Shockingly Bright Pulsar - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
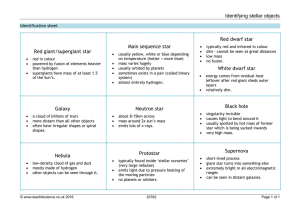
... The chart illustrates the relative masses of super-dense cosmic objects, from white dwarf stars to supermassive black holes inhabiting the cores of most galaxies. Credit: NASA/JPLCaltech/SAO. ...
... The chart illustrates the relative masses of super-dense cosmic objects, from white dwarf stars to supermassive black holes inhabiting the cores of most galaxies. Credit: NASA/JPLCaltech/SAO. ...
Chapter 2 Cosmic tombstones
... Since the magnetic axis and the rotation axis are not aligned, the pulsar operates like a lighthouse an observer sees periodic pulses of radio emission According to the leading theory, this emission is produced by fast particles propagating along the magnetic field lines Particles are extracted fr ...
... Since the magnetic axis and the rotation axis are not aligned, the pulsar operates like a lighthouse an observer sees periodic pulses of radio emission According to the leading theory, this emission is produced by fast particles propagating along the magnetic field lines Particles are extracted fr ...
X-ray Sources in Nearby Galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
... • Evolution of HMXBs and LMXBs (talk by Andreas Zezas). • Discrete source populations such as SNe, SNRs, YSOs. • Effects of AGN energy injection, accretion from the IGM, clustering environment on diffuse hot plasma. • Diffuse hard X-rays: e.g., reflection, inverse Compton scattering, & synchrotr ...
... • Evolution of HMXBs and LMXBs (talk by Andreas Zezas). • Discrete source populations such as SNe, SNRs, YSOs. • Effects of AGN energy injection, accretion from the IGM, clustering environment on diffuse hot plasma. • Diffuse hard X-rays: e.g., reflection, inverse Compton scattering, & synchrotr ...
Astronomy news
... X-ray modulation at the orbital period are known from several black hole x-ray binaries. The high inferred luminosity indicates that the black hole is gravitationally pulling the mass directly from the outer surface of its companion star. Because of the geometry of the binary system, the orbital per ...
... X-ray modulation at the orbital period are known from several black hole x-ray binaries. The high inferred luminosity indicates that the black hole is gravitationally pulling the mass directly from the outer surface of its companion star. Because of the geometry of the binary system, the orbital per ...
Pathways to Habitability: from disks to active stars, planets and life
... Pathways to Habitability: from disks to active stars, planets and life Colin P. Johnstone ...
... Pathways to Habitability: from disks to active stars, planets and life Colin P. Johnstone ...
Stellar Remnants White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars & Black Holes
... • Neutron stars have very intense magnetic fields and very rapid rotation. ...
... • Neutron stars have very intense magnetic fields and very rapid rotation. ...
Document
... • We can see X-rays from black holes because? a. X-rays are more energetic than visible light and so can escape from the event horizon. b. X-rays can pass through ordinary matter showing us things we can’t normally see. c. Light given off by objects as they enter the event horizon are gravitationall ...
... • We can see X-rays from black holes because? a. X-rays are more energetic than visible light and so can escape from the event horizon. b. X-rays can pass through ordinary matter showing us things we can’t normally see. c. Light given off by objects as they enter the event horizon are gravitationall ...
Draft A101 Slide Set #1 - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
... •The newly identified pulsar is one of a class of objects called “ultraluminous X-ray sources,” or ULXs—which are extremely bright in X-ray emissions. •ULXs were previously all suspected to be “intermediate mass” black holes—black holes up to a few hundred solar masses--accreting matter that heated ...
... •The newly identified pulsar is one of a class of objects called “ultraluminous X-ray sources,” or ULXs—which are extremely bright in X-ray emissions. •ULXs were previously all suspected to be “intermediate mass” black holes—black holes up to a few hundred solar masses--accreting matter that heated ...
The Galactic Super Star Cluster Westerlund 1
... times the mass of Orion. Therefore, we would have expected diffuse emission with L x = 3x10 35 erg s-1, which is five times more flux than we observe. We suggest that the IMF is nonstandard, as is often claimed for young, massive star clusters. ...
