src
... from one animal to another by a “filterable virus”. Filterable virus: A term that had been coined a decade or so earlier to describe pathogenic agents that were small enough to pass through filters that were impermeable to bacteria. ...
... from one animal to another by a “filterable virus”. Filterable virus: A term that had been coined a decade or so earlier to describe pathogenic agents that were small enough to pass through filters that were impermeable to bacteria. ...
Document
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
What Genes are You Wearing? Teacher Lesson
... addition, there is a pair of chromosomes, which determine sex: a female contains two X chromosomes and a male contains one X and one Y chromosome. Transmission of genetic information to offspring occurs through egg and sperm cells that contain only one representative from each chromosome pair. An eg ...
... addition, there is a pair of chromosomes, which determine sex: a female contains two X chromosomes and a male contains one X and one Y chromosome. Transmission of genetic information to offspring occurs through egg and sperm cells that contain only one representative from each chromosome pair. An eg ...
Click here for the Study Guide Answer Key
... are only seen when there are no dominant traits in a genotype. ...
... are only seen when there are no dominant traits in a genotype. ...
Genes and Hearing Loss
... heterozygous parent has two types of the same gene (in this case, one mutated and the other normal) and can produce two types of gametes (reproductive cells). One gamete will carry the mutant form of the gene of interest, and the other the normal form. Each of these gametes then has an equal chance ...
... heterozygous parent has two types of the same gene (in this case, one mutated and the other normal) and can produce two types of gametes (reproductive cells). One gamete will carry the mutant form of the gene of interest, and the other the normal form. Each of these gametes then has an equal chance ...
Genetics and Heredity
... Traits are controlled by genes • Genes are located on your chromosomes • Individuals inherit genes from their parents • Your cells contain 23 chromosome pairs ...
... Traits are controlled by genes • Genes are located on your chromosomes • Individuals inherit genes from their parents • Your cells contain 23 chromosome pairs ...
BIO520 Bioinformatics 2005 EXAM2 You may use any books, notes
... materials to complete this exam. You MAY NOT consult with any person regarding the exam’s intellectual content. Consulting with others on the exam is a violation of the Student Rights and Responsibilities code against cheating, and the minimum punishment for cheating is an E in the course. Submit th ...
... materials to complete this exam. You MAY NOT consult with any person regarding the exam’s intellectual content. Consulting with others on the exam is a violation of the Student Rights and Responsibilities code against cheating, and the minimum punishment for cheating is an E in the course. Submit th ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... Phenotype – organism’s Physical/observable characteristics Hybrid - heterozygous Purebred – homozygous Test cross – involves breeding of an organism that has the unknown genotype with on that is homozygous recessive for the desired trait ...
... Phenotype – organism’s Physical/observable characteristics Hybrid - heterozygous Purebred – homozygous Test cross – involves breeding of an organism that has the unknown genotype with on that is homozygous recessive for the desired trait ...
Name
... 23. What causes the following conditions? A. Down’s Syndrome? B. Turner’s Syndrome, C. Klinefelter’s syndrome, D. fragile X disease. 24. What is a “Hox” gene. What do these genes control? What could theoretically happen if the gene for a fly antennae were inserted into the human gene for the head? ...
... 23. What causes the following conditions? A. Down’s Syndrome? B. Turner’s Syndrome, C. Klinefelter’s syndrome, D. fragile X disease. 24. What is a “Hox” gene. What do these genes control? What could theoretically happen if the gene for a fly antennae were inserted into the human gene for the head? ...
B2.7 Topic outcome sheet
... ethical issues concerning the use of stem cells from embryos in medical research and treatments ■ make informed judgements about the economic, social and ethical issues concerning embryo screening. You will need to know: a) In body cells the chromosomes are normally found in pairs. Body cells divide ...
... ethical issues concerning the use of stem cells from embryos in medical research and treatments ■ make informed judgements about the economic, social and ethical issues concerning embryo screening. You will need to know: a) In body cells the chromosomes are normally found in pairs. Body cells divide ...
