Keystone Bio Practice Test
... In an ecosystem, the growth and survival of organisms are dependent on the availability of the energy from the Sun. This energy is available to organisms in the ecosystem because (1) producers have the ability to store energy from light in organic molecules (2) consumers have the ability to transfer ...
... In an ecosystem, the growth and survival of organisms are dependent on the availability of the energy from the Sun. This energy is available to organisms in the ecosystem because (1) producers have the ability to store energy from light in organic molecules (2) consumers have the ability to transfer ...
1. NATURE VS. NURTURE
... should be impossible because the previous stage is no longer present 3. The stages follow an invariant sequence: - Since each stage is derived from the preceding stage, the stages must proceed in a particular order. 4. Stages are universal: - Of course, people with a low IQ may not progress through ...
... should be impossible because the previous stage is no longer present 3. The stages follow an invariant sequence: - Since each stage is derived from the preceding stage, the stages must proceed in a particular order. 4. Stages are universal: - Of course, people with a low IQ may not progress through ...
How Does Evolution Occur? - Downtown Magnets High School
... • DNA: code that forms your traits. • DNA makes up genes- set of instructions for one trait. • Chromosomes carry the genes. • Some traits are dominant (shows up in offspring) or recessive (doesn’t show). ...
... • DNA: code that forms your traits. • DNA makes up genes- set of instructions for one trait. • Chromosomes carry the genes. • Some traits are dominant (shows up in offspring) or recessive (doesn’t show). ...
Ch 14 Test Tomorrow
... new individuals of the species move into or out of the region, it can affect the gene pool. Because new individuals add new genes to the population. This affects the number of alleles in the gene pool as well as the types of alleles in the gene pool: At one time the only people in North America were ...
... new individuals of the species move into or out of the region, it can affect the gene pool. Because new individuals add new genes to the population. This affects the number of alleles in the gene pool as well as the types of alleles in the gene pool: At one time the only people in North America were ...
text s9: yellow/major royal jelly protein family
... using RAxML v7.2.6 [10]. Nodal support values were obtained by the rapid bootstrap algorithm as implemented in RAxML (500 replicates). The tree (Fig. 1) reveals twelve gene subfamilies within insect yellow/MRJP genes, most of which are characterized by a one-to-one orthologous relationship among th ...
... using RAxML v7.2.6 [10]. Nodal support values were obtained by the rapid bootstrap algorithm as implemented in RAxML (500 replicates). The tree (Fig. 1) reveals twelve gene subfamilies within insect yellow/MRJP genes, most of which are characterized by a one-to-one orthologous relationship among th ...
Evolution Learning Objectives
... 2. What is a species? 3. Describe Darwin’s voyage and the observations that he made. 4. How are artificial selection and natural selection similar? How are they different? 5. What is a population? 6. Describe the four ways that natural selection causes evolution. 7. What is meant by the phrases ‘sur ...
... 2. What is a species? 3. Describe Darwin’s voyage and the observations that he made. 4. How are artificial selection and natural selection similar? How are they different? 5. What is a population? 6. Describe the four ways that natural selection causes evolution. 7. What is meant by the phrases ‘sur ...
Additional Glossary and Concepts List for Vertebrate Genetics
... genome by random integration (cf. gene targeting). Thus, a transgenic construct, unless stated otherwise, means a DNA plasmid designed to be introduced into the genome by transgenesis (pronuclear injection, for example). In my lectures, I will use transgene in this context only. Confusingly, a trans ...
... genome by random integration (cf. gene targeting). Thus, a transgenic construct, unless stated otherwise, means a DNA plasmid designed to be introduced into the genome by transgenesis (pronuclear injection, for example). In my lectures, I will use transgene in this context only. Confusingly, a trans ...
NONRANDOM GENE DISTRIBUTION ON HUMAN CHROMOSOMES
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
Applications for Toxicogenomics in Risk Assess
... proliferation. The gene expression analysis indicated no changes in gene expression at the lowest exposure concentration. Fifteen genes were changed at the intermediate concentration level after 5 days of exposure, but the effect had resolved by day 15 of the experiment and no genes were changed ver ...
... proliferation. The gene expression analysis indicated no changes in gene expression at the lowest exposure concentration. Fifteen genes were changed at the intermediate concentration level after 5 days of exposure, but the effect had resolved by day 15 of the experiment and no genes were changed ver ...
draft key
... 19. [10 POINTS] Red-green colorblindness in humans is due to the expression of a recessive allele of an Xlinked gene. A woman with normal vision whose mother was color-blind has a child fathered by a color-blind man. What is the probability that their first child will be color blind? ...
... 19. [10 POINTS] Red-green colorblindness in humans is due to the expression of a recessive allele of an Xlinked gene. A woman with normal vision whose mother was color-blind has a child fathered by a color-blind man. What is the probability that their first child will be color blind? ...
Genetics Unit Organization
... This unit follows Big Idea #3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes and Big Idea #4: Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. The four understandings of these big ideas are what will g ...
... This unit follows Big Idea #3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes and Big Idea #4: Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. The four understandings of these big ideas are what will g ...
Review #2
... Sex-linked genes • Sex-linked gene on X or Y • Females (XX), male (XY) – Eggs = X, sperm = X or Y • Fathers pass X-linked genes to daughters, but not sons • Males express recessive trait on the single X (hemizygous) • Females can be affected or carrier ...
... Sex-linked genes • Sex-linked gene on X or Y • Females (XX), male (XY) – Eggs = X, sperm = X or Y • Fathers pass X-linked genes to daughters, but not sons • Males express recessive trait on the single X (hemizygous) • Females can be affected or carrier ...
Mendelian Genetics
... Genetics often comes down to probability Mendel stated that traits in an organism are controlled by different factors ◦ We know that each allele is controlled by a unique gene (sequence of nucleotides) ...
