CS311 - NUS School of Computing
... The first machines with real programs were developed in the 1940’s. In those days, the programmer would put his or her name down on a computer time chart (say for an hour), and then would have total control of the machine for that time. The programmer operated the computer, put in a program, debugge ...
... The first machines with real programs were developed in the 1940’s. In those days, the programmer would put his or her name down on a computer time chart (say for an hour), and then would have total control of the machine for that time. The programmer operated the computer, put in a program, debugge ...
Unix processes and threads
... invokes command string from program e.g., system("date > file"); handled by shell (/usr/bin/ksh) never call from setuid programs ...
... invokes command string from program e.g., system("date > file"); handled by shell (/usr/bin/ksh) never call from setuid programs ...
ch02
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
CS-502, Distributed and Multiprocessor Systems
... – One copy and move as needed – Multiple copies • Make each frame read-only • On write tell other processors to invalidate page to be written • Write through CS502 Spring 2006 ...
... – One copy and move as needed – Multiple copies • Make each frame read-only • On write tell other processors to invalidate page to be written • Write through CS502 Spring 2006 ...
10B17CI307: UNIX Programming Lab
... Introduction to Unix Operating System and comparing it with Windows OS. Overview to Open Source Software. Writing and studying about how to execute C program in Unix environment using GCC compiler along with phases of compilation. Executing simple Hello World C program in UNIX environment using ed / ...
... Introduction to Unix Operating System and comparing it with Windows OS. Overview to Open Source Software. Writing and studying about how to execute C program in Unix environment using GCC compiler along with phases of compilation. Executing simple Hello World C program in UNIX environment using ed / ...
slides-2
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
No Slide Title
... Executive — Local Procedure Call Facility The LPC passes requests and results between client and server ...
... Executive — Local Procedure Call Facility The LPC passes requests and results between client and server ...
Handout13
... can be accessed transparently Location independence is a stronger requirement than Location ...
... can be accessed transparently Location independence is a stronger requirement than Location ...
ThreadsWinAndCpp11
... t.join() blocks until thread t completes, e.g., exits its thread function t.detach() disassociates thread object t from underlying OS thread. All theads must be joined or detached (not both) before thread object goes ...
... t.join() blocks until thread t completes, e.g., exits its thread function t.detach() disassociates thread object t from underlying OS thread. All theads must be joined or detached (not both) before thread object goes ...
Multiprocessor and Distributed Systems
... • Make each frame read-only • On write tell other processors to invalidate page to be written • Write through CS-3013 & CS-502, Summer 2006 ...
... • Make each frame read-only • On write tell other processors to invalidate page to be written • Write through CS-3013 & CS-502, Summer 2006 ...
ppt
... The environment vector is a list of “NAME=VALUE” pairs that associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. ...
... The environment vector is a list of “NAME=VALUE” pairs that associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. ...
The Case for VOS: The Vector Operating System Abstract Carnegie Mellon University,
... 1. Application-agnostic changes: One way to provide opportunities for making vector calls without application support is to introduce system call queues to coalesce similar requests. An application issues a system call through libc, which inserts the call into a syscall queue while the application w ...
... 1. Application-agnostic changes: One way to provide opportunities for making vector calls without application support is to introduce system call queues to coalesce similar requests. An application issues a system call through libc, which inserts the call into a syscall queue while the application w ...
Week-2
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program ...
6-up pdf
... Because the cluster size is smaller than for the 16-bit FAT file system, the amount of internal fragmentation is reduced ...
... Because the cluster size is smaller than for the 16-bit FAT file system, the amount of internal fragmentation is reduced ...
No Slide Title
... Local Procedure Call Facility The LPC passes requests and results between client and server ...
... Local Procedure Call Facility The LPC passes requests and results between client and server ...
1.) Process is A.) program in High level language kept on disk B
... second pass, after the symbol table is complete, it does the actual assembly by translating the operations and so on. 2) In Two pass assembler the object code generation is done during the ? a. b. c. d. ...
... second pass, after the symbol table is complete, it does the actual assembly by translating the operations and so on. 2) In Two pass assembler the object code generation is done during the ? a. b. c. d. ...
Software review The Bioà toolkits – a brief overview
... Tk), it is a failing that is not nearly as well supported as it is in Java or Python. Perl does, however, have a non-trivial advantage over Python and Java in that it can be automatically upgraded and enhanced using the CPAN module (for Comprehensive Perl Archive Network), included in the default in ...
