A systematic screen for tube morphogenesis and branching genes in the Drosophila tracheal system. PLoS Genetics 7: e1002087.
... secondary, and terminal branching, branch fusion, and tube size control [11,28]. Mapping and molecular characterization of these genes identified many components and modulators of the Breathless FGFR signaling pathway. These include Branchless FGF, which activates Breathless FGFR and plays a central ...
... secondary, and terminal branching, branch fusion, and tube size control [11,28]. Mapping and molecular characterization of these genes identified many components and modulators of the Breathless FGFR signaling pathway. These include Branchless FGF, which activates Breathless FGFR and plays a central ...
Cloning - Allegiance
... plant; the original tree spread its roots, which later sprouted new trees. When earthworms are cut in half, they regenerate the missing parts of their bodies, leading to two worms with the same set of genes. However, the ability to intentionally create a clone in the animal kingdom by working on the ...
... plant; the original tree spread its roots, which later sprouted new trees. When earthworms are cut in half, they regenerate the missing parts of their bodies, leading to two worms with the same set of genes. However, the ability to intentionally create a clone in the animal kingdom by working on the ...
Genetics Terminology Illustrated III Epistasis
... them. The “trigger” genes produce proteins that will activate an incompletely penetrant trait, perhaps by simply uncoiling a segment of DNA and exposing a gene to an “on” position.. • A well-nourished, unstressed fish is more likely to have all the necessary genes acting in concert, and thus express ...
... them. The “trigger” genes produce proteins that will activate an incompletely penetrant trait, perhaps by simply uncoiling a segment of DNA and exposing a gene to an “on” position.. • A well-nourished, unstressed fish is more likely to have all the necessary genes acting in concert, and thus express ...
3. Inheritance and hereditary
... The simplest cases of Mendelian inheritance are those in which the multiple alleles of a gene exhibit clear dominant-recessive relationships. In such a situation, a diploid animal will express the phenotype associated with the dominant allele whenever at least one dominant allele is present, while a ...
... The simplest cases of Mendelian inheritance are those in which the multiple alleles of a gene exhibit clear dominant-recessive relationships. In such a situation, a diploid animal will express the phenotype associated with the dominant allele whenever at least one dominant allele is present, while a ...
The SELF-PRUNING gene of tomato regulates
... resulting in a single cycle consisting of vegetative, inflorescence and floral phases, with a clear separation of the vegetative and reproductive phases. By contrast, in the sympodial shoots of the day-neutral tomato plant the vegetative and reproductive phases alternate regularly. The primary (juve ...
... resulting in a single cycle consisting of vegetative, inflorescence and floral phases, with a clear separation of the vegetative and reproductive phases. By contrast, in the sympodial shoots of the day-neutral tomato plant the vegetative and reproductive phases alternate regularly. The primary (juve ...
Identification of Genetic and Epigenetic Risk Factors for Psoriasis
... of the European population. ~10–30% of patients develop psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Genetic variation in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) increases risk of developing PS. However, only ~10% of individuals with this risk factor develop PS, indicating that other genetic effects and environmen ...
... of the European population. ~10–30% of patients develop psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Genetic variation in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) increases risk of developing PS. However, only ~10% of individuals with this risk factor develop PS, indicating that other genetic effects and environmen ...
The Molecular and Genetic Bases of S-RNase
... S-RNase gene, the bulk of the sequence was from one allele of the S-RNase gene, with the sequence of the region to be examined contributed by another allele. Transgenic plants that produce each chimeric S-RNase then were examined for their ability to reject pollen of the two alleles used in the chim ...
... S-RNase gene, the bulk of the sequence was from one allele of the S-RNase gene, with the sequence of the region to be examined contributed by another allele. Transgenic plants that produce each chimeric S-RNase then were examined for their ability to reject pollen of the two alleles used in the chim ...
Natural variation in nucleolar dominance reveals
... opportunity to study the same NORs in an active or silenced state, an opportunity we exploited to deduce the relationships between NOR chromatin topology, transcriptional activity, and NOR localization relative to the nucleolus. We show that partial, but not complete, NOR decondensation is the cytog ...
