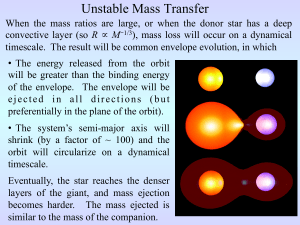
A propelling neutron star in the enigmatic Be-star γ Cassiopeia
... However, for matter to reach the NS surface, it should penetrate through its magnetosphere with the characteristic radius RA ∼ 108 –109 cm, defined by the pressure balance between the ambient matter and the magnetic field (see equation 7). Besides the magnetospheric barrier, the centrifugal barrier ...
... However, for matter to reach the NS surface, it should penetrate through its magnetosphere with the characteristic radius RA ∼ 108 –109 cm, defined by the pressure balance between the ambient matter and the magnetic field (see equation 7). Besides the magnetospheric barrier, the centrifugal barrier ...
Apparent magnitude
... orbits (in one year ~1 M new stars) The metallicity of young stars increases Open star clusters, interstellar matter Also an “outer” disc of hydrogen (15 000 ly away) and a large disc of warm gas ( ~10 000K) High-velocity clouds (HVC), intermediate-velocity clouds (IVC) “Star ribbons”, caused by dw ...
... orbits (in one year ~1 M new stars) The metallicity of young stars increases Open star clusters, interstellar matter Also an “outer” disc of hydrogen (15 000 ly away) and a large disc of warm gas ( ~10 000K) High-velocity clouds (HVC), intermediate-velocity clouds (IVC) “Star ribbons”, caused by dw ...
Accretion Disk
... • DQ Her Stars (Intermediate Polars): The magnetic field strength is not quite as strong as in the AM Her stars, so an outer accretion disk exists. However, close to the white dwarf, the disk is disrupted as again, matter is forced to flow along with the field lines to the pole. Intermediate polars ...
... • DQ Her Stars (Intermediate Polars): The magnetic field strength is not quite as strong as in the AM Her stars, so an outer accretion disk exists. However, close to the white dwarf, the disk is disrupted as again, matter is forced to flow along with the field lines to the pole. Intermediate polars ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about ...
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about ...
Disk Galaxies: Structural Components
... • Collapse of an over-dense region of space (containing more gas and dark matter than average) under gravity • Disks are produced as the cloud of material spins faster and faster as the gravitational collapse progresses • To conserve angular momentum, the spin speed must increase inversely proportio ...
... • Collapse of an over-dense region of space (containing more gas and dark matter than average) under gravity • Disks are produced as the cloud of material spins faster and faster as the gravitational collapse progresses • To conserve angular momentum, the spin speed must increase inversely proportio ...
Lecture 5: Matter Dominated Universe: CMB Anisotropies and Large
... Sachs-Wolfe (ΔT/T ~ -Δρ/ρ), Doppler (ΔT/T ~ V/c) and Sunyaev-Zeldovich (Re-ionisation) effects. • From the CMB Power Spectrum, most cosmological parameters are determined to a few percent. This determines the redshifttime relationship, R( t ) = 1 + z( t ) . • Supercomputer simulations, with initia ...
... Sachs-Wolfe (ΔT/T ~ -Δρ/ρ), Doppler (ΔT/T ~ V/c) and Sunyaev-Zeldovich (Re-ionisation) effects. • From the CMB Power Spectrum, most cosmological parameters are determined to a few percent. This determines the redshifttime relationship, R( t ) = 1 + z( t ) . • Supercomputer simulations, with initia ...
Fig.4
... J2310-437 (Fig.1) is hosted by an elliptical galaxy of z=0.0886, at the centre of a cluster of Abell richness class 0 (Ref.1), where Abell richness is the number of galaxies in a cluster that lie within the magnitude range m3 to m3+2 (m3 is the magnitude of the third brightest member of the cluster) ...
... J2310-437 (Fig.1) is hosted by an elliptical galaxy of z=0.0886, at the centre of a cluster of Abell richness class 0 (Ref.1), where Abell richness is the number of galaxies in a cluster that lie within the magnitude range m3 to m3+2 (m3 is the magnitude of the third brightest member of the cluster) ...
Neutron stars and black holes
... Since the Schwarzschild radius of a black hole is rSch = 2 GM / c2, the radius of a black hole is proportional to its mass. A one billion solar mass black hole will have a radius of 3 X 109 km. Since one Astronomical Unit ~ 1.5 X 108 km, it follows that a one billion solar mass black hole has a rad ...
... Since the Schwarzschild radius of a black hole is rSch = 2 GM / c2, the radius of a black hole is proportional to its mass. A one billion solar mass black hole will have a radius of 3 X 109 km. Since one Astronomical Unit ~ 1.5 X 108 km, it follows that a one billion solar mass black hole has a rad ...
ms
... follow the Bayesian method discussed in detail in Özel et al. (2009, 2012a). For each observable, we assign an independent probability distribution function. For the touchdown flux P (FT D )dFT D , the apparent angular size P (A)dA, and the distance P (D)dD, we use Gaussian probability distribution ...
... follow the Bayesian method discussed in detail in Özel et al. (2009, 2012a). For each observable, we assign an independent probability distribution function. For the touchdown flux P (FT D )dFT D , the apparent angular size P (A)dA, and the distance P (D)dD, we use Gaussian probability distribution ...
Two prevailing theories on how the universe was created
... galaxy. This is a photo graph made by the Hubble telescope of deep space. What was once thought to be individual stars turned out to be huge collections of stars. ...
