Section 3-3(rev04) 2
... • After the supernova a mass of five times our sun may remain. The gases pull in and a mass of five times our sun is in a diameter the size of NYC. • The gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape. This is called a black hole. • We cannot detect a black hole directly. Any gas near it will b ...
... • After the supernova a mass of five times our sun may remain. The gases pull in and a mass of five times our sun is in a diameter the size of NYC. • The gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape. This is called a black hole. • We cannot detect a black hole directly. Any gas near it will b ...
Summary - Chandra X
... Mdot does not uniquely determine spectral state at high luminosities. Peak luminosity is determined by hard to soft transition luminosity. Brighter sources show flaring, resulting in additional structure in hardness-intensity diagram. Associated with steep power law state. This and intermediate “sta ...
... Mdot does not uniquely determine spectral state at high luminosities. Peak luminosity is determined by hard to soft transition luminosity. Brighter sources show flaring, resulting in additional structure in hardness-intensity diagram. Associated with steep power law state. This and intermediate “sta ...
The Satellites of Uranus and Neptune: A New Astrometrie Programme
... chance, Dr. Danks showed some plates of the cluster of galaxies Klemola 44 which he had obtained a few nights before with the 3.6 m telescope. Dr. Tarenghi told that he had observed the same galaxies spectroscopically the night before at Tololo. An intense exchange of information resulted. The edito ...
... chance, Dr. Danks showed some plates of the cluster of galaxies Klemola 44 which he had obtained a few nights before with the 3.6 m telescope. Dr. Tarenghi told that he had observed the same galaxies spectroscopically the night before at Tololo. An intense exchange of information resulted. The edito ...
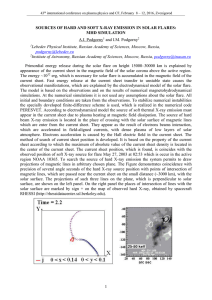
sources of hard and soft x-ray emission in solar flares: mhd simulation
... the specially developed finite-difference scheme is used, which is realized in the numerical code PERESVET. According to electrodynamical model the source of soft thermal X-ray emission must appear in the current sheet due to plasma heating at magnetic field dissipation. The source of hard beam X-ra ...
... the specially developed finite-difference scheme is used, which is realized in the numerical code PERESVET. According to electrodynamical model the source of soft thermal X-ray emission must appear in the current sheet due to plasma heating at magnetic field dissipation. The source of hard beam X-ra ...
Solar-B - to Nobeyama Radio Observatory
... Largest optical telescope ever to observe the Sun from space Diffraction-limited (0.2 – 0.3 arcsec) imaging in 388 – 668 nm Vector magnetic field measurement at the photosphere • X-Ray Telescope (XRT) Highest angular resolution imaging at > 3 MK corona Wide temperature coverage from below 1 MK to ab ...
... Largest optical telescope ever to observe the Sun from space Diffraction-limited (0.2 – 0.3 arcsec) imaging in 388 – 668 nm Vector magnetic field measurement at the photosphere • X-Ray Telescope (XRT) Highest angular resolution imaging at > 3 MK corona Wide temperature coverage from below 1 MK to ab ...
Death of Stars - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... 1 Similar to a nova where a dwarf takes material from a giant. This time the explosion destroys the dwarf. Typically this takes place when the mass of the white dwarf is over 1.4 solar masses. 2 When a star has a mass greater than 8 solar masses. The red giant swells so much it collapses in on itsel ...
... 1 Similar to a nova where a dwarf takes material from a giant. This time the explosion destroys the dwarf. Typically this takes place when the mass of the white dwarf is over 1.4 solar masses. 2 When a star has a mass greater than 8 solar masses. The red giant swells so much it collapses in on itsel ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... 29 galaxies with good spectra in the CDFS and emission line ratios consistent with starbursts or normal galaxies give the X-ray priors. A Bayesian approach allows us to identify 74 galaxies in the CDFS and 136 in the CDFN (2 Ms) Norman et al. 2004 ...
... 29 galaxies with good spectra in the CDFS and emission line ratios consistent with starbursts or normal galaxies give the X-ray priors. A Bayesian approach allows us to identify 74 galaxies in the CDFS and 136 in the CDFN (2 Ms) Norman et al. 2004 ...
X-ray Observations of Cosmic Accelerators Greg Madejski SLAC/KIPAC
... -> Flares come from dissipation of gravitational energy What is the origin of the hot plasma? Observed X-ray spectra (up to at least 100 keV) indicate that accretion disks must be sites of vigorous particle acceleration - Most likely associated with “plasma viscosity” provided by the magneto-rotatio ...
... -> Flares come from dissipation of gravitational energy What is the origin of the hot plasma? Observed X-ray spectra (up to at least 100 keV) indicate that accretion disks must be sites of vigorous particle acceleration - Most likely associated with “plasma viscosity” provided by the magneto-rotatio ...
投影片 1
... It represents the end state of stellar evolution of stars like the Sun Its progenitor had an original mass about seven times the Sun’s From the death of GD362,it passed two to five billion years based on the cooling rate ...
... It represents the end state of stellar evolution of stars like the Sun Its progenitor had an original mass about seven times the Sun’s From the death of GD362,it passed two to five billion years based on the cooling rate ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #3 Key (Chapter 2
... 2-4. If you double the Kelvin temperature of a hot piece of steel, how much more energy will it radiate per second? The Stefan-Boltzmann Equation (p.43) tells us that the energy radiated per second from a black body is proportion to its temperature in Kelvins raised to the fourth power. We expect ou ...