... opportunity to study the same NORs in an active or silenced state, an opportunity we exploited to deduce the relationships between NOR chromatin topology, transcriptional activity, and NOR localization relative to the nucleolus. We show that partial, but not complete, NOR decondensation is the cytog ...
Hox patterning of the vertebrate rib cage
... genes located in a single cluster, mammals have 39 Hox genes arranged in four clusters, which are further subdivided into thirteen paralogous groups based on sequence similarity and position within the cluster. Hox expression along the vertebrate AP axis exhibits overlapping expression domains with ...
... genes located in a single cluster, mammals have 39 Hox genes arranged in four clusters, which are further subdivided into thirteen paralogous groups based on sequence similarity and position within the cluster. Hox expression along the vertebrate AP axis exhibits overlapping expression domains with ...
Hox patterning of the vertebrate rib cage
... genes located in a single cluster, mammals have 39 Hox genes arranged in four clusters, which are further subdivided into thirteen paralogous groups based on sequence similarity and position within the cluster. Hox expression along the vertebrate AP axis exhibits overlapping expression domains with ...
... genes located in a single cluster, mammals have 39 Hox genes arranged in four clusters, which are further subdivided into thirteen paralogous groups based on sequence similarity and position within the cluster. Hox expression along the vertebrate AP axis exhibits overlapping expression domains with ...
Ces locus embedded proteins control the non
... the emetic strain F4810/72 were constructed and their impact on cereulide biosynthesis was assessed. The hydrolase CesH turned out to be a part of the complex regulatory network controlling cereulide synthesis on a transcriptional level, while the ABC transporter CesCD was found to be essential for ...
... the emetic strain F4810/72 were constructed and their impact on cereulide biosynthesis was assessed. The hydrolase CesH turned out to be a part of the complex regulatory network controlling cereulide synthesis on a transcriptional level, while the ABC transporter CesCD was found to be essential for ...
Slide 1
... The Role of Fertilization Mendel’s garden had several stocks of pea plants that were “truebreeding,” meaning that they were self-pollinating, and would produce offspring with identical traits to themselves. In other words, the traits of each successive generation would be the same. A trait is a spec ...
... The Role of Fertilization Mendel’s garden had several stocks of pea plants that were “truebreeding,” meaning that they were self-pollinating, and would produce offspring with identical traits to themselves. In other words, the traits of each successive generation would be the same. A trait is a spec ...
Epigenetic Control of Apomixis
... Pennisetum squamulatum (L.) R.Br. was reported to express in egg cells before fertilization and induced parthenogenesis, thus produced haploid offsprings in transgenic sexual pearl millet [4]. Spatial and temporal shift in the expression of the genes of reproductive pathways in sexual and apomictic ...
... Pennisetum squamulatum (L.) R.Br. was reported to express in egg cells before fertilization and induced parthenogenesis, thus produced haploid offsprings in transgenic sexual pearl millet [4]. Spatial and temporal shift in the expression of the genes of reproductive pathways in sexual and apomictic ...
CHAPTER 6 Gregor Mendel and Genetics
... genotype alleles an individual inherits at a particular genetic locus heterozygote organism that inherits two different alleles for a given gene homozygote organism that inherits two alleles of the same type for a given gene hybrid offspring that results from a cross between two different types of p ...
... genotype alleles an individual inherits at a particular genetic locus heterozygote organism that inherits two different alleles for a given gene homozygote organism that inherits two alleles of the same type for a given gene hybrid offspring that results from a cross between two different types of p ...
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
... (C) Evolution is occurring, as allele frequencies are changing greatly over time (D) Clearly there is a heterozygote advantage (E) The frequencies above violate Hardy-Weinberg expectations ...
... (C) Evolution is occurring, as allele frequencies are changing greatly over time (D) Clearly there is a heterozygote advantage (E) The frequencies above violate Hardy-Weinberg expectations ...
REVIEW Why Do Bacterial Plasmids Carry Some Genes and Not
... other functions and winning out in competition between clones. This could be an important advantage if sequential replacements of clones such as those observed in intestinal Escherichia coli (Caugant et al., 1981) are common modes of evolution in bacteria. 3. Some antibiotic resistance genes on plas ...