... galaxy. This is a photo graph made by the Hubble telescope of deep space. What was once thought to be individual stars turned out to be huge collections of stars. ...
powerpoint file
... We are confident that very massive black holes exist at the centers of most galaxies. Black holes of a few solar masses are believed to form when massive stars undergo core collapse if the collapsed core exceeds the maximum of ~ 3 M permitted for neutron stars. The best evidence for such black hole ...
... We are confident that very massive black holes exist at the centers of most galaxies. Black holes of a few solar masses are believed to form when massive stars undergo core collapse if the collapsed core exceeds the maximum of ~ 3 M permitted for neutron stars. The best evidence for such black hole ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Lab Science Schedule
... oxygen and nitrogen. Fusion continues until iron forms. ...
... oxygen and nitrogen. Fusion continues until iron forms. ...
Stellar Structure - Astronomy Centre : Research
... • Neutron degeneracy pressure can support core against gravity • Remnant of SN explosion may be neutron star ...
... • Neutron degeneracy pressure can support core against gravity • Remnant of SN explosion may be neutron star ...
Astronomy
... the inward pull of the force of gravity. Stars live different lengths of time depending on the size. The hotter and brighter a star is, the ...
... the inward pull of the force of gravity. Stars live different lengths of time depending on the size. The hotter and brighter a star is, the ...
PSR J1833-1034
... – The pulsed signal is strong in gamma-ray(~6 significance) – No X-rays pulsation detection – It is a young pulsar, maybe the youngest in our Galaxy – Its gamma-rays light curve show two peaks separated by ~0.435 in phase and also the Interpulse – The ratio P1/P2 decrease with increasing energies – ...
... – The pulsed signal is strong in gamma-ray(~6 significance) – No X-rays pulsation detection – It is a young pulsar, maybe the youngest in our Galaxy – Its gamma-rays light curve show two peaks separated by ~0.435 in phase and also the Interpulse – The ratio P1/P2 decrease with increasing energies – ...
Stars!!!!
... • Super Nova is when a giant or super giant star explodes • What is left over is called a neutron star – Smaller and denser than white dwarfs – They can have the same mass as the sun but can be the size of an asteroid ...
... • Super Nova is when a giant or super giant star explodes • What is left over is called a neutron star – Smaller and denser than white dwarfs – They can have the same mass as the sun but can be the size of an asteroid ...
Alanna Connors, for the AstroStatistics Working Group at Harvard
... Chandra X-Ray Observatory Jul Observatory (Apr '91 – Jun '00; COMPTEL: 0.8-30 MeV; EGRET 20 MeV-100 GeV) ...
... Chandra X-Ray Observatory Jul Observatory (Apr '91 – Jun '00; COMPTEL: 0.8-30 MeV; EGRET 20 MeV-100 GeV) ...
Document
... EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been detected in the TeV range by ground-based gamma-ray telescopes. All of them, except M87, are BL Lacs at z<0.2 (more percisely, to high-frequency-peaked BL Lac – HBL). ...
... EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been detected in the TeV range by ground-based gamma-ray telescopes. All of them, except M87, are BL Lacs at z<0.2 (more percisely, to high-frequency-peaked BL Lac – HBL). ...
here
... 1: Red dwarf (e.g., an M star) implies low-mass. Low-metallicity implies Pop II. Perpendicular through the disk implies not a disk-like orbit. Thus, this is likely an old, Pop II star from the stellar halo of the Milky Way. 2: Before Big Bang Nucleosynthesis, the universe was too hot for nuclei like ...
... 1: Red dwarf (e.g., an M star) implies low-mass. Low-metallicity implies Pop II. Perpendicular through the disk implies not a disk-like orbit. Thus, this is likely an old, Pop II star from the stellar halo of the Milky Way. 2: Before Big Bang Nucleosynthesis, the universe was too hot for nuclei like ...
11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... carbon and oxygen with a thin surface layer of hydrogen and helium. There is far too little gas to ever combust, however. White dwarfs simply continue to cool and reach a core temperature of around 20,000 K. ...
... carbon and oxygen with a thin surface layer of hydrogen and helium. There is far too little gas to ever combust, however. White dwarfs simply continue to cool and reach a core temperature of around 20,000 K. ...
Review for Midterm 1
... How many stars are typically born in a group and how many groups are typically formed at once? Why? How does spin affect the formation of a star? What are stars formed from and how big is that object? How does the mass of a star affect the time it takes to form? 4. Stellar energy: Where does the ene ...
... How many stars are typically born in a group and how many groups are typically formed at once? Why? How does spin affect the formation of a star? What are stars formed from and how big is that object? How does the mass of a star affect the time it takes to form? 4. Stellar energy: Where does the ene ...
Chapter 10- Stars, Galaxies and the Universe
... 33. The length of a star’s life is determined by its ____________________. 34. A dying high-mass star can suddenly explode, becoming a(n) ____________________. 35. A galaxy that does not have a regular shape is classified as a(n) ____________________ galaxy. 36. According to the big bang theory, the ...
... 33. The length of a star’s life is determined by its ____________________. 34. A dying high-mass star can suddenly explode, becoming a(n) ____________________. 35. A galaxy that does not have a regular shape is classified as a(n) ____________________ galaxy. 36. According to the big bang theory, the ...
The Milky Way - Chandra X
... Today we know that the Milky Way is our home galaxy - a vast rotating spiral of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. The Sun and its planetary system formed in the outer reaches of the Milky Way about 4.5 billion years ago. In the center of the galaxy is the bar-shaped galactic bulge which ...
... Today we know that the Milky Way is our home galaxy - a vast rotating spiral of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. The Sun and its planetary system formed in the outer reaches of the Milky Way about 4.5 billion years ago. In the center of the galaxy is the bar-shaped galactic bulge which ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.