Unit 3 PreTest Heredity and Genetics
... Unit 3 Pretest: Heredity and Genetics » Form A (Master Copy) Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. ...
... Unit 3 Pretest: Heredity and Genetics » Form A (Master Copy) Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. ...
Lesson 7: Genetic Disorders & Gene Therapy
... • It is difficult to get the gene inserted into the tissue so that it can take over control of protein synthesis ...
... • It is difficult to get the gene inserted into the tissue so that it can take over control of protein synthesis ...
A very large amount of genetic variation exists in the human
... Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a prototypic biochemical genetic disorder. It is an autosomally recessive disorder in which mutations demonstrated in a sizable number of families lead, when present in the genes on both chromosomes, to defective activity of the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the me ...
... Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a prototypic biochemical genetic disorder. It is an autosomally recessive disorder in which mutations demonstrated in a sizable number of families lead, when present in the genes on both chromosomes, to defective activity of the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the me ...
Genetic Disorders and Genetic Testing
... diagnose a genetic disease or condition before the embryo is implanted in the uterus. • A single cell is removed from an embryo and examined for chromosome abnormalities or genetic changes. • Parents and doctors can then choose which embryos to implant. • Secrets of the Sequence – Chosen Child video ...
... diagnose a genetic disease or condition before the embryo is implanted in the uterus. • A single cell is removed from an embryo and examined for chromosome abnormalities or genetic changes. • Parents and doctors can then choose which embryos to implant. • Secrets of the Sequence – Chosen Child video ...
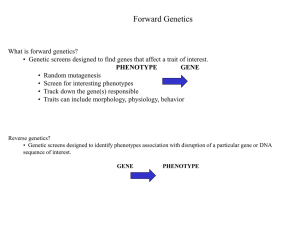
Complementation
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
X n Y
... X-linked diseases • Most are recessive • Examples-hemophilia, red-green colorblindness • Males are more likely to have these because they cannot be carriers • Why? • Males are XY-if their ‘X’ has a bad gene, there is nothing on the ‘Y’ to dominate over it ...
... X-linked diseases • Most are recessive • Examples-hemophilia, red-green colorblindness • Males are more likely to have these because they cannot be carriers • Why? • Males are XY-if their ‘X’ has a bad gene, there is nothing on the ‘Y’ to dominate over it ...
Genetic Engineering: How and why scientists manipulate DNA in
... Study revealed that 20,000 boxers genetically look like 70 – this leads disorders like heart disease, cancer, and epilepsy in boxers. ...
... Study revealed that 20,000 boxers genetically look like 70 – this leads disorders like heart disease, cancer, and epilepsy in boxers. ...
Reproduction and variation
... Inheritance and DNA • Organisms pass inherited traits to their offspring in one of two ways: • Either asexually or sexually • Asexual reproduction pass traits to their offspring by cell division and mitosis and are identical to their parents • Sexual reproduction, produce offspring's that are simil ...
... Inheritance and DNA • Organisms pass inherited traits to their offspring in one of two ways: • Either asexually or sexually • Asexual reproduction pass traits to their offspring by cell division and mitosis and are identical to their parents • Sexual reproduction, produce offspring's that are simil ...
If there are errors in the gene (bases are missing or out of order
... Categories of Factors Responsible for Birth Defects 1.Abnormalities of Individual Genes (Single Gene Defects) 2.Chromosomal Abnormalities 3.Intrauterine Injury 4.Multifactorial Circumstances ...
... Categories of Factors Responsible for Birth Defects 1.Abnormalities of Individual Genes (Single Gene Defects) 2.Chromosomal Abnormalities 3.Intrauterine Injury 4.Multifactorial Circumstances ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
Answers-to-examination-in-Gene-technology_20121020
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
Gene Technology
... understand their risk for genetic conditions (such as cystic fibrosis, cancer, or Down syndrome), educate the person or family about that disease, and assess the risk of passing those diseases on to children. • A genetic counselor will often work with families to identify members who are at risk. • ...
... understand their risk for genetic conditions (such as cystic fibrosis, cancer, or Down syndrome), educate the person or family about that disease, and assess the risk of passing those diseases on to children. • A genetic counselor will often work with families to identify members who are at risk. • ...
Human Blood Type Genetics
... Most blood group genes are co-dominant. For example, in the ABO system, A and B genes are co-dominant. Many blood group antigens are indirect gene products. For example, A and B antigens are carbohydrates. Their genes produce proteins (enzymes) called transferases which transfer sugars from carrier ...
