FY1995 Q1 Oct-Dec NO.. - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... energetics of these supernovae may have been responsible for clearing the gas from the early clusters, thus ending the star formation process in these systems.) It has long been known, however, that the abundances of light elements, such as carbon (C) and nitrogen (N), vary substantially from star t ...
... energetics of these supernovae may have been responsible for clearing the gas from the early clusters, thus ending the star formation process in these systems.) It has long been known, however, that the abundances of light elements, such as carbon (C) and nitrogen (N), vary substantially from star t ...
The Lagoon Nebula and its Vicinity
... The surface density of cluster stars, derived from X-ray data (Damiani et al. 2004), shows a compact core about 10′ across, surrounded by a broad extended component to the southeast, south and west. To the northeast, the surface density of X-ray sources falls off very quickly, and there is a seconda ...
... The surface density of cluster stars, derived from X-ray data (Damiani et al. 2004), shows a compact core about 10′ across, surrounded by a broad extended component to the southeast, south and west. To the northeast, the surface density of X-ray sources falls off very quickly, and there is a seconda ...
슬라이드 1
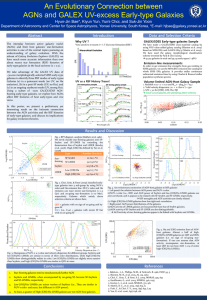
... Fig. 4. An evolutionary connection of AGN-host galaxies to RSF galaxies • Left panel: the relation between AGN power and NUV-r color. (1)NUV-r color (i.e., RSF) and AGN power of Seyfert and low-[OII]/Hα LINER galaxies are anti-correlated, and it appears to be related with SF-Seyfert and SF-LINER, re ...
... Fig. 4. An evolutionary connection of AGN-host galaxies to RSF galaxies • Left panel: the relation between AGN power and NUV-r color. (1)NUV-r color (i.e., RSF) and AGN power of Seyfert and low-[OII]/Hα LINER galaxies are anti-correlated, and it appears to be related with SF-Seyfert and SF-LINER, re ...
Roche accretion of stars close to massive black holes
... the stellar evolution as discussed in Syer, Clarke & Rees (1991). We also have not considered how the external radiation pressure affects the star and the Roche evolution. Such irradiation effects are important for large mass-ratio binaries, as they can change the Roche geometry and may stop the Roc ...
... the stellar evolution as discussed in Syer, Clarke & Rees (1991). We also have not considered how the external radiation pressure affects the star and the Roche evolution. Such irradiation effects are important for large mass-ratio binaries, as they can change the Roche geometry and may stop the Roc ...
on the evolution of anomalous x-ray pulsars and soft gamma
... We show that the period clustering of anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) and soft gamma-ray repeaters (SGRs), their X-ray luminosities, ages, and statistics can be explained with fall back disks with large initial specific angular momentum. The disk evolution models are developed by comparison to self-s ...
... We show that the period clustering of anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) and soft gamma-ray repeaters (SGRs), their X-ray luminosities, ages, and statistics can be explained with fall back disks with large initial specific angular momentum. The disk evolution models are developed by comparison to self-s ...
REVIEWS 18 years of science with the Hubble Space Telescope Julianne J. Dalcanton
... when studying poorly understood types of star. Unfortunately, most stars are far enough away that the images of the two stars in the binary cannot be separated in a typical image, making it difficult to measure the orbits, luminosities, colours and spectra of the two components. This step is particu ...
... when studying poorly understood types of star. Unfortunately, most stars are far enough away that the images of the two stars in the binary cannot be separated in a typical image, making it difficult to measure the orbits, luminosities, colours and spectra of the two components. This step is particu ...
Understanding Mass-Loss and the Late Evolution of Intermediate
... binaries, given the limitations of the search techniques which reveal only binaries with very short periods ...
... binaries, given the limitations of the search techniques which reveal only binaries with very short periods ...
The X-ray emission from shock cooling zones in O star winds
... the order of a few cooling times. Since the density and temperature stratification of the post-shock region change during the course of this contraction and expansion, and since these quantities enter non-linearly into the shock emission coefficient, the thermal instability will certainly affect the ...
... the order of a few cooling times. Since the density and temperature stratification of the post-shock region change during the course of this contraction and expansion, and since these quantities enter non-linearly into the shock emission coefficient, the thermal instability will certainly affect the ...
