
Searching for the Secrets of Massive Star Birth
... hypercompact HII region. Accretion must continue if the star is to become an O star; thus its accretion disk is expected to be at least partially ionized. Both ionized accretion (Keto 2002) and outflow (Keto 2007a) are possible. Massive protostars can continue to grow until their increasing Lyman co ...
... hypercompact HII region. Accretion must continue if the star is to become an O star; thus its accretion disk is expected to be at least partially ionized. Both ionized accretion (Keto 2002) and outflow (Keto 2007a) are possible. Massive protostars can continue to grow until their increasing Lyman co ...
variable star type designations in vsx
... slash characters are used to indicate some properties of the system, as in the degree of polarization (NA/DQ) or the nature of their components (UG/IBWD). In some cases, these subtypes also constitute an independent main variable star type, because the main type of variability they are usually assoc ...
... slash characters are used to indicate some properties of the system, as in the degree of polarization (NA/DQ) or the nature of their components (UG/IBWD). In some cases, these subtypes also constitute an independent main variable star type, because the main type of variability they are usually assoc ...
Maximum Mass Restraint of Neutron Stars
... mentioned in a brief explanation and their effects on EOS will be detailed in the next section, but for now it is more important to detail structure. Some models of neutron stars will choose to include the atmosphere/envelope structure of the star while some of them will not. This is due to the fact ...
... mentioned in a brief explanation and their effects on EOS will be detailed in the next section, but for now it is more important to detail structure. Some models of neutron stars will choose to include the atmosphere/envelope structure of the star while some of them will not. This is due to the fact ...
The effect of helium sedimentation on galaxy cluster masses and
... Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect (SZE) may be used to infer the helium abundance in the ICM (Markevitch 2007); however, the limited resolution and sensitivity of current SZE interferometers have so far not enabled the measurement of the distribution of helium, even in the cluster cores where the sedimentati ...
... Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect (SZE) may be used to infer the helium abundance in the ICM (Markevitch 2007); however, the limited resolution and sensitivity of current SZE interferometers have so far not enabled the measurement of the distribution of helium, even in the cluster cores where the sedimentati ...
Radio pulsars
... than doubled the number of known pulsars • New population of high-B pulsars and new SNR associations • Globular clusters contain many millisecond pulsars • Precision timing of binary millisecond pulsars measures many properties of binary stars and tests general relativity. • Discovery of highly rela ...
... than doubled the number of known pulsars • New population of high-B pulsars and new SNR associations • Globular clusters contain many millisecond pulsars • Precision timing of binary millisecond pulsars measures many properties of binary stars and tests general relativity. • Discovery of highly rela ...
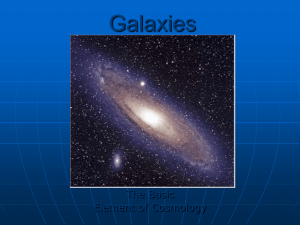
13 Galaxies - Journigan-wiki
... the exact causes of galaxy types. Spiral disks rotate rapidly when compared to elliptical halos. However, halos and bulges in spiral galaxies rotate much more slowly. Thus astronomers believe that more than a galaxy’s rotation determines its type. ...
... the exact causes of galaxy types. Spiral disks rotate rapidly when compared to elliptical halos. However, halos and bulges in spiral galaxies rotate much more slowly. Thus astronomers believe that more than a galaxy’s rotation determines its type. ...
arXiv:astro-ph/9909369 v1 22 Sep 1999
... the bands do not break up into a family of lines (as suggested e.g. by Léger et al., 1989). In fact, in most regions of the ISM, the band profiles are very constant, and much better represented by Lorentzian than by Gaussian functions (see e.g. Boulanger et al., 1998b; Mattila et al., 1999). Given ...
... the bands do not break up into a family of lines (as suggested e.g. by Léger et al., 1989). In fact, in most regions of the ISM, the band profiles are very constant, and much better represented by Lorentzian than by Gaussian functions (see e.g. Boulanger et al., 1998b; Mattila et al., 1999). Given ...
The Formation of a Realistic Disk Galaxy in Lambda Dominated
... rotationally supported stellar component, although in many cases a massive stellar spheroid is formed as well. In runs that use less than a few thousand particles to represent the virialized part of a galaxy DM halo (e.g., Eke et al. 2001), the rotating stellar component does not allow one to distin ...
... rotationally supported stellar component, although in many cases a massive stellar spheroid is formed as well. In runs that use less than a few thousand particles to represent the virialized part of a galaxy DM halo (e.g., Eke et al. 2001), the rotating stellar component does not allow one to distin ...
X-ray Emission Line Profiles from ... Confined Wind Shock Model
... This model can simulate data that would be observed from a star with this wind structure. We now have the ability to obtain data with enough detail to allow fruitful comparison because of new instrumentation. The Chandra satellite has spectroscopic resolution capability that is better than the Einst ...
