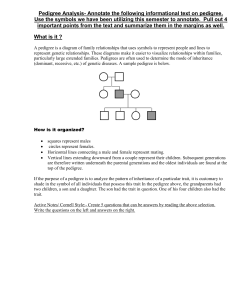
Application of Pedigree Analysis
... 1. The pedigree below is for a genetic disease or abnormality. We do not yet know if it is dominant or recessive. We will determine if it is possible that the trait is autosomal dominant. If the trait were dominant, we would use the following designations: A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnorma ...
... 1. The pedigree below is for a genetic disease or abnormality. We do not yet know if it is dominant or recessive. We will determine if it is possible that the trait is autosomal dominant. If the trait were dominant, we would use the following designations: A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnorma ...
Brief introduction to whole-genome selection in cattle using single
... individual animal will have three possibilities for the allelic composition of a regulatory region of the GH gene: (1) high from father and high from mother; (2) low from father and low from mother; or (3) high from one parent and low from the other. For many genes, there are more than two alleles p ...
... individual animal will have three possibilities for the allelic composition of a regulatory region of the GH gene: (1) high from father and high from mother; (2) low from father and low from mother; or (3) high from one parent and low from the other. For many genes, there are more than two alleles p ...
PDF
... of them are restricted to populations under Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE; see, e.g., Falconer and MacKay, 1996), including a special case of gene frequency being one half (Mather and Jinks, 1982). Others also adequately account for Hardy–Weinberg disequilibrium (HWD; e.g., Cockerham, 1954; Yang, ...
... of them are restricted to populations under Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE; see, e.g., Falconer and MacKay, 1996), including a special case of gene frequency being one half (Mather and Jinks, 1982). Others also adequately account for Hardy–Weinberg disequilibrium (HWD; e.g., Cockerham, 1954; Yang, ...
Mendel`s Pea experiments Why did Mendel choose pea plants? Pea
... and short) are now called alleles. When he crossed two true-breeding plants with opposite traits (for example tall with short), the offspring showed only one of the traits, which Mendel called the ________ trait. He called the “weaker” trait which did not appear in those offspring ________. How are ...
... and short) are now called alleles. When he crossed two true-breeding plants with opposite traits (for example tall with short), the offspring showed only one of the traits, which Mendel called the ________ trait. He called the “weaker” trait which did not appear in those offspring ________. How are ...
Modifiers of epigenetic reprogramming show paternal effects in the mouse
... the black coat), the single Avy allele in Avy/a individuals is responsible for the yellowness of the coat. We set up crosses between FVB/NJ males heterozygous for the Smarca5MommeD4 allele with yellow C57BL/6J females heterozygous for the Avy allele. As reported previously, in offspring that inherit ...
... the black coat), the single Avy allele in Avy/a individuals is responsible for the yellowness of the coat. We set up crosses between FVB/NJ males heterozygous for the Smarca5MommeD4 allele with yellow C57BL/6J females heterozygous for the Avy allele. As reported previously, in offspring that inherit ...
Basic Horse Genetics - Alabama Cooperative Extension System
... only one gene for any allele that he or she has to the offspring. For example, the base coat color of any horse may be either black with a genotype of EE or Ee or chestnut (sorrel) with a genotype of ee. The homozygous black horse (EE) can contribute only an E gene to the offspring. The homozygous c ...
... only one gene for any allele that he or she has to the offspring. For example, the base coat color of any horse may be either black with a genotype of EE or Ee or chestnut (sorrel) with a genotype of ee. The homozygous black horse (EE) can contribute only an E gene to the offspring. The homozygous c ...
The Frequency and Effects of CCR5 Delta 32 Allele in Gondar
... The CCR5 delta32 variant and AIDS A common genetic variant in the coding region of the CCR5 structural gene involves a 32 base pair deletion (CCR5-_32) that shifts the open reading frame to create a truncated protein. This protein fails to reach the cell surface in individuals homozygous for the var ...
... The CCR5 delta32 variant and AIDS A common genetic variant in the coding region of the CCR5 structural gene involves a 32 base pair deletion (CCR5-_32) that shifts the open reading frame to create a truncated protein. This protein fails to reach the cell surface in individuals homozygous for the var ...
Supplementary table I: Yeast strains Used in this study
... away from the nuclear envelope over accumulated time-lapse imaging. This was performed by computing the square of the radial distance (distance from the locus to the nuclear periphery or the center of the nucleus) between the locus positions (d) as a function of time interval (t). This scores locus ...
... away from the nuclear envelope over accumulated time-lapse imaging. This was performed by computing the square of the radial distance (distance from the locus to the nuclear periphery or the center of the nucleus) between the locus positions (d) as a function of time interval (t). This scores locus ...
Importance of Genetic Studies in Consanguineous Populations for
... selection on disease phenotypes in humans. Our “phenotypic ascertainment” claim is backed up by the high proportion of autosomal dominant disorder causal mutations identified in comparison to autosomal recessive disorder causal ones. The Hardy–Weinberg (H-W) equation clearly states that in an outbre ...
... selection on disease phenotypes in humans. Our “phenotypic ascertainment” claim is backed up by the high proportion of autosomal dominant disorder causal mutations identified in comparison to autosomal recessive disorder causal ones. The Hardy–Weinberg (H-W) equation clearly states that in an outbre ...
Relative expression of wild-type and activated Ki
... within the same reaction vessel from the same primers, and PCR products are of identical length. Initially we were concerned that the relationship between RNA transcript and amplified cDNA might be significantly distorted by the extent of heteroduplex formation, since this could influence the kineti ...