... Tk), it is a failing that is not nearly as well supported as it is in Java or Python. Perl does, however, have a non-trivial advantage over Python and Java in that it can be automatically upgraded and enhanced using the CPAN module (for Comprehensive Perl Archive Network), included in the default in ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... • Files have attributes, usually including the following: – Name: human-readable file name – Identifier: numeric identifier within the file system – Type: some systems formally support different file types – Location: address of the file in a storage device – Size: number of bytes (or words, or bloc ...
... • Files have attributes, usually including the following: – Name: human-readable file name – Identifier: numeric identifier within the file system – Type: some systems formally support different file types – Location: address of the file in a storage device – Size: number of bytes (or words, or bloc ...
The Operating System
... For billing For usage statistics (later used for tuning and development of mechanisms) Protection and security - concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
... For billing For usage statistics (later used for tuning and development of mechanisms) Protection and security - concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
Week-3
... System calls cause transfer to VM monitor VM monitor changes the register contents and program counter and transfer control back to guest OS ...
... System calls cause transfer to VM monitor VM monitor changes the register contents and program counter and transfer control back to guest OS ...
PowerPoint Format
... that associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. Passing environment variables among processes and inheriting variables by a process’s children are flexible means of passing information to components of the user-mode system software. The environment-variable mechanism provi ...
... that associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. Passing environment variables among processes and inheriting variables by a process’s children are flexible means of passing information to components of the user-mode system software. The environment-variable mechanism provi ...
Threads
... • When a traditional, single-threaded program requests a service from the operating system, it must wait for that service to complete, often leaving the CPU idle • Multithreading provides progress even though one or more threads wait for an event as long as other threads are active Ceng 334 - Operat ...
... • When a traditional, single-threaded program requests a service from the operating system, it must wait for that service to complete, often leaving the CPU idle • Multithreading provides progress even though one or more threads wait for an event as long as other threads are active Ceng 334 - Operat ...
UNIT-1 Introduction to System Programming
... 4 main functions: i. Allocation of space in main memory for the programs. ii. Linking of object modules with each other. iii. Adjust all address dependent locations. iv. Physically loading the machine instructions and data into the main memory. ...
... 4 main functions: i. Allocation of space in main memory for the programs. ii. Linking of object modules with each other. iii. Adjust all address dependent locations. iv. Physically loading the machine instructions and data into the main memory. ...
Operating System Structures - McMaster Computing and Software
... Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block is passed as a parameter in a register This approach taken by Linux and Solaris Parameters placed, or pushed, onto the stack b ...
... Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block is passed as a parameter in a register This approach taken by Linux and Solaris Parameters placed, or pushed, onto the stack b ...
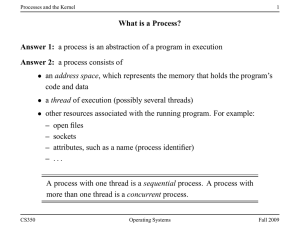
What is a Process? Answer 1: a process is an abstraction of a
... • multiprogramming means having multiple processes existing at the same time • most modern, general purpose operating systems support multiprogramming • all processes share the available hardware resources, with the sharing coordinated by the operating system: – Each process uses some of the availab ...
... • multiprogramming means having multiple processes existing at the same time • most modern, general purpose operating systems support multiprogramming • all processes share the available hardware resources, with the sharing coordinated by the operating system: – Each process uses some of the availab ...
Library (computing)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.In computer science, a library is a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. This means that as long as a higher level program uses a library to make system calls, it does not need to be re-written to implement those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal function-call. What distinguishes the call as being to a library, versus being to another function in the same program, is the way that the code is organized in the system. Library code is organized in such a way that it can be used by multiple programs that have no connection to each other, while code that is part of a program is organized to only be used within that one program. This distinction can gain a hierarchical notion when a program grows large, such as a multi-million-line program. In that case, there may be internal libraries that are reused by independent sub-portions of the large program. The distinguishing feature is that a library is organized for the purposes of being reused by independent programs or sub-programs, and the user only needs to know the interface, and not the internal details of the library.The value of a library is the reuse of the behavior. When a program invokes a library, it gains the behavior implemented inside that library without having to implement that behavior itself. Libraries encourage the sharing of code in a modular fashion, and ease the distribution of the code. The behavior implemented by a library can be connected to the invoking program at different program lifecycle phases. If the code of the library is accessed during the build of the invoking program, then the library is called a static library. An alternative is to build the executable of the invoking program and distribute that, independently from the library implementation. The library behavior is connected after the executable has been invoked to be executed, either as part of the process of starting the execution, or in the middle of execution. In this case the library is called a dynamic library. A dynamic library can be loaded and linked as part of preparing a program for execution, by the linker. Alternatively, in the middle of execution, an application may explicitly request that a module be loaded.Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services. Such libraries have commoditized the services which a modern application requires. As such, most code used by modern applications is provided in these system libraries.