... This model can simulate data that would be observed from a star with this wind structure. We now have the ability to obtain data with enough detail to allow fruitful comparison because of new instrumentation. The Chandra satellite has spectroscopic resolution capability that is better than the Einst ...
Cosmological Constraints from the Virial Mass
... In this thesis, I present a new determination of the cluster mass function in a volume 107 h -3 Mpc3 using the ROSAT-2MASS-FAST Group Survey (R2FGS). R2FGS is an X-ray-selected sample of systems from the ROSAT All-Sky Survey in the region 6 > 0' and 0.01 < z < 0.06, with target galaxies for each sys ...
... In this thesis, I present a new determination of the cluster mass function in a volume 107 h -3 Mpc3 using the ROSAT-2MASS-FAST Group Survey (R2FGS). R2FGS is an X-ray-selected sample of systems from the ROSAT All-Sky Survey in the region 6 > 0' and 0.01 < z < 0.06, with target galaxies for each sys ...
Accreting Neutron Stars: Strong Gravity and Type I Bursts
... radius1 . In consequence, we can obtain strong constraints on the nature of the EOS by measuring mass and radius of NSs. In general, the outer crust is thought to be made of a lattice of ions and (increasingly) relativistic, degenerate electrons. Where the density reaches the threshold of neutron dr ...
... radius1 . In consequence, we can obtain strong constraints on the nature of the EOS by measuring mass and radius of NSs. In general, the outer crust is thought to be made of a lattice of ions and (increasingly) relativistic, degenerate electrons. Where the density reaches the threshold of neutron dr ...
Ionized gas discs in elliptical and S0 galaxies at z < 1
... We analyse the extended, ionized-gas emission of 24 early-type galaxies (ETGs) at 0 < z < 1 from the ESO Distant Cluster Survey (EDisCS). We discuss different possible sources of ionization and favour star formation as the main cause of the observed emission. 10 galaxies have disturbed gas kinematic ...
... We analyse the extended, ionized-gas emission of 24 early-type galaxies (ETGs) at 0 < z < 1 from the ESO Distant Cluster Survey (EDisCS). We discuss different possible sources of ionization and favour star formation as the main cause of the observed emission. 10 galaxies have disturbed gas kinematic ...
Confronting predictions of the galaxy stellar mass function with
... 4 to effectively convert the observed UV LF into a GSMF. To make a proper simulation prediction, we must take into account any difference between the relation between UV luminosity and the stellar mass-to-light ratio used by González et al. (2011, 2012) and that in the simulations. Fig. 2 shows the ...
... 4 to effectively convert the observed UV LF into a GSMF. To make a proper simulation prediction, we must take into account any difference between the relation between UV luminosity and the stellar mass-to-light ratio used by González et al. (2011, 2012) and that in the simulations. Fig. 2 shows the ...
Observations of Jets and Outflows from Young Stars
... The primary jets and winds transfer momentum and entrain their surroundings by means of shock waves propagating into the medium. These shocks tend to have much lower velocities than the jets; they can be seen in H2 emission when the interaction is with a molecular cloud, or in Hα or forbidden lines ...
... The primary jets and winds transfer momentum and entrain their surroundings by means of shock waves propagating into the medium. These shocks tend to have much lower velocities than the jets; they can be seen in H2 emission when the interaction is with a molecular cloud, or in Hα or forbidden lines ...
THE LUMINOSITY FUNCTION OF X
... Over more than two decades, X-ray surveys have been improving and extending the known AGN luminosity function by including sources at low luminosity, with or without optical emission lines, and hidden by a dense obscuring medium. The Extended Medium Sensitivity Survey (Gioia et al. 1990) was one of ...
... Over more than two decades, X-ray surveys have been improving and extending the known AGN luminosity function by including sources at low luminosity, with or without optical emission lines, and hidden by a dense obscuring medium. The Extended Medium Sensitivity Survey (Gioia et al. 1990) was one of ...
PDF file
... mass, and bolometric luminosity can differ by several orders of magnitude. Until recently it was not even clear whether all young stars are highly X-ray active, or whether an “X-ray quiet” population of stars with suppressed magnetic activity may exist, which would have introduced a serious bias in ...
... mass, and bolometric luminosity can differ by several orders of magnitude. Until recently it was not even clear whether all young stars are highly X-ray active, or whether an “X-ray quiet” population of stars with suppressed magnetic activity may exist, which would have introduced a serious bias in ...
The white dwarf binary pathways survey – I. A sample of FGK stars
... SN Ia spectra (Branch et al. 1995). Moreover, there is both theoretical and observational evidence for a large population of close double white dwarf binaries (Yungelson et al. 1994; Nelemans & Tout 2005; Napiwotzki et al. 2001). However, there is some uncertainty as to whether the merger leads to a ...
