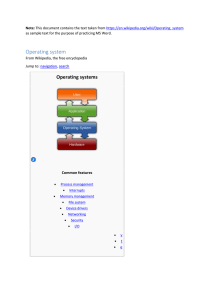
Windows 95/98/NT (Introduction)
... Win32-based programs do not need to yield to share resources. This is because Win32based applications (called processes) use multithreading, which provides for multiprocessing. A thread in a program is a unit of code that can get a time slice from the operating system to run concurrently with other ...
... Win32-based programs do not need to yield to share resources. This is because Win32based applications (called processes) use multithreading, which provides for multiprocessing. A thread in a program is a unit of code that can get a time slice from the operating system to run concurrently with other ...
12_Pthreads
... • Because threads within the same process share resources: – Changes made by one thread to shared system resources (such as closing a file) will be seen by all other threads – Two pointers having the same value point to the same data – Reading and writing to the same memory locations is possible – T ...
... • Because threads within the same process share resources: – Changes made by one thread to shared system resources (such as closing a file) will be seen by all other threads – Two pointers having the same value point to the same data – Reading and writing to the same memory locations is possible – T ...
A real-time operating system
... Main article: Mainframe computer See also: History of IBM mainframe operating systems ...
... Main article: Mainframe computer See also: History of IBM mainframe operating systems ...
sample unformatted document
... Mac OS by Apple Computer became the first widespread OS to feature a graphical user interface. Many of its features such as windows and icons would later become commonplace in GUIs. The first microcomputers did not have the capacity or need for the elaborate operating systems that had been developed ...
... Mac OS by Apple Computer became the first widespread OS to feature a graphical user interface. Many of its features such as windows and icons would later become commonplace in GUIs. The first microcomputers did not have the capacity or need for the elaborate operating systems that had been developed ...
Handout
... fileManager objects. FileControlBlock and OpenFile objects will be handled much like Threads and ProcessControlBlocks. They are a limited resource. A limited supply is created at start-up time and then they are managed by the fileManager. There is a free list of FileControlBlock objects and a free l ...
... fileManager objects. FileControlBlock and OpenFile objects will be handled much like Threads and ProcessControlBlocks. They are a limited resource. A limited supply is created at start-up time and then they are managed by the fileManager. There is a free list of FileControlBlock objects and a free l ...
System Software
... program written in a procedural language such as BASIC into machine language that can be directly executed by the computer. Computers can execute only machine language programs. Programs written in any other language must be translated into a machine language load module, which is suitable for loadi ...
... program written in a procedural language such as BASIC into machine language that can be directly executed by the computer. Computers can execute only machine language programs. Programs written in any other language must be translated into a machine language load module, which is suitable for loadi ...
Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
... Filesystem manipulation The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission ...
... Filesystem manipulation The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission ...
Chapter 9 Streams and File I/O
... • When providing a file name as an argument for opening a file, a simple file name may be used if the file is in the same directory as the program being run. • A full or relative path name also can be used. • A full path name is the complete path name, starting from the root directory. ...
... • When providing a file name as an argument for opening a file, a simple file name may be used if the file is in the same directory as the program being run. • A full or relative path name also can be used. • A full path name is the complete path name, starting from the root directory. ...
Operating-System Structures
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
Providing Dynamic Update in an Operating System
... In addition to the above mentioned impact on availability, dynamically updatable systems have other benefits. Such systems provide a good prototyping environment. They allow, for example, a new page replacement, file system, or network policy to be tested without rebooting. Further, in more mature s ...
... In addition to the above mentioned impact on availability, dynamically updatable systems have other benefits. Such systems provide a good prototyping environment. They allow, for example, a new page replacement, file system, or network policy to be tested without rebooting. Further, in more mature s ...
2.01 - Suan Dusit Rajabhat University
... be recovered after a crash, just that the file system data structures (the metadata files) are undamaged and reflect some consistent state prior to the crash. The log is stored in the third metadata file at the beginning of ...
... be recovered after a crash, just that the file system data structures (the metadata files) are undamaged and reflect some consistent state prior to the crash. The log is stored in the third metadata file at the beginning of ...
Processes - UC Davis Computer Science
... PCB may hang around for a while (exit code, etc.) eventually, OS deallocates the PCB ECS 150 (Operating Systems) ...
... PCB may hang around for a while (exit code, etc.) eventually, OS deallocates the PCB ECS 150 (Operating Systems) ...
Threads - McMaster Computing and Software
... Machine, the implementation of threads is based upon whatever OS and hardware the JVM is running on, i.e. either Pthreads or Win32 threads depending on the system. ...
... Machine, the implementation of threads is based upon whatever OS and hardware the JVM is running on, i.e. either Pthreads or Win32 threads depending on the system. ...
Discovering Computers 2005
... stand-alone operating systems Summarize the startup process on a personal computer Identify various network operating systems Describe the functions of an operating system ...
... stand-alone operating systems Summarize the startup process on a personal computer Identify various network operating systems Describe the functions of an operating system ...
