Lec 25.2- STELLAR EVOLUTION SUMMARY
... Stars are believed to originate in enormous clouds of dust and (mostly hydrogen) gas. There are many such clouds in our Universe': They are assumed to contain nearly all of the matter between the stars. Gravity is a key to star evolution. You may recall that according to Newton's law of gravity, all ...
... Stars are believed to originate in enormous clouds of dust and (mostly hydrogen) gas. There are many such clouds in our Universe': They are assumed to contain nearly all of the matter between the stars. Gravity is a key to star evolution. You may recall that according to Newton's law of gravity, all ...
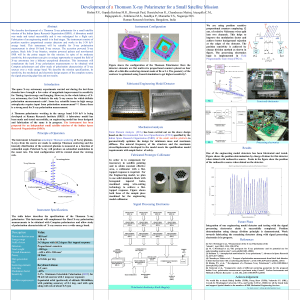
Polarimeter - Raman Research Institute
... was made and tested successfully and it was redesigned for a flight unit. Fabrication of an engineering model is in final stages. The instrument consists of position sensitive proportional counter detectors and works in the 5-30 keV energy band. This instrument will be suitable for X-ray polarisatio ...
... was made and tested successfully and it was redesigned for a flight unit. Fabrication of an engineering model is in final stages. The instrument consists of position sensitive proportional counter detectors and works in the 5-30 keV energy band. This instrument will be suitable for X-ray polarisatio ...
Stars and Black Holes: Stars A star is a massive, luminous ball of
... There are _____________ of galaxies in the ______________. Galaxies are ________________: they contain ________, ___________, and _______. The farthest galaxies and the stars we see shining in them may be also the _____________ because it takes the _____________ so long to reach us. ...
... There are _____________ of galaxies in the ______________. Galaxies are ________________: they contain ________, ___________, and _______. The farthest galaxies and the stars we see shining in them may be also the _____________ because it takes the _____________ so long to reach us. ...
The Swansong of Stars Orbiting Massive Black Holes
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
MIDTERM #2 THURSDAY APRIL 16, 2015 AST142 1. Black hole
... say about the dark matter fraction in the cluster? (Ignore the mass in X-ray emitting gas in the intercluster medium). ...
... say about the dark matter fraction in the cluster? (Ignore the mass in X-ray emitting gas in the intercluster medium). ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 8
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
Background Science - Faulkes Telescope Project
... the X-ray, we are looking at the parts of the shell that are much hotter than the areas shining in the optical. The X-rays come from the extremely hot material at around 10 million degrees Kelvin. These high energy rays are emitted from the chemical elements in the gas, for example, from silicon, ir ...
... the X-ray, we are looking at the parts of the shell that are much hotter than the areas shining in the optical. The X-rays come from the extremely hot material at around 10 million degrees Kelvin. These high energy rays are emitted from the chemical elements in the gas, for example, from silicon, ir ...
The coolest White Dwarf— older than the age of the universe?
... its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that it will become a ‘black dwarf’ and will b ...
... its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that it will become a ‘black dwarf’ and will b ...
Ch.21 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 3: Lives of Stars
... When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly The supernovas can become part of a nebula This nebula can then contract to form a new, partly recycled star o Neutron Stars: are the remains of high-mass stars They are even smaller and denser than white dwarfs A neutron star may ...
... When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly The supernovas can become part of a nebula This nebula can then contract to form a new, partly recycled star o Neutron Stars: are the remains of high-mass stars They are even smaller and denser than white dwarfs A neutron star may ...
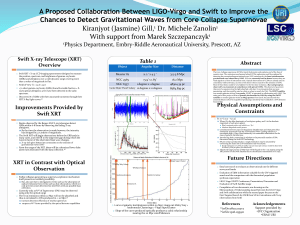
A Proposed Collaboration Between LIGO
... Theorized larger portion of SNe that will be found in the x-ray region using the XRT portion of the Swift Satellite due to the efficient transmission of X-rays. ...
... Theorized larger portion of SNe that will be found in the x-ray region using the XRT portion of the Swift Satellite due to the efficient transmission of X-rays. ...
zaneposter
... layers. However, independently of the model parameters, the degree of polarization crosses zero at the very vicinity of the proton cyclotron energy, where the mode absorption coefficients of the two modes (O-X) cross each other. This means that measures of polarization can correctly identify a proto ...
... layers. However, independently of the model parameters, the degree of polarization crosses zero at the very vicinity of the proton cyclotron energy, where the mode absorption coefficients of the two modes (O-X) cross each other. This means that measures of polarization can correctly identify a proto ...
AMUSE-Virgo on the survival of super
... AMUSE-Virgo: latest results 26/100 nuclear super-massive Point-like nuclearX-ray X-raysources source likley detected in 32p/100 black objectsholes ...
... AMUSE-Virgo: latest results 26/100 nuclear super-massive Point-like nuclearX-ray X-raysources source likley detected in 32p/100 black objectsholes ...
doc - University of Texas Astronomy
... Italian-Dutch BeppoSAX satellite) to see the xray “afterglow” from a gamma ray burst to locate its position in the sky more accurately, and then see spectral lines in its optical “afterglow.” The resulting Doppler shift was a redshift and it was enormous. As we’ll see later, because the universe is ...