... SN Ia spectra (Branch et al. 1995). Moreover, there is both theoretical and observational evidence for a large population of close double white dwarf binaries (Yungelson et al. 1994; Nelemans & Tout 2005; Napiwotzki et al. 2001). However, there is some uncertainty as to whether the merger leads to a ...
arXiv:1604.01613v2 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Aug 2016
... SN Ia spectra (Branch et al. 1995). Moreover, there is both theoretical and observational evidence for a large population of close double white dwarf binaries (Yungelson et al. 1994; Nelemans & Tout 2005; Napiwotzki et al. 2001). However, there is some uncertainty as to whether the merger leads to a ...
... SN Ia spectra (Branch et al. 1995). Moreover, there is both theoretical and observational evidence for a large population of close double white dwarf binaries (Yungelson et al. 1994; Nelemans & Tout 2005; Napiwotzki et al. 2001). However, there is some uncertainty as to whether the merger leads to a ...
Draft paper (submitted to MNRAS)
... We explore the impact of cosmic reionization on nearby isolated dwarf galaxies using a compilation of star formation histories estimated from deep HST data and a cosmological hydrodynamical simulation of the Local Group. The nearby dwarfs show a wide diversity of star formation histories; from ancie ...
... We explore the impact of cosmic reionization on nearby isolated dwarf galaxies using a compilation of star formation histories estimated from deep HST data and a cosmological hydrodynamical simulation of the Local Group. The nearby dwarfs show a wide diversity of star formation histories; from ancie ...
potenza dei jet nei nuclei galattici attivi radio
... “spiral nebulae”, some of the most enigmatic sources at the time when scientists were struggling to understand whether these objects were nearby gaseous objects similar to the Orion nebula or very distant collections of unresolved stars. For ...
... “spiral nebulae”, some of the most enigmatic sources at the time when scientists were struggling to understand whether these objects were nearby gaseous objects similar to the Orion nebula or very distant collections of unresolved stars. For ...
and galaxies
... Early studies of UV radiation showed spectral features at 220 nm wavelength, corresponding to known transitions from graphite (carbon). Infra-red astronomy then showed that some stars were surrounded by dust shells which heat up and subsequently re-radiate in the infra-red region. Although these spe ...
... Early studies of UV radiation showed spectral features at 220 nm wavelength, corresponding to known transitions from graphite (carbon). Infra-red astronomy then showed that some stars were surrounded by dust shells which heat up and subsequently re-radiate in the infra-red region. Although these spe ...
here - ISAS/JAXA
... the Evolving ISM in Dusty Star-Forming Galaxies Christopher Fuller Galaxy Evolution in Coma, Fornax and Virgo nearby and Clusters as seen by Herschel Yusei Koyama SPICA distant cluster survey: unveiling the dust-obscured star formation activity triggered by young cluster environments Kazumi Murata E ...
... the Evolving ISM in Dusty Star-Forming Galaxies Christopher Fuller Galaxy Evolution in Coma, Fornax and Virgo nearby and Clusters as seen by Herschel Yusei Koyama SPICA distant cluster survey: unveiling the dust-obscured star formation activity triggered by young cluster environments Kazumi Murata E ...
The magnetic field and wind confinement of b Cephei: new clues for
... The magnetic field and wind confinement of b Cephei literature for b Cep. We must therefore estimate these parameters based on measurements of normal non-supergiant B stars of similar spectral type, using for instance the survey of Prinja (1989). We first obtain that b Cep should have a terminal ve ...
... The magnetic field and wind confinement of b Cephei literature for b Cep. We must therefore estimate these parameters based on measurements of normal non-supergiant B stars of similar spectral type, using for instance the survey of Prinja (1989). We first obtain that b Cep should have a terminal ve ...
Giant molecular clouds in the dwarf galaxy NGC 1569
... dwarf starburst galaxy NGC 1569 with the IRAM interferometer on Plateau de Bure. We find the CO emission is not spatially associated with the two super star clusters in the galaxy, but rather is found in the vicinity of an HII region. With the resolution of our data, we can resolve the CO emission i ...
... dwarf starburst galaxy NGC 1569 with the IRAM interferometer on Plateau de Bure. We find the CO emission is not spatially associated with the two super star clusters in the galaxy, but rather is found in the vicinity of an HII region. With the resolution of our data, we can resolve the CO emission i ...
Session 1: Stellar winds, diagnostics across the electromagnetic
... Polarimetry is an important observational technique in the study of hot stars. Practiced across the full range of wavelengths, polarimetry provides a window into a variety of stellar phenomena not accessible by other means. For example, polarimetry constrains the properties of circumstellar disks, u ...
... Polarimetry is an important observational technique in the study of hot stars. Practiced across the full range of wavelengths, polarimetry provides a window into a variety of stellar phenomena not accessible by other means. For example, polarimetry constrains the properties of circumstellar disks, u ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.















![arXiv:1604.01613v2 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Aug 2016](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015708841_1-69411a0a7e7ee9a8690efbc066a22153-300x300.png)