... 2-4. If you double the Kelvin temperature of a hot piece of steel, how much more energy will it radiate per second? The Stefan-Boltzmann Equation (p.43) tells us that the energy radiated per second from a black body is proportion to its temperature in Kelvins raised to the fourth power. We expect ou ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... The escape velocity of a neutron star (speed you need to escape it) is about ________. A planetary nebula is typically formed at the same time as a(n) _______________. The process in which many stars form from a single interstellar cloud is called _______. Interstellar clouds cause stars behind them ...
... The escape velocity of a neutron star (speed you need to escape it) is about ________. A planetary nebula is typically formed at the same time as a(n) _______________. The process in which many stars form from a single interstellar cloud is called _______. Interstellar clouds cause stars behind them ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Fortunately not pointed at us, we think. • Other stars old too… ...
... • Fortunately not pointed at us, we think. • Other stars old too… ...
Unit 1
... cannot escape a black hole, how can we see one?” • If a black hole is in orbit around a companion star, the black hole can pull material away from it. ...
... cannot escape a black hole, how can we see one?” • If a black hole is in orbit around a companion star, the black hole can pull material away from it. ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... While fusion of elements lighter than _______ produce energy, fusion of this element produces no energy, triggering the implosion of the core. ...
... While fusion of elements lighter than _______ produce energy, fusion of this element produces no energy, triggering the implosion of the core. ...
Feigelson, E. (PSU)
... X-rays & disk ionization YSO X-ray ionization rate dominates CRs in the disk by 108 for 1Mo PMS star at 1 AU: z = 6x10-9 (Lx/2x1030 erg s-1) (r/1 AU)-2 s-1 The ionization fraction is uncertain due to recombination processes. Hard (5-15 keV) X-rays should penetrate 1-100 g/cm2. Igea & Glassgold 1997 ...
... X-rays & disk ionization YSO X-ray ionization rate dominates CRs in the disk by 108 for 1Mo PMS star at 1 AU: z = 6x10-9 (Lx/2x1030 erg s-1) (r/1 AU)-2 s-1 The ionization fraction is uncertain due to recombination processes. Hard (5-15 keV) X-rays should penetrate 1-100 g/cm2. Igea & Glassgold 1997 ...
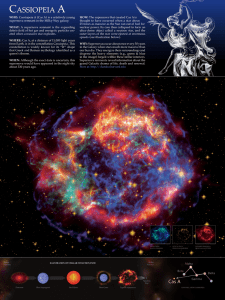
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... HOW: The supernova that created Cas A is thought to have occurred when a star about 25 times as massive as the Sun ran out of fuel for nuclear power. Its core then collapsed to form an ultra-dense object called a neutron star, and the outer layers of the star were ejected at enormous speeds (see ill ...
... HOW: The supernova that created Cas A is thought to have occurred when a star about 25 times as massive as the Sun ran out of fuel for nuclear power. Its core then collapsed to form an ultra-dense object called a neutron star, and the outer layers of the star were ejected at enormous speeds (see ill ...
Normal Stars - Chandra X
... The release of magnetic energy can occur steadily and provide for the heating of the tubes of hot gas which make up the stellar corona. Or it can occur violently and produce flares. Flares can occur on the Sun at any time, but their frequency tends to rise from a peak of five to ten a day and fall ...
... The release of magnetic energy can occur steadily and provide for the heating of the tubes of hot gas which make up the stellar corona. Or it can occur violently and produce flares. Flares can occur on the Sun at any time, but their frequency tends to rise from a peak of five to ten a day and fall ...
The Easily Visible Sky Tools of Astronomy Stars Galaxies Cosmology
... or less; it occurs in an active region where oppositely directed magnetic fields meet and cancel each other. It radiates X-ray, ultraviolet, and visible radiation, plus streams of high-energy protons and electrons. A large flare can be a billion times more energetic than a large hydrogen bomb. ...
... or less; it occurs in an active region where oppositely directed magnetic fields meet and cancel each other. It radiates X-ray, ultraviolet, and visible radiation, plus streams of high-energy protons and electrons. A large flare can be a billion times more energetic than a large hydrogen bomb. ...
Astrosat (India) - X-ray Astronomy Group at ISAS
... Point Astrosat, carry out optical identification and obtain system parameters like mass function, binary period, mass of the compact object etc.. ...
... Point Astrosat, carry out optical identification and obtain system parameters like mass function, binary period, mass of the compact object etc.. ...
Unique observations of a newborn star provide information on the
... been caught in the act of flaring, it is the first that has occurred in modern times when its behavior could be monitored not only in visible light, but also in radio, infrared and X-ray wavelengths. “In FU-Orionis stars, these outbursts are very brief,” says Weintraub, associate professor of astron ...
... been caught in the act of flaring, it is the first that has occurred in modern times when its behavior could be monitored not only in visible light, but also in radio, infrared and X-ray wavelengths. “In FU-Orionis stars, these outbursts are very brief,” says Weintraub, associate professor of astron ...
M What is the emptiness before the Big Bang? R Read the variables
... this area where gravity is so strong that nothing can exist, not even light? ...
... this area where gravity is so strong that nothing can exist, not even light? ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.