GALEX UV Light-curves of M-Dwarf Flare Stars: THE FLARING UV
... • The magnetic field-lines of a star stretch up into their outer atmosphere - the corona - in loop-like structures • When adjacent magnetic field lines “re-connect” (probably due to disturbances within the stellar interior) they release energy in the form of electrons that gyrate down the field line ...
... • The magnetic field-lines of a star stretch up into their outer atmosphere - the corona - in loop-like structures • When adjacent magnetic field lines “re-connect” (probably due to disturbances within the stellar interior) they release energy in the form of electrons that gyrate down the field line ...
Lecture 2. Isolated Neutron Stars – I.
... however, there was a paper by Malofeev et al., in which the authors claim that they had detect two of the M7 at very low wavelength (<~100 MHz). At the moment the most strict limits are given by Kondratiev et al. Non-detection is still consistent with narrow beams. ...
... however, there was a paper by Malofeev et al., in which the authors claim that they had detect two of the M7 at very low wavelength (<~100 MHz). At the moment the most strict limits are given by Kondratiev et al. Non-detection is still consistent with narrow beams. ...
arXiv 2011 Feroci
... are also observed during type I X-ray bursts, which are mostly the result of thermally unstable helium ignition in the accreted envelope of a neutron star. This generates a thermonuclear explosion that is observed as an X-ray burst with a rapid rise (∼1 s) followed by a slower decay (∼10–100 s). X-r ...
... are also observed during type I X-ray bursts, which are mostly the result of thermally unstable helium ignition in the accreted envelope of a neutron star. This generates a thermonuclear explosion that is observed as an X-ray burst with a rapid rise (∼1 s) followed by a slower decay (∼10–100 s). X-r ...
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide
... • Hence σ varies based on where you measure it • We see 150-300 km/s near south BH (may be low because our stars are young; recently formed in disk) • Tecza et al. (2000) measure 236 km/s integrated over whole 0.8”x0.7” region Plot: Tremaine et al 2002 ...
... • Hence σ varies based on where you measure it • We see 150-300 km/s near south BH (may be low because our stars are young; recently formed in disk) • Tecza et al. (2000) measure 236 km/s integrated over whole 0.8”x0.7” region Plot: Tremaine et al 2002 ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... When you look up at the night sky you can see many stars. When you look at the sky during the day you can see one star. That star is our Sun. Our Sun is only one of many, many stars. Stars are glowing balls of hot gases –mostly hydrogen and helium. However, stars vary dramatically in size, temperatu ...
... When you look up at the night sky you can see many stars. When you look at the sky during the day you can see one star. That star is our Sun. Our Sun is only one of many, many stars. Stars are glowing balls of hot gases –mostly hydrogen and helium. However, stars vary dramatically in size, temperatu ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
UV-Optical Colors as Probes of Early-Type Galaxy Evolution
... Cold Gas found in many early-type galaxies CMRs (Ferraras and Silk 2000) for early-types in cluster A851 (tobs= ~4.5 Ga) consistent with 10% of galaxy SF less than 500Ma UV-Upturn studies find blue colors in some early types can not be fully explained by old (EHB and later) stars ...
... Cold Gas found in many early-type galaxies CMRs (Ferraras and Silk 2000) for early-types in cluster A851 (tobs= ~4.5 Ga) consistent with 10% of galaxy SF less than 500Ma UV-Upturn studies find blue colors in some early types can not be fully explained by old (EHB and later) stars ...
Heart of darkness: The cluster Abell 545 and its “star pile”
... at the center of a massive cluster. As an old and metal rich population, its origin is probably connected to stripping and/or disruption of dwarf (giant) galaxies passing through the clusters' center. It is an unrivaled object to test dark matter theories in cluster scales. ...
... at the center of a massive cluster. As an old and metal rich population, its origin is probably connected to stripping and/or disruption of dwarf (giant) galaxies passing through the clusters' center. It is an unrivaled object to test dark matter theories in cluster scales. ...
Stellar Evolution
... Synchrotron Emission and Cosmic-Ray Acceleration The shocks of supernova remnants accelerate protons and electrons to extremely high, relativistic energies. ...