Benu: Operating System Increments for Embedded
... tools that will be used as a base. The operating system and development tools might be selected from the available commercial off the shelf tools (COTS), such as µC/OS-II [1], QNX [2], VxWorks [3], or from freely available tools, such as Linux [4] and and FreeRTOS [5]. Possible disadvantages of COTS ...
... tools that will be used as a base. The operating system and development tools might be selected from the available commercial off the shelf tools (COTS), such as µC/OS-II [1], QNX [2], VxWorks [3], or from freely available tools, such as Linux [4] and and FreeRTOS [5]. Possible disadvantages of COTS ...
Tornado: Maximizing Locality and Concurrency in a Shared Memory
... Localizing data structures in the Tornado fashion results in some new implementation and policy tradeoffs. For example, without a global page cache, it is difficult to implement global policies like a clock replacement algorithm in its purest form. Memory management in Tornado is based on a working ...
... Localizing data structures in the Tornado fashion results in some new implementation and policy tradeoffs. For example, without a global page cache, it is difficult to implement global policies like a clock replacement algorithm in its purest form. Memory management in Tornado is based on a working ...
9. Exceptions
... “time- A.timefreq.bldrdoc.gov”, 13); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream( ) ) ); ...
... “time- A.timefreq.bldrdoc.gov”, 13); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream( ) ) ); ...
linux: a product of the internet
... install multi-user operating systems on microcomputers. Second, with the cost of hardware continually dropping, hardware manufactures can no longer afford to develop and support proprietary operating systems. A proprietary operating system is usually written and always owned by the manufacturer of t ...
... install multi-user operating systems on microcomputers. Second, with the cost of hardware continually dropping, hardware manufactures can no longer afford to develop and support proprietary operating systems. A proprietary operating system is usually written and always owned by the manufacturer of t ...
Import Settings: Base Settings: Brownstone Default Highest Answer
... Ans: The code can be written faster, is more compact, and is easier to understand and debug. In addition, improvements in compiler technology will improve the generated code for the entire operating system by simple recompilation. Finally, an operating system is far easier to port — to move to some ...
... Ans: The code can be written faster, is more compact, and is easier to understand and debug. In addition, improvements in compiler technology will improve the generated code for the entire operating system by simple recompilation. Finally, an operating system is far easier to port — to move to some ...
File
... Ans: The code can be written faster, is more compact, and is easier to understand and debug. In addition, improvements in compiler technology will improve the generated code for the entire operating system by simple recompilation. Finally, an operating system is far easier to port — to move to some ...
... Ans: The code can be written faster, is more compact, and is easier to understand and debug. In addition, improvements in compiler technology will improve the generated code for the entire operating system by simple recompilation. Finally, an operating system is far easier to port — to move to some ...
Operating System Structure
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) ...
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Third Edition ANDREW S
... protection from each other The stacks of each thread are intended to be in separate RAM, but if one thread has a problem (e.g., with pointers or array addressing), it could write over the stack of another thread ...
... protection from each other The stacks of each thread are intended to be in separate RAM, but if one thread has a problem (e.g., with pointers or array addressing), it could write over the stack of another thread ...
JavaProgramming
... Java Resources • All Presentation Programs: http://www.mcs.lugave.net/CSSVC. • Developer Resources for Java Technology: http://java.sun.com/ • Java Tutorials: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/index.html • Java SE Downloads: http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp • Java Standard API & ...
... Java Resources • All Presentation Programs: http://www.mcs.lugave.net/CSSVC. • Developer Resources for Java Technology: http://java.sun.com/ • Java Tutorials: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/index.html • Java SE Downloads: http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp • Java Standard API & ...
Library (computing)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.In computer science, a library is a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. This means that as long as a higher level program uses a library to make system calls, it does not need to be re-written to implement those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal function-call. What distinguishes the call as being to a library, versus being to another function in the same program, is the way that the code is organized in the system. Library code is organized in such a way that it can be used by multiple programs that have no connection to each other, while code that is part of a program is organized to only be used within that one program. This distinction can gain a hierarchical notion when a program grows large, such as a multi-million-line program. In that case, there may be internal libraries that are reused by independent sub-portions of the large program. The distinguishing feature is that a library is organized for the purposes of being reused by independent programs or sub-programs, and the user only needs to know the interface, and not the internal details of the library.The value of a library is the reuse of the behavior. When a program invokes a library, it gains the behavior implemented inside that library without having to implement that behavior itself. Libraries encourage the sharing of code in a modular fashion, and ease the distribution of the code. The behavior implemented by a library can be connected to the invoking program at different program lifecycle phases. If the code of the library is accessed during the build of the invoking program, then the library is called a static library. An alternative is to build the executable of the invoking program and distribute that, independently from the library implementation. The library behavior is connected after the executable has been invoked to be executed, either as part of the process of starting the execution, or in the middle of execution. In this case the library is called a dynamic library. A dynamic library can be loaded and linked as part of preparing a program for execution, by the linker. Alternatively, in the middle of execution, an application may explicitly request that a module be loaded.Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services. Such libraries have commoditized the services which a modern application requires. As such, most code used by modern applications is provided in these system libraries.