode's reverse leakage current, and low IR rectifier diodes have less power dissipation in the reverse direction for power reduction. Junction Capacitance (CJ) is the junction capacitance, and Reverse Recovery Time (Trr) is the turn-off delay from the forward dir ...
Test Procedure for the NCP2823BGEVB Evaluation Board
... J11 terminal. Like this the device can be evaluate under powering condition very similar that battery power supplies. These tests are provided in order to guarantee a good assembly of the NCP2823 on its dedicated board, it do not consist in parametric test which is already done at chip level. ...
... J11 terminal. Like this the device can be evaluate under powering condition very similar that battery power supplies. These tests are provided in order to guarantee a good assembly of the NCP2823 on its dedicated board, it do not consist in parametric test which is already done at chip level. ...
BU1-AC - AC-voltage relay
... Unit BU1-AC is equipped with an independent over(U>) and undervoltage supervision (U<) with separate adjustable pickup values and common trip delay (t) and hysteresis (DIFF). The voltages are compared with the set reference values. For three-phase overvoltage supervision the highest voltage in each ...
... Unit BU1-AC is equipped with an independent over(U>) and undervoltage supervision (U<) with separate adjustable pickup values and common trip delay (t) and hysteresis (DIFF). The voltages are compared with the set reference values. For three-phase overvoltage supervision the highest voltage in each ...
MIL-STD-883H METHOD 3007.1 LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE 1
... LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE 1. PURPOSE. This method establishes the means for assuring circuit performance to the limits specified in the applicable acquisition document with regard to LOW level output drive which is specified as a maximum value (V OL max) or a minimum value (V OL min). This method app ...
... LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE 1. PURPOSE. This method establishes the means for assuring circuit performance to the limits specified in the applicable acquisition document with regard to LOW level output drive which is specified as a maximum value (V OL max) or a minimum value (V OL min). This method app ...
Position Indicators
... Our range of position indicators is designed for use in indicator panels and mimic panels. Position indicators for electrical circuit breakers and isolators are available with indicator discs in 'Bar', 'Angle' and 'Disconnector' designs. Indicator discs for valves are available in 'Amber-White' and ...
... Our range of position indicators is designed for use in indicator panels and mimic panels. Position indicators for electrical circuit breakers and isolators are available with indicator discs in 'Bar', 'Angle' and 'Disconnector' designs. Indicator discs for valves are available in 'Amber-White' and ...
A dc-Side Sensorless Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converter
... In conventional CHB-MC based PV systems the dc current sensors are required by the MPPT module and the dc voltage sensors are required for the capacitors’ voltages control system and the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) generator. Hence, in higher level converters, many isolated dc sensors are required, ...
... In conventional CHB-MC based PV systems the dc current sensors are required by the MPPT module and the dc voltage sensors are required for the capacitors’ voltages control system and the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) generator. Hence, in higher level converters, many isolated dc sensors are required, ...
SWREGv1.1 Low Noise Switching Regulator FEATURES
... TYPICAL APPLICATION Figure 1 demonstrates how the SRv1.1 might power a UAV video system. This system contains gimbaled EO and IR cameras, a video switch, and a video transmitter. ...
... TYPICAL APPLICATION Figure 1 demonstrates how the SRv1.1 might power a UAV video system. This system contains gimbaled EO and IR cameras, a video switch, and a video transmitter. ...
Get a Constant +5V Output by Switching Between a +5V Input and a
... to charge a single-cell battery. Resistors RIDC and RISET set the DC-input current limit and charge-current set points, respectively. Since the SYS output (pins 23 and 24) is not used, the charge current will be constant and not dictated by the load current. Q1 and Q2 are dual PNP transistors, avail ...
... to charge a single-cell battery. Resistors RIDC and RISET set the DC-input current limit and charge-current set points, respectively. Since the SYS output (pins 23 and 24) is not used, the charge current will be constant and not dictated by the load current. Q1 and Q2 are dual PNP transistors, avail ...
Product Sheet MKP-C1X-9,5-75
... Creepage between terminals (mm): 16 Clearance (mm): 11 Box qty (pcs): 36 ...
... Creepage between terminals (mm): 16 Clearance (mm): 11 Box qty (pcs): 36 ...
DN561 High Voltage, High Efficiency Positive to Negative Converter
... widely used in LCD devices, OLED displays, audio amplifiers, industrial machinery, semiconductor manufacturing process control equipment, measurement tools, testing systems, LED drivers and battery chargers. Many of these applications require high power levels and extended input voltage ranges, two ...
... widely used in LCD devices, OLED displays, audio amplifiers, industrial machinery, semiconductor manufacturing process control equipment, measurement tools, testing systems, LED drivers and battery chargers. Many of these applications require high power levels and extended input voltage ranges, two ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.