... Synchrotron Emission and Cosmic-Ray Acceleration The shocks of supernova remnants accelerate protons and electrons to extremely high, relativistic energies. ...
on the mass of the black hole in gs
... We assume for the moment that the accretion disk contribution is negligible at J and K9 (see § 4 for further discussion of this point). The assumption that the secondary fills its Roche lobe is an essential one, since the ellipsoidal amplitudes are strongly dependent on this; however, we believe thi ...
... We assume for the moment that the accretion disk contribution is negligible at J and K9 (see § 4 for further discussion of this point). The assumption that the secondary fills its Roche lobe is an essential one, since the ellipsoidal amplitudes are strongly dependent on this; however, we believe thi ...
Astronomy 1
... The Milky Way Galaxy, commonly referred to as just the Milky Way, or sometimes simply as the Galaxy,[a] is the home galaxy of the Solar System, and of Earth. It is agreed that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, with observations suggesting that it is a barred spiral galaxy. It contains 100-400 billio ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy, commonly referred to as just the Milky Way, or sometimes simply as the Galaxy,[a] is the home galaxy of the Solar System, and of Earth. It is agreed that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, with observations suggesting that it is a barred spiral galaxy. It contains 100-400 billio ...
PPT - Cornell University
... matter, forming a disk Baryonic matter has high spin parameter: large-scale rotation ...
... matter, forming a disk Baryonic matter has high spin parameter: large-scale rotation ...
Accreting magnetars: a new type of high-mass X-ray binaries? P. Reig,
... of the nature of the compact object in the high-mass X-ray binary 4U 2206+54 but has posed new ones. According to spin evolutionary models in close binary systems, such slow pulsations require a neutron star magnetic field strength larger than the quantum critical value of 4.4 × 1013 G, suggesting t ...
... of the nature of the compact object in the high-mass X-ray binary 4U 2206+54 but has posed new ones. According to spin evolutionary models in close binary systems, such slow pulsations require a neutron star magnetic field strength larger than the quantum critical value of 4.4 × 1013 G, suggesting t ...
2017 Maryland Regional
... 22. __This object will eventually end it life in a white-dwarf merger to produce a Type Ia supernova. This is the first documented case of a supernova candidate through white-dwarf merger.__ 23. __ The star, Mira, is thermally pulsing every 10,000 years, with each causing it to increase in luminosit ...
... 22. __This object will eventually end it life in a white-dwarf merger to produce a Type Ia supernova. This is the first documented case of a supernova candidate through white-dwarf merger.__ 23. __ The star, Mira, is thermally pulsing every 10,000 years, with each causing it to increase in luminosit ...
NEUTRON STARS AND PULSARS Discovery Were it not for
... built by themselves, such as Herschell’s 48 inch reflecting telescope built with a grant from King George III. Today, the instruments used to search out and measure the radiations from neutron stars are many and varied and at a very high level of technology. The Hubble Space Telescope that orbits the ...
... built by themselves, such as Herschell’s 48 inch reflecting telescope built with a grant from King George III. Today, the instruments used to search out and measure the radiations from neutron stars are many and varied and at a very high level of technology. The Hubble Space Telescope that orbits the ...
DTU 8e Chap 17 Quasars and Other Active Galaxies
... An active galaxy is an extremely luminous galaxy that has one or more unusual features: an unusually bright, starlike nucleus; strong emission lines in its spectrum; rapid variations in luminosity; and jets or beams of radiation that emanate from its core. Active galaxies include quasars, Seyfert ga ...
... An active galaxy is an extremely luminous galaxy that has one or more unusual features: an unusually bright, starlike nucleus; strong emission lines in its spectrum; rapid variations in luminosity; and jets or beams of radiation that emanate from its core. Active galaxies include quasars, Seyfert ga ...
get ready for rtmc may 26-28th!
... eventually fell to Earth), this one named the Nakhla meteorite after the place in Egypt where it fell in 1911, has been found to have a series of microscopic tunnels in it similar in size, shape and distribution to the tunnels left in Earth rocks by bacteria that eat rocks. In Earth rocks with such ...