... other functions and winning out in competition between clones. This could be an important advantage if sequential replacements of clones such as those observed in intestinal Escherichia coli (Caugant et al., 1981) are common modes of evolution in bacteria. 3. Some antibiotic resistance genes on plas ...
PPTX - Bioinformatics.ca
... Important details • To test for under-enrichment of “black”, test for overenrichment of “red”. • The EASE score used by DAVID subtracts one from the observed overlap between gene list and gene set to ensure >1 from the list is in the gene set. • Need to choose “background population” appropriately, ...
... Important details • To test for under-enrichment of “black”, test for overenrichment of “red”. • The EASE score used by DAVID subtracts one from the observed overlap between gene list and gene set to ensure >1 from the list is in the gene set. • Need to choose “background population” appropriately, ...
Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory: rerouting of carbon metabolism
... bacteria, many sugars are imported via this PTS system, which is an energetically efficient system for sugar transport because sugar import is directly coupled to sugar phosphorylation at the expense of one ATP that would otherwise be generated by PEP conversion to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase (pyk) ...
... bacteria, many sugars are imported via this PTS system, which is an energetically efficient system for sugar transport because sugar import is directly coupled to sugar phosphorylation at the expense of one ATP that would otherwise be generated by PEP conversion to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase (pyk) ...
Mendelian Genetics— patterns of Inheritance
... Gametes are formed during meiosis. As you learned in Chapter 4, during anaphase of meiosis I (Section 4.2 Figure 4), homologous chromosomes separate. This ensures that each gamete receives only one chromosome from the pair and therefore receives only one allele for each gene. In other words, only on ...
... Gametes are formed during meiosis. As you learned in Chapter 4, during anaphase of meiosis I (Section 4.2 Figure 4), homologous chromosomes separate. This ensures that each gamete receives only one chromosome from the pair and therefore receives only one allele for each gene. In other words, only on ...
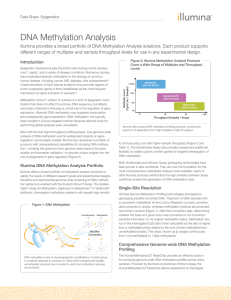
DNA Methylation Analysis
... Database9 (Genome Build 36). Additional markers provide increased resolution focused on 144 established cancer genes that have shown differential methylation patterns. To ensure the most important loci were represented, Illumina designed markers to cover nearly 1,000 cancer-related genes described i ...
... Database9 (Genome Build 36). Additional markers provide increased resolution focused on 144 established cancer genes that have shown differential methylation patterns. To ensure the most important loci were represented, Illumina designed markers to cover nearly 1,000 cancer-related genes described i ...
Chip-seq analysis
... chromosomes and genomic features enriched in peak of interest. One very interesting feature is that any kind of genomic feature can be provided for analysis. Here we will also try to test whether ESR1 peaks are biased toward regions marked for H3K4me1. ...
... chromosomes and genomic features enriched in peak of interest. One very interesting feature is that any kind of genomic feature can be provided for analysis. Here we will also try to test whether ESR1 peaks are biased toward regions marked for H3K4me1. ...
Control of notochord gene expression by Brachyury
... -In Ciona, Brachyury controls its direct transcriptional targets through two mechanisms: small clusters of cooperative binding sites or individual binding sites -cooperative and individual binding sites control earlyonset and middle-onset targets, respectively ...
... -In Ciona, Brachyury controls its direct transcriptional targets through two mechanisms: small clusters of cooperative binding sites or individual binding sites -cooperative and individual binding sites control earlyonset and middle-onset targets, respectively ...
Contents - BITS
... 1. The software calculates RQs (Relative Quantities) for each gene/sample combination by comparing the Cq of a given sample with the average Cq across all samples for that gene, taking into account differences in PCR amplification efficiencies. Genes have different amplification efficiencies because ...
... 1. The software calculates RQs (Relative Quantities) for each gene/sample combination by comparing the Cq of a given sample with the average Cq across all samples for that gene, taking into account differences in PCR amplification efficiencies. Genes have different amplification efficiencies because ...