The physics of neutron stars
... by ground-based antennas, they have already been registered in observations of “space antennas” – double neutron stars. Two stars orbiting a common center of masses are known to emit gravitational waves. The first pulsar rotating in an orbit together with another neutron star was discovered by Hulse ...
... by ground-based antennas, they have already been registered in observations of “space antennas” – double neutron stars. Two stars orbiting a common center of masses are known to emit gravitational waves. The first pulsar rotating in an orbit together with another neutron star was discovered by Hulse ...
The masses and spins of neutron stars and stellar
... As the remnants of core-collapse supernovae, neutron stars and black holes are also windows into the collapse and explosion processes. The further evolution of these systems in accreting binaries can tell us about the accretion process, e.g., the total amount of mass that is typically deposited on t ...
... As the remnants of core-collapse supernovae, neutron stars and black holes are also windows into the collapse and explosion processes. The further evolution of these systems in accreting binaries can tell us about the accretion process, e.g., the total amount of mass that is typically deposited on t ...
Joint formation of QSOs and spheroids: QSOs as clocks of star
... In the introduction we have reviewed several pieces of evidence suggesting that star formation begins in the hosting spheroids at a time t* and proceeds vigoursly at least until the time tQSO, when the QSO shines. Here we estimate the duration of the star formation phase and its possible dependence ...
... In the introduction we have reviewed several pieces of evidence suggesting that star formation begins in the hosting spheroids at a time t* and proceeds vigoursly at least until the time tQSO, when the QSO shines. Here we estimate the duration of the star formation phase and its possible dependence ...
This presentation
... explosion. The image at the right is taken from the BATSE instrument on NASA’s Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. Spot size=peak flux during gamma ray bursts. Spot color= average energy, blue is of highest energy. It is clear that they don’t come from our galaxy, so in order for us to see them they must ...
... explosion. The image at the right is taken from the BATSE instrument on NASA’s Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. Spot size=peak flux during gamma ray bursts. Spot color= average energy, blue is of highest energy. It is clear that they don’t come from our galaxy, so in order for us to see them they must ...
Identifying Young far from Giant Stars Molecular Clouds
... It is speculated that classical T Tauri stars evolve into weak T Tauri stars, their accretion disks gradually dissipating over time (Walter et al. 1988). The two types of stars are similar in luminosities and effective temperature, implying a potential evolutionary relationship. The dust and gas wit ...
... It is speculated that classical T Tauri stars evolve into weak T Tauri stars, their accretion disks gradually dissipating over time (Walter et al. 1988). The two types of stars are similar in luminosities and effective temperature, implying a potential evolutionary relationship. The dust and gas wit ...
The behaviour of dark matter associated with 4 bright cluster
... We map the distribution of associated dark matter, using new Hubble Space Telescope imaging and VLT/MUSE integral field spectroscopy of a gravitationally lensed system threaded through the cluster core. We find that each of the central galaxies retains a dark matter halo, but that (at least) one of ...
... We map the distribution of associated dark matter, using new Hubble Space Telescope imaging and VLT/MUSE integral field spectroscopy of a gravitationally lensed system threaded through the cluster core. We find that each of the central galaxies retains a dark matter halo, but that (at least) one of ...
AGN Science Collaboration - Active Galactic Nuclei Science
... • Many galaxies contain an active nucleus which contributes light and skews the galaxy colors. • AGN contributions need to be taken into account if you want accurate photometric redshifts. • These contributions have been modeled in the galaxy simulations with “mixed” results. ...
... • Many galaxies contain an active nucleus which contributes light and skews the galaxy colors. • AGN contributions need to be taken into account if you want accurate photometric redshifts. • These contributions have been modeled in the galaxy simulations with “mixed” results. ...
The white dwarf cooling sequence of 47 Tucanae
... we employ a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of the cumulative distributions of effective temperatures. We first compute the statistic separation D, which measures the largest separation between the cumulative distribution of our simulations and the observed data. The statistical distances computed in this w ...
... we employ a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of the cumulative distributions of effective temperatures. We first compute the statistic separation D, which measures the largest separation between the cumulative distribution of our simulations and the observed data. The statistical distances computed in this w ...