... Genetics often comes down to probability Mendel stated that traits in an organism are controlled by different factors ◦ We know that each allele is controlled by a unique gene (sequence of nucleotides) ...
WORKSHEET PATTERNS OF HEREDITY
... 15.In which generation does the first case of sickle cell anemia appear? 16.Which generation contains the most male carriers? 17.Can two carriers produce an individual with sickle-cell anemia? 18.Can a normal individual produce offspring with sickle-cell anemia? 19.Which parents produce two children ...
... 15.In which generation does the first case of sickle cell anemia appear? 16.Which generation contains the most male carriers? 17.Can two carriers produce an individual with sickle-cell anemia? 18.Can a normal individual produce offspring with sickle-cell anemia? 19.Which parents produce two children ...
7th Grade Science - lafayette co c-1
... including the type and number of cells involved and the number of gene sets passed from parent to offspring. ...
... including the type and number of cells involved and the number of gene sets passed from parent to offspring. ...
Sickle Cell Anemia: A Mutation Story
... during periods of high activity. These sickled cells become stuck in small blood vessels, causing a "crisis" of pain, fever, swelling, and tissue damage that can lead to death. This is sickle cell anemia. ...
... during periods of high activity. These sickled cells become stuck in small blood vessels, causing a "crisis" of pain, fever, swelling, and tissue damage that can lead to death. This is sickle cell anemia. ...
The Little Things About the Little Things Inside of Us The Eukaryotic
... The function of the transposons is unclear. They may be cellular parasites. If a transposon is inserted into a coding region, a mutation results. If it’s in a somatic cell, cancer can result. Transposons can carry genes to new locations—adding to genetic variation. Transposons may have played a role ...
... The function of the transposons is unclear. They may be cellular parasites. If a transposon is inserted into a coding region, a mutation results. If it’s in a somatic cell, cancer can result. Transposons can carry genes to new locations—adding to genetic variation. Transposons may have played a role ...
trait
... • Traits are passed on from one generation to the next. • Traits are controlled by genes. • Organisms inherit genes in pairs (2 alleles for every trait, 1 on each strand). • Some genes are dominant, some are recessive. • Dominant genes hide recessive genes when both are inherited by an organism. • S ...
... • Traits are passed on from one generation to the next. • Traits are controlled by genes. • Organisms inherit genes in pairs (2 alleles for every trait, 1 on each strand). • Some genes are dominant, some are recessive. • Dominant genes hide recessive genes when both are inherited by an organism. • S ...
Slide 1
... • Uncertainties associated with gene tests for susceptibilities and complex conditions (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease). • Fairness in access to advanced genomic technologies. • Conceptual and philosophical implications regarding human responsibility, free will vs genetic det ...
... • Uncertainties associated with gene tests for susceptibilities and complex conditions (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease). • Fairness in access to advanced genomic technologies. • Conceptual and philosophical implications regarding human responsibility, free will vs genetic det ...
Transgenic Core Facility Pennington Biomedical Research Center
... Approximately 200 C57BL/6J one-cell eggs are injected with the transgene. The anticipated time for delivery is 2 months after initial date of pronuclear microinjection. ...
... Approximately 200 C57BL/6J one-cell eggs are injected with the transgene. The anticipated time for delivery is 2 months after initial date of pronuclear microinjection. ...
Concept 18.3. How get genetic variation in prokaryotes: • E. coli is
... Enzyme molecules recognize these as boundaries of insertion sequences and bind inverted repeats and to target site and catalyze cutting and resealing. If sequence goes into coding region of a gene or region required for regulation then mutation results. 1 every 10 million generations. Same as for ot ...
... Enzyme molecules recognize these as boundaries of insertion sequences and bind inverted repeats and to target site and catalyze cutting and resealing. If sequence goes into coding region of a gene or region required for regulation then mutation results. 1 every 10 million generations. Same as for ot ...
American Berkshire Association
... Testing will take two – six weeks, so please plan accordingly. The ABA reserves the right to use any licensed laboratory for testing. MC4R* - The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) genetic test is associated with controlling growth and leanness. The producer and breeder can decide if they wish to choose ...
... Testing will take two – six weeks, so please plan accordingly. The ABA reserves the right to use any licensed laboratory for testing. MC4R* - The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) genetic test is associated with controlling growth and leanness. The producer and breeder can decide if they wish to choose ...
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
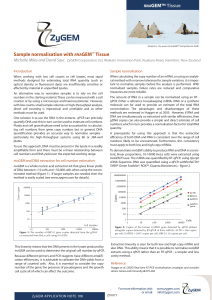
... Ploidy and cell growth-phase need to be accounted for in calculating cell numbers from gene copy number, but in general, DNA quantification provides an accurate way to normalise samples particularly for high-throughput systems using 96 or 384-well plates. To use this approach, DNA must be present in ...
... Ploidy and cell growth-phase need to be accounted for in calculating cell numbers from gene copy number, but in general, DNA quantification provides an accurate way to normalise samples particularly for high-throughput systems using 96 or 384-well plates. To use this approach, DNA must be present in ...
Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing
... • Moores Law: Advances in technology are driving the ability to address questions on a genomic scale • Optimized Array Design Achievable – Requires Control Spike-In Data for Changes in Assay and Oligo Synthesis Approaches – Time consuming and costly • High Throughput Sequencing (Unbiased Functional ...
... • Moores Law: Advances in technology are driving the ability to address questions on a genomic scale • Optimized Array Design Achievable – Requires Control Spike-In Data for Changes in Assay and Oligo Synthesis Approaches – Time consuming and costly • High Throughput Sequencing (Unbiased Functional ...