... Most blood group genes are co-dominant. For example, in the ABO system, A and B genes are co-dominant. Many blood group antigens are indirect gene products. For example, A and B antigens are carbohydrates. Their genes produce proteins (enzymes) called transferases which transfer sugars from carrier ...
Big Idea 16 : Heredity and Reproduction
... 1. Name three types of breeding and a reason why they are used. Selective breeding, hybridization, inbreeding. All 3 can be used to make specific higher yielding crops. Crops less vulnerable to disease and animals for specified jobs 2. What is Genetic engineering? Processes in which genes with speci ...
... 1. Name three types of breeding and a reason why they are used. Selective breeding, hybridization, inbreeding. All 3 can be used to make specific higher yielding crops. Crops less vulnerable to disease and animals for specified jobs 2. What is Genetic engineering? Processes in which genes with speci ...
Clustering for Accuracy, Performance, and Alternative
... “Allelic association studies provide the most powerful method for locating genes of small effect contributing to complex diseases and traits.” Daniels, Am J Hum Genet 62:1189-1197, ...
... “Allelic association studies provide the most powerful method for locating genes of small effect contributing to complex diseases and traits.” Daniels, Am J Hum Genet 62:1189-1197, ...
IS IT GENETIC? How do genes, environment and chance interact to
... polygenic: a character determined by the combined action of a number of different genetic loci; mathematical polygenic theory assumes there are very many loci, each with a small, additive effect quantitative character: a character that shows continuous distribution • like height, which everyone has, ...
... polygenic: a character determined by the combined action of a number of different genetic loci; mathematical polygenic theory assumes there are very many loci, each with a small, additive effect quantitative character: a character that shows continuous distribution • like height, which everyone has, ...
Chapter 17
... death – your fingers have to separate! The same 131 cells always die during development of the nematode worm – under genetic control. Same in humans. Transfer human bcl-2 gene to nematode with defective ced-9 gene – apoptosis is avoided. ...
... death – your fingers have to separate! The same 131 cells always die during development of the nematode worm – under genetic control. Same in humans. Transfer human bcl-2 gene to nematode with defective ced-9 gene – apoptosis is avoided. ...
Crossing Over and Independent Assortment Notes
... In meiosis, the new cells have different combinations of genetic material than the parent cell n As opposed to mitosis in which the daughter and parent cell have identical genetic material ...
... In meiosis, the new cells have different combinations of genetic material than the parent cell n As opposed to mitosis in which the daughter and parent cell have identical genetic material ...
Objectives Case 1 - Precision Medicine Pathway
... • Inadequacy of ethnicity-‐based screening: • 2010 US Census data – 32% increase in individuals repor4ng ...
... • Inadequacy of ethnicity-‐based screening: • 2010 US Census data – 32% increase in individuals repor4ng ...
Lecture 7
... Shih and Weinberg used the chemical carcinogen benzopyrene to create human tumor cell lines. Human tumor cell DNA and mouse cell lines were used in gene transfer expermiments. Presence of oncogene gives dominant phenotype of “transformation” (very cancer-like). Required recombinant DNA methods to “c ...
... Shih and Weinberg used the chemical carcinogen benzopyrene to create human tumor cell lines. Human tumor cell DNA and mouse cell lines were used in gene transfer expermiments. Presence of oncogene gives dominant phenotype of “transformation” (very cancer-like). Required recombinant DNA methods to “c ...
THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... Nondisjunction: chromosomes fail to separate properly in Meiosis I or Meiosis II • Aneuploidy: incorrect # chromosomes – Monosomy (1x) or Trisomy (3x) • Polyploidy: 2+ complete sets of chromosomes; 3n or 4n – Rare in animals, frequent in plants ...
... Nondisjunction: chromosomes fail to separate properly in Meiosis I or Meiosis II • Aneuploidy: incorrect # chromosomes – Monosomy (1x) or Trisomy (3x) • Polyploidy: 2+ complete sets of chromosomes; 3n or 4n – Rare in animals, frequent in plants ...
CHAPTER 18 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION I. Student
... Students may find the large number of control points regulating eukaryotic gene expression bewildering. It is important to remind them of the significance of these mechanisms in allowing exquisite control of gene expression during development and in changing environments. ...
... Students may find the large number of control points regulating eukaryotic gene expression bewildering. It is important to remind them of the significance of these mechanisms in allowing exquisite control of gene expression during development and in changing environments. ...