... Italian-Dutch BeppoSAX satellite) to see the xray “afterglow” from a gamma ray burst to locate its position in the sky more accurately, and then see spectral lines in its optical “afterglow.” The resulting Doppler shift was a redshift and it was enormous. As we’ll see later, because the universe is ...
glossary - Discovery Education
... nebula and a white dwarf. parsec — a distance of 3.26 light-years; used to measure immense distances in space. planetary nebula — a ring of dust and gas blown off a red giant star after it undergoes an explosion. pulsar — a rapidly spinning neutron star that sends out pulses of radiation at regular ...
... nebula and a white dwarf. parsec — a distance of 3.26 light-years; used to measure immense distances in space. planetary nebula — a ring of dust and gas blown off a red giant star after it undergoes an explosion. pulsar — a rapidly spinning neutron star that sends out pulses of radiation at regular ...
Lecture103002
... as closely packed as inside of nucleus 1 billion times density of Sun as if the Earth were condensed to the size of Doak Campbell Stadium ...
... as closely packed as inside of nucleus 1 billion times density of Sun as if the Earth were condensed to the size of Doak Campbell Stadium ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
solution
... is very long, nearly 107 yr; however, there is a lot of hydrogen out there (see §§22.32, below). 22.13 Many old black-and-white photographs of spiral galaxies were taken using film that was most sensitive to blue light. Explain why the spiral arms were particularly prominent in such photographs.? Th ...
... is very long, nearly 107 yr; however, there is a lot of hydrogen out there (see §§22.32, below). 22.13 Many old black-and-white photographs of spiral galaxies were taken using film that was most sensitive to blue light. Explain why the spiral arms were particularly prominent in such photographs.? Th ...
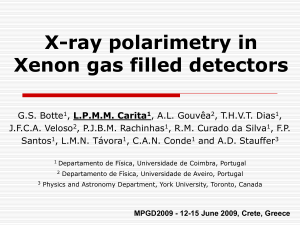
X-ray polarimetry in Xenon gas filled detectors
... azimuthal angles relative to the polarization direction, β is the dipole asymmetry parameter and P2 is the 2nd Legendre polynomial) Derevianko et. al., At.Dat.Nucl.Dat. Tables 73 (1999) 153 ...
... azimuthal angles relative to the polarization direction, β is the dipole asymmetry parameter and P2 is the 2nd Legendre polynomial) Derevianko et. al., At.Dat.Nucl.Dat. Tables 73 (1999) 153 ...
White Dwarfs - Chandra X
... type star after the astronomers who first identified these objects. This star has a surface temperature of about 50,000 degrees Celsius and is furiously boiling off its outer layers in a "fast" wind traveling 6 million kilometers per hour. The radiation from the hot star heats the slowly moving red ...
... type star after the astronomers who first identified these objects. This star has a surface temperature of about 50,000 degrees Celsius and is furiously boiling off its outer layers in a "fast" wind traveling 6 million kilometers per hour. The radiation from the hot star heats the slowly moving red ...
Stellar Evolution
... Considering that material in the accretion disk around a white dwarf heats up to ~ 1 million oK, in which wavelength band do you expect that it radiates the most strongly? ...
... Considering that material in the accretion disk around a white dwarf heats up to ~ 1 million oK, in which wavelength band do you expect that it radiates the most strongly? ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 14. (2 pts.) Everything that has mass has a Schwarzschild radius. If that mass is somehow compressed inside a volume of that radius, it’ll become a black hole. What is the Schwarzschild radius of Jupiter (mass 2 10 27 kg)? What is your Schwarzschild radius (1 lb = 0.454 kg)? (You may use 75 kg a ...
... 14. (2 pts.) Everything that has mass has a Schwarzschild radius. If that mass is somehow compressed inside a volume of that radius, it’ll become a black hole. What is the Schwarzschild radius of Jupiter (mass 2 10 27 kg)? What is your Schwarzschild radius (1 lb = 0.454 kg)? (You may use 75 kg a ...
lecture2 - X-Ray
... Accretion in close binaries Accretion is the most powerful source of energy realized in Nature, which can give a huge energy output. When matter fall down onto the surface of a neutron star up to 10% of mc2 can be released. ...
... Accretion in close binaries Accretion is the most powerful source of energy realized in Nature, which can give a huge energy output. When matter fall down onto the surface of a neutron star up to 10% of mc2 can be released. ...
The Application of Forbidden Line X-Ray Diagnostics to the Hot Star
... the forbidden to intercombination line indicates the strength of the UV field.* In a strong UV field, electrons are often excited out of the long-lived upper level of the forbidden line before they spontaneously de-excite, weakening the forbidden line. * If electron densities are high enough, collis ...
... the forbidden to intercombination line indicates the strength of the UV field.* In a strong UV field, electrons are often excited out of the long-lived upper level of the forbidden line before they spontaneously de-excite, weakening the forbidden line. * If electron densities are high enough, collis ...
Astr40 HWIII(new) - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... 37. There is a mass of about a hundred billion solar masses inside of the Sun's orbit about galactic center. The sun' orbital radius and velocity tells us that. (T or F) 38. Spiral arms of a spiral galaxy are waves of star formation passing through the interstellar medium. (T or F) 39. The disk star ...
... 37. There is a mass of about a hundred billion solar masses inside of the Sun's orbit about galactic center. The sun' orbital radius and velocity tells us that. (T or F) 38. Spiral arms of a spiral galaxy are waves of star formation passing through the interstellar medium. (T or F) 39. The disk star ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.