Ch 6 Test C
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
X - My Teacher Site
... 3) During early embryonic development of female carriers for color blindness, the normal allele is inactivated by chance in about half of the cells. Why, then, aren’t 50% of female carriers color-blind? ...
... 3) During early embryonic development of female carriers for color blindness, the normal allele is inactivated by chance in about half of the cells. Why, then, aren’t 50% of female carriers color-blind? ...
So you say you want extra credit…
... 7. Fertilization — fusion of male and female gametes 8. Gamete — male and female sex cells, sperm and eggs 9. Genetic recombination — major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by reassortment or crossing over during meiosis 10. Genetics — branch of biology that studies heredity 11. Ge ...
... 7. Fertilization — fusion of male and female gametes 8. Gamete — male and female sex cells, sperm and eggs 9. Genetic recombination — major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by reassortment or crossing over during meiosis 10. Genetics — branch of biology that studies heredity 11. Ge ...
Using a HMM to Identify Ectopic Gene Conversion Events
... The divergence time between duplicate genes is estimated using sequence divergence which can be greatly affected by the presence of gene conversions. An ectopic gene conversion event causes the sequence of one duplicate to overwrite the other, thereby removing any nucleotide sequence divergence pres ...
... The divergence time between duplicate genes is estimated using sequence divergence which can be greatly affected by the presence of gene conversions. An ectopic gene conversion event causes the sequence of one duplicate to overwrite the other, thereby removing any nucleotide sequence divergence pres ...
Unit 7.2 ws
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation In many eukaryotes, a short region of DNA containing the base sequence TATATA or TATAAA is known as the TATA box. The TATA box marks the beginning of a gene. It also helps position the RNA polymerase. When RNA polymerase binds in the correct position, transcription can oc ...
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation In many eukaryotes, a short region of DNA containing the base sequence TATATA or TATAAA is known as the TATA box. The TATA box marks the beginning of a gene. It also helps position the RNA polymerase. When RNA polymerase binds in the correct position, transcription can oc ...
genetic ppt melanie - IB
... allowing annealing of the primers to the single-stranded DNA template. Stable DNADNA hydrogen bonds are only formed when the primer sequence very closely matches the template sequence. The polymerase binds to the primer-template hybrid and begins DNA formation. Extension/elongation step: commonly a ...
... allowing annealing of the primers to the single-stranded DNA template. Stable DNADNA hydrogen bonds are only formed when the primer sequence very closely matches the template sequence. The polymerase binds to the primer-template hybrid and begins DNA formation. Extension/elongation step: commonly a ...
Crossing Over and Gene Mapping
... chromosome and about the distances between those genes. This reasoning depends on this basic principle: • To a first approximation, crossovers are equally likely to occur at any point along the length of a chromosome. It follows that: • the probability of a crossover between two genes is proportiona ...
... chromosome and about the distances between those genes. This reasoning depends on this basic principle: • To a first approximation, crossovers are equally likely to occur at any point along the length of a chromosome. It follows that: • the probability of a crossover between two genes is proportiona ...
“This is getting really old . . . ” The Genetics of Aging
... of damage to macromolecules, intracellular organelles, cells, tissues, organs. ...
... of damage to macromolecules, intracellular organelles, cells, tissues, organs. ...
Lab Section: TA
... anagenesis can occur without cladogenesis 2 A photoheterotroph is an organism that obtains its energy A from sunlight and carbon from an inorganic source 3 All animals have at least one cluster of homeotic genes A 4 All species are defined as interbreeding groups of individuals A reproductively isol ...
... anagenesis can occur without cladogenesis 2 A photoheterotroph is an organism that obtains its energy A from sunlight and carbon from an inorganic source 3 All animals have at least one cluster of homeotic genes A 4 All species are defined as interbreeding groups of individuals A reproductively isol ...
Let`s talk about sex... chromosomes Examples of well known human
... This can happen in at least 2 different ways. The more common way is for an embryo to undergo a mitotic error early in development, which usually results in chromosome loss. If the resulting cells can survive without the chromosome, both populations of cells may continue to expand, resulting in a mo ...