... eventually fell to Earth), this one named the Nakhla meteorite after the place in Egypt where it fell in 1911, has been found to have a series of microscopic tunnels in it similar in size, shape and distribution to the tunnels left in Earth rocks by bacteria that eat rocks. In Earth rocks with such ...
Astrophysics Questions (DRAFT)
... 97. Explain quantitatively why stimulated emission is important and spontaneous emission is usually ignored in the radio domain, whereas the reverse is true in the optical domain. Given a thermal spectrum at some temperature T , at what frequency would the two emission rates be equal? 98. Name ve m ...
... 97. Explain quantitatively why stimulated emission is important and spontaneous emission is usually ignored in the radio domain, whereas the reverse is true in the optical domain. Given a thermal spectrum at some temperature T , at what frequency would the two emission rates be equal? 98. Name ve m ...
SUMMARY White dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes are the
... White dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes are the remnants of dead stars. A white dwarf forms when a lowmass star expels its outer layers to form a planetary nebula shell and leaves its hot core exposed. The radius of a white dwarf is about the same as the radius of the Earth. Its matter is dege ...
... White dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes are the remnants of dead stars. A white dwarf forms when a lowmass star expels its outer layers to form a planetary nebula shell and leaves its hot core exposed. The radius of a white dwarf is about the same as the radius of the Earth. Its matter is dege ...
Lecture 1, Overview and Basic Concepts (April 2)
... - Integral (2002-), 3 keV-10 MeV - Swift (2004-), 15-150 keV, GRB monitor with large FoV Future: - NuSTAR (2012-), hard X-ray imaging - eROSITA (2014), all-sky survey - ASTRO-H (2014), high-res spectra - ATHENA (formerly IXO, formerly Con-X and XEUS)?? ...
... - Integral (2002-), 3 keV-10 MeV - Swift (2004-), 15-150 keV, GRB monitor with large FoV Future: - NuSTAR (2012-), hard X-ray imaging - eROSITA (2014), all-sky survey - ASTRO-H (2014), high-res spectra - ATHENA (formerly IXO, formerly Con-X and XEUS)?? ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... ____ 3. Protostar ____ 4. Gravity causes this to condense into a protostar ____ 5. Main sequence star ____ 6. When a star begins to run out of fuel and grows larger ____ 7. Neutron star ...
... ____ 3. Protostar ____ 4. Gravity causes this to condense into a protostar ____ 5. Main sequence star ____ 6. When a star begins to run out of fuel and grows larger ____ 7. Neutron star ...
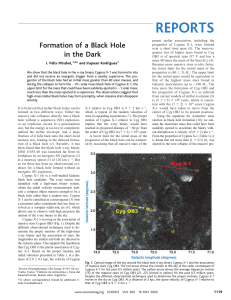
Here you can get a Science reprint
... momentum for Cygnus X-1 is 2.5 times smaller than the linear momentum imparted by the SN (2) to the runaway black hole system GRO J1655-40. The upper limit for the runaway kinetic energy of Cygnus X-1 is at least 20 times smaller than that estimated (3) for GRO J1655-40 and ⬃2 ⫻ 10⫺5 that of a SN of ...
... momentum for Cygnus X-1 is 2.5 times smaller than the linear momentum imparted by the SN (2) to the runaway black hole system GRO J1655-40. The upper limit for the runaway kinetic energy of Cygnus X-1 is at least 20 times smaller than that estimated (3) for GRO J1655-40 and ⬃2 ⫻ 10⫺5 that of a SN of ...
Letter to the Editor ASTRONOMY ASTROPHYSICS
... Toomre and Toomre (1972) and more recently Barnes (1988), have shown that the gigantic streamers of the type seen in the Antennae are likely to be provoked by gravity during a direct encounter of similarly massive disk galaxies. The remarkable slender tails would have been caused during a previous e ...
... Toomre and Toomre (1972) and more recently Barnes (1988), have shown that the gigantic streamers of the type seen in the Antennae are likely to be provoked by gravity during a direct encounter of similarly massive disk galaxies. The remarkable slender tails would have been caused during a previous e ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.