The low-spin black hole in LMC X-3 Please share
... 2012; Reis et al. 2013; Reynolds 2014, and references therein). Both methods, but especially the Fe-line method, are also being applied to measure the spins of supermassive BHs in active galactic nuclei. LMC X-3 is ideal for continuum-fitting as it offers a strong, dominantly thermal continuum at ne ...
... 2012; Reis et al. 2013; Reynolds 2014, and references therein). Both methods, but especially the Fe-line method, are also being applied to measure the spins of supermassive BHs in active galactic nuclei. LMC X-3 is ideal for continuum-fitting as it offers a strong, dominantly thermal continuum at ne ...
Giant molecular clouds: star factories
... lead to much higher know how these clouds are whole galaxy, however, other star formation dispersed, or destroyed. The simulations do not explicitly rates gas in GMCs could all be turned model the dark matter halo and into stars, but this would lead to stars. Rather, these are assumed to much higher ...
... lead to much higher know how these clouds are whole galaxy, however, other star formation dispersed, or destroyed. The simulations do not explicitly rates gas in GMCs could all be turned model the dark matter halo and into stars, but this would lead to stars. Rather, these are assumed to much higher ...
Today Only, A New Exhibit: M,L, and T Dwarfs!
... filters can be used to measure band strength and tus give spectral types I-J is a good bet! ...
... filters can be used to measure band strength and tus give spectral types I-J is a good bet! ...
X-ray Binaries in Nearby Galaxies - CIERA
... to host LMXBs than Blue Clusters? Maccarone, Kundu, & Zepf 2004: Z-dependence of Irradiation-Induced Winds Ivanova 2005: Z-dependence of Magnetic Braking A.M. Loss In Blue, Metal-poor GCs MS donors w/ 0.85-1.25Mo have no outer convective zone ---> no MB ---> harder to start MT Even if MT starts, NS- ...
... to host LMXBs than Blue Clusters? Maccarone, Kundu, & Zepf 2004: Z-dependence of Irradiation-Induced Winds Ivanova 2005: Z-dependence of Magnetic Braking A.M. Loss In Blue, Metal-poor GCs MS donors w/ 0.85-1.25Mo have no outer convective zone ---> no MB ---> harder to start MT Even if MT starts, NS- ...
W. Couch "Environment of E+A galaxies"
... •Yang et al. (2004) – obtained HST/WFPC2 high resoln imaging of the 5 bluest E+A’s in the Z96 sample: ...
... •Yang et al. (2004) – obtained HST/WFPC2 high resoln imaging of the 5 bluest E+A’s in the Z96 sample: ...
multiwavelength observations of the gamma-ray
... Blazars (BL Lac objects and gamma-ray loud flat spectrum radio quasars (FSRQs)) are the most extreme type of active galactic nuclei (AGNs). They were historically defined through extreme flux variability throughout the electromagnetic spectrum, and sometimes strong and variable linear polarization a ...
... Blazars (BL Lac objects and gamma-ray loud flat spectrum radio quasars (FSRQs)) are the most extreme type of active galactic nuclei (AGNs). They were historically defined through extreme flux variability throughout the electromagnetic spectrum, and sometimes strong and variable linear polarization a ...
The extended structure of the dwarf irregular galaxy Sagittarius⋆⋆⋆
... bearing fundamental information on their original structure and mass distribution. In previous papers of this series (Bellazzini et al. 2011a, 2014, hereafter Papers I and II, respectively), we demonstrated that the outer structures of these galaxies can be traced down to extremely low surface brigh ...
... bearing fundamental information on their original structure and mass distribution. In previous papers of this series (Bellazzini et al. 2011a, 2014, hereafter Papers I and II, respectively), we demonstrated that the outer structures of these galaxies can be traced down to extremely low surface brigh ...
Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics
... Collisional systems are systems where interactions between particles are EFFICIENT with respect to the lifetime of the system Collisionless systems are systems where interactions are negligible R When is a system collisional/collisionless? RELAXATION TIMESCALE Gravity is a LONG-RANGE force → cumulat ...
... Collisional systems are systems where interactions between particles are EFFICIENT with respect to the lifetime of the system Collisionless systems are systems where interactions are negligible R When is a system collisional/collisionless? RELAXATION TIMESCALE Gravity is a LONG-RANGE force → cumulat ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.