... within the same reaction vessel from the same primers, and PCR products are of identical length. Initially we were concerned that the relationship between RNA transcript and amplified cDNA might be significantly distorted by the extent of heteroduplex formation, since this could influence the kineti ...
7.27 Spring 2006 PROBLEM SET DUE MAY 12, 2006 1. A couple
... heart defect and does not survive to term. A karyotype is performed on both the mother and the father. The father is discovered to carry a balanced translocation between chromosomes 8 and 21 while the mother’s karyotype is normal. In their next pregnancy what possible outcomes could occur? Draw each ...
... heart defect and does not survive to term. A karyotype is performed on both the mother and the father. The father is discovered to carry a balanced translocation between chromosomes 8 and 21 while the mother’s karyotype is normal. In their next pregnancy what possible outcomes could occur? Draw each ...
significance of milk protein genes polymorphism for bulgarian
... 70 bp). Animals homozygous for the A allele (AA) were observed with a frequency of about 40 % and this genotype was electrophoretically visualized with two bands (144 bp and 108 bp). With the lowest frequency (about 2 %) were homozygous BB animals which were identified with three electrophoreti ...
... 70 bp). Animals homozygous for the A allele (AA) were observed with a frequency of about 40 % and this genotype was electrophoretically visualized with two bands (144 bp and 108 bp). With the lowest frequency (about 2 %) were homozygous BB animals which were identified with three electrophoreti ...
It Skips a Generation: Traits, Genes, and Crosses
... food plants and genetic maps of economically important traits like tomato color. ...
... food plants and genetic maps of economically important traits like tomato color. ...
userfiles/153/my files/15_lecture_presentation?id=3403
... Morgan found that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific combinations (parental phenotypes) He noted that these genes do not assort independently, and reasoned that they were on the same chromosome • Note, however, that nonparental phenotypes were also produced • Un ...
... Morgan found that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific combinations (parental phenotypes) He noted that these genes do not assort independently, and reasoned that they were on the same chromosome • Note, however, that nonparental phenotypes were also produced • Un ...
How to catch epistasis: theory and practice - Montefiore
... Step1: For every pair of markers, each multilocus genotype (MLG) is tested for association with a trait against of the group of other MLGs. Basing on this statistics each MLG is classified as “high risk”, “low risk” or “no evidence for risk” (by default risk threshold = 0.1), and than all MLGs of th ...
... Step1: For every pair of markers, each multilocus genotype (MLG) is tested for association with a trait against of the group of other MLGs. Basing on this statistics each MLG is classified as “high risk”, “low risk” or “no evidence for risk” (by default risk threshold = 0.1), and than all MLGs of th ...
x-linked female-sterile loci in drosophzla melanogaster
... indicating that these gene functions are also required for viability. Most of these loci are represented by only one female-sterile allele; however, there are three exceptions: fused, rudimentary and fs( I)h, in which multiple alleles have been isolated. In the case of fused and rudimentary, most mu ...
... indicating that these gene functions are also required for viability. Most of these loci are represented by only one female-sterile allele; however, there are three exceptions: fused, rudimentary and fs( I)h, in which multiple alleles have been isolated. In the case of fused and rudimentary, most mu ...
Detection of Polymorphism of Growth Hormone Gene for the
... allele indicated the presence of restriction site while its absence was assigned as allele V. In L allele the restriction site contained the nucleotide C while a transition with G at the same site indicated the absence of AluI restriction site. The total length of amino acid in growth hormone is 191 ...
... allele indicated the presence of restriction site while its absence was assigned as allele V. In L allele the restriction site contained the nucleotide C while a transition with G at the same site indicated the absence of AluI restriction site. The total length of amino acid in growth hormone is 191 ...
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance -States that genes or alleles
... -The less often a gene crosses over with another one, the closer it must be to it, so if the frequency is low, the distance between the two must be small ...
... -The less often a gene crosses over with another one, the closer it must be to it, so if the frequency is low, the distance between the two must be small ...
a demographic framework mapping genes to communities Coulson, T
... This component of the framework specifies the link between alleles, the proteins they code for, and phenotypic traits – the domain of systems biology including evolutionary developmental biology. Systems biology is the quantitative study of biological processes as whole systems instead of isolated p ...
... This component of the framework specifies the link between alleles, the proteins they code for, and phenotypic traits – the domain of systems biology including evolutionary developmental biology. Systems biology is the quantitative study of biological processes as whole systems instead of isolated p ...
Note: Remove this blank sheet of paper from the exam and use it to
... since they already have a cystic fibrosis child, they reason that the next three will be healthy. How are they wrong? ...
... since they already have a cystic fibrosis child, they reason that the next three will be healthy. How are they wrong? ...
The Wahlund Effect and F Statistics -- The Interaction of - IB-USP
... Hence the subdivision of the population into genetically distinct demes causes deviations from Hardy-Weinberg that are identical in form to those caused by an inbreeding system of mating within demes. This “inbreeding coefficient” is called Fst because it refers to the deviation from Hardy-Weinberg ...
... Hence the subdivision of the population into genetically distinct demes causes deviations from Hardy-Weinberg that are identical in form to those caused by an inbreeding system of mating within demes. This “inbreeding coefficient” is called Fst because it refers to the deviation from Hardy-Weinberg ...
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
... can be synthesized. This is a case of haploinsufficiency, 50% protein product is not sufficient for completely normal bone structure. However, mutations that result in a mutant proα1 protein that is synthesized, but not functional, cause much more severe cases of osteogenesis (types II, III, and IV) ...
... can be synthesized. This is a case of haploinsufficiency, 50% protein product is not sufficient for completely normal bone structure. However, mutations that result in a mutant proα1 protein that is synthesized, but not functional, cause much