... This can happen in at least 2 different ways. The more common way is for an embryo to undergo a mitotic error early in development, which usually results in chromosome loss. If the resulting cells can survive without the chromosome, both populations of cells may continue to expand, resulting in a mo ...
Sex chromosomes, dosage compensation, and aneuploidy
... This can happen in at least 2 different ways. The more common way is for an embryo to undergo a mitotic error early in development, which usually results in chromosome loss. If the resulting cells can survive without the chromosome, both populations of cells may continue to expand, resulting in a mo ...
... This can happen in at least 2 different ways. The more common way is for an embryo to undergo a mitotic error early in development, which usually results in chromosome loss. If the resulting cells can survive without the chromosome, both populations of cells may continue to expand, resulting in a mo ...
Applications for Toxicogenomics in Risk Assess
... physiological function (Slikker et al., 2004). There is evidence for a dose-dependent transition for formaldehyde, in that inflammatory and proliferative responses in the nasal epithelium do not occur at doses lower than those that are tumorigenic (Conolly et al., 2003). However, it is possible that ...
... physiological function (Slikker et al., 2004). There is evidence for a dose-dependent transition for formaldehyde, in that inflammatory and proliferative responses in the nasal epithelium do not occur at doses lower than those that are tumorigenic (Conolly et al., 2003). However, it is possible that ...
Section 11-3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH11.QXD
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
Section 11-3 - Pearson School
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
... A Summary of Mendel’s Principles (page 272) 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Mendel’s principles. a. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by genes that are passed from parents to their offspring. b. Two or more forms of the gene for a single trait can ...
Heredity Inherited Traits - Saint Mary Catholic School
... • The gametes are the sex cells of the parents. When formed they undergo meiosis. In the process, the chromosomes are duplicated, then separated and packaged as separate sets in the sex cells. • If this were not the case, the number of chromosomes would double every time a new organism was created. ...
... • The gametes are the sex cells of the parents. When formed they undergo meiosis. In the process, the chromosomes are duplicated, then separated and packaged as separate sets in the sex cells. • If this were not the case, the number of chromosomes would double every time a new organism was created. ...
PPT - Med Study Group
... chromosomal regions that have been associated with a complex trait • If a QTL is correct then one of the genes residing in this region should be directly involved in causing trait Remember – More than one gene! therefore – more than one QTL too ...
... chromosomal regions that have been associated with a complex trait • If a QTL is correct then one of the genes residing in this region should be directly involved in causing trait Remember – More than one gene! therefore – more than one QTL too ...
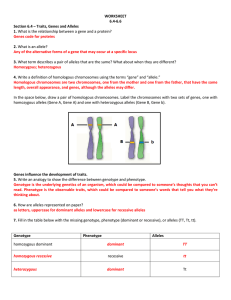
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... No. The two genes are unlikely to be separated by crossing over, so they will be inherited together. 4. Which does sexual reproduction create; new alleles or new combinations of alleles? New combinations of alleles 5. How is the production of unique genetic combinations an advantage to organisms and ...
... No. The two genes are unlikely to be separated by crossing over, so they will be inherited together. 4. Which does sexual reproduction create; new alleles or new combinations of alleles? New combinations of alleles 5. How is the production of unique genetic combinations an advantage to organisms and ...
Meiosis and Mendel
... E. Heredity patterns can be calculated with probability 1. probability - the likelihood that a particular event will happen 2. Probability applies to random events such as meiosis and fertilization ...
... E. Heredity patterns can be calculated with probability 1. probability - the likelihood that a particular event will happen 2. Probability applies to random events such as meiosis and fertilization ...
Gene Section FGA7 (Fused Gene 7 to AML1) in Oncology and Haematology
... Metaphase FISH analysis using the BAC probe RP11-104M2 hybridized to the patient's metaphase shows one normal green signal on the intact chromosome 4 (dashed arrow) and two smaller green signals on der(21) (arrowhead) and on der(4) (arrow) as a result of the t(4;21)(q28;q22). ...
... Metaphase FISH analysis using the BAC probe RP11-104M2 hybridized to the patient's metaphase shows one normal green signal on the intact chromosome 4 (dashed arrow) and two smaller green signals on der(21) (arrowhead) and on der(4) (arrow) as a result of the t(4;21)(q28;q22). ...