... times the mass of Orion. Therefore, we would have expected diffuse emission with L x = 3x10 35 erg s-1, which is five times more flux than we observe. We suggest that the IMF is nonstandard, as is often claimed for young, massive star clusters. ...
LETG Spring, 2015
... debate even where exactly in the solar interior most of the field originates. It has been about 70 years since it was realized that the solar corona comprises a plasma with a temperature of a million degrees, and 50 years since coronal X-ray emission was found to be clearly associated with sunspots ...
... debate even where exactly in the solar interior most of the field originates. It has been about 70 years since it was realized that the solar corona comprises a plasma with a temperature of a million degrees, and 50 years since coronal X-ray emission was found to be clearly associated with sunspots ...
Gravitationally redshifted absorption lines in the x
... Obs. Results of GS 1826-24 XMM-Newton RGS average ...
... Obs. Results of GS 1826-24 XMM-Newton RGS average ...
Life and Evolution of a Massive Star
... Black Hole Formation • Neutron star can hold itself up against gravity with neutron degeneracy pressure • A star that is so massive that it collapses past the neutron degeneracy limit will become a black hole • The result is a singularity ...
... Black Hole Formation • Neutron star can hold itself up against gravity with neutron degeneracy pressure • A star that is so massive that it collapses past the neutron degeneracy limit will become a black hole • The result is a singularity ...
the free PDF resource
... sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
... sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
Complex Spatio-Spectral Structure of Diffuse X-Ray
... A rapid brightening (~ t7): The shock continues interacting w/ a steep density increase. Radial expansion: v ~ 7800 km/s to 1700 km/s at day ~6000 Slower brightening in hard X-rays: ~6 x brighter than 2000. Synchrotron emission? But, steeper than radio light curves (f ~ t4 vs t2.6). Shock-CSM intera ...
... A rapid brightening (~ t7): The shock continues interacting w/ a steep density increase. Radial expansion: v ~ 7800 km/s to 1700 km/s at day ~6000 Slower brightening in hard X-rays: ~6 x brighter than 2000. Synchrotron emission? But, steeper than radio light curves (f ~ t4 vs t2.6). Shock-CSM intera ...
Tom Maccarone (Texas Tech University)
... Can do fundamental physics with these objects, but they are also important probes of globular cluster dynamics We are starting to see the first Milky Way globular cluster black ...
... Can do fundamental physics with these objects, but they are also important probes of globular cluster dynamics We are starting to see the first Milky Way globular cluster black ...
Equation of state constraints for the cold dense matter inside neutron
... Kazan Federal University, 420008, Kremlevskaya 18, Kazan, Russia ...
... Kazan Federal University, 420008, Kremlevskaya 18, Kazan, Russia ...
ppt
... same density as the Earth, and whose diameter should be two hundred and fifty times larger than that of the Sun, would not, in consequence of its attraction, allow any of its rays to arrive at us; it is therefore possible that the largest luminous bodies in the universe may, through this cause, be i ...
... same density as the Earth, and whose diameter should be two hundred and fifty times larger than that of the Sun, would not, in consequence of its attraction, allow any of its rays to arrive at us; it is therefore possible that the largest luminous bodies in the universe may, through this cause, be i ...
White Dwarf Stars
... we see pulses of radiation. Such objects are called pulsars. Not all neutron stars are observable as pulsars. • Pulsars were discovered by Anthony Hewish and Jocelyn ...
... we see pulses of radiation. Such objects are called pulsars. Not all neutron stars are observable as pulsars. • Pulsars were discovered by Anthony Hewish and Jocelyn ...
X-ray effects on protoplanetary disks
... • The X-ray studies of young stars show that powerful magnetic flares are ubiquitous throughout the epoch of planet formation, 103 above solar levels. The astrophysics resembles gigantic solar flares. • X-rays can efficiently irradiate protoplanetary disks. X-ray evidence: IR evidence: ...
... • The X-ray studies of young stars show that powerful magnetic flares are ubiquitous throughout the epoch of planet formation, 103 above solar levels. The astrophysics resembles gigantic solar flares. • X-rays can efficiently irradiate protoplanetary disks. X-ray evidence: IR evidence: ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.