$doc.title
... or flanking regulatory sequences, but far away from the gene location, although it still influences its function. This scenario would make it impossible to detect the adaptive variant without a prior evidence of the regulatory elements of the given gene. It could be difficult to interpret patterns o ...
... or flanking regulatory sequences, but far away from the gene location, although it still influences its function. This scenario would make it impossible to detect the adaptive variant without a prior evidence of the regulatory elements of the given gene. It could be difficult to interpret patterns o ...
Variation and Selection
... certain chemicals on the rate of mutations ***Describe sickle cell anaemia as an example of mutation Starter: Make two lines http://biology-animations.blogspot.com/2011/07/genetic-mutation-animation.html ...
... certain chemicals on the rate of mutations ***Describe sickle cell anaemia as an example of mutation Starter: Make two lines http://biology-animations.blogspot.com/2011/07/genetic-mutation-animation.html ...
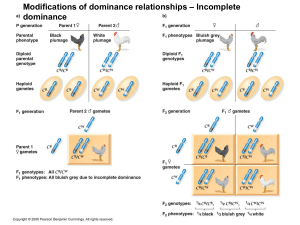
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... 1. More males that females affected 2. Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, zig-zag pattern – from grandfather to grandson through an unaffected female. 3. Approximately 50% of the progeny of a carrier female are affected 4. It is never passed from father to son 5. All daughters of ...
... 1. More males that females affected 2. Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, zig-zag pattern – from grandfather to grandson through an unaffected female. 3. Approximately 50% of the progeny of a carrier female are affected 4. It is never passed from father to son 5. All daughters of ...
BIO101 Unit 4
... a haploid sex cell; the egg or sperm which contain one-half the normal number of chromosomes; the egg unites with a sperm to form the zygote during fertilization. gastrula an early cleavage stage of embryonic development between 32 and 64 cells big which results in the formation of the three germ la ...
... a haploid sex cell; the egg or sperm which contain one-half the normal number of chromosomes; the egg unites with a sperm to form the zygote during fertilization. gastrula an early cleavage stage of embryonic development between 32 and 64 cells big which results in the formation of the three germ la ...
Option B: Biotechnology and Bioinformatics AHL
... function in other organisms. Handout 8. Multiple sequence alignment is used in the study of phylogenetics. 541-542; Handout 9. EST is an expressed sequence tag that can be used to identify potential genes. 429-431; Handout Applications and Skills: Application: Use of knockout technology in mice to d ...
... function in other organisms. Handout 8. Multiple sequence alignment is used in the study of phylogenetics. 541-542; Handout 9. EST is an expressed sequence tag that can be used to identify potential genes. 429-431; Handout Applications and Skills: Application: Use of knockout technology in mice to d ...
The Future of Genetic Testing is Now
... question of what causes the studied trait or disease and exactly how the gene causes it. Not all studies identify disease. In 2011, Scripps Lab announced collaboration with Dr. Eric Topol in studying the genome of 1,000 individuals who ...
... question of what causes the studied trait or disease and exactly how the gene causes it. Not all studies identify disease. In 2011, Scripps Lab announced collaboration with Dr. Eric Topol in studying the genome of 1,000 individuals who ...
Genetics - My Teacher Pages
... A living thing has two copies of each gene, one from its mother, and one from its father. There can be multiple types of each gene, which give different instructions: one version might cause a person to have blue eyes, another might cause them to have brown. ...
... A living thing has two copies of each gene, one from its mother, and one from its father. There can be multiple types of each gene, which give different instructions: one version might cause a person to have blue eyes, another might cause them to have brown. ...
11 Gregor Mendel - Schurz High School
... Tall x Short = all tall offspring (hybrids) Some traits are dominant over others. *Tall is the dominant trait since it is the observed trait •Short is recessive since it is the trait that disappears in the cross ...
... Tall x Short = all tall offspring (hybrids) Some traits are dominant over others. *Tall is the dominant trait since it is the observed trait •Short is recessive since it is the trait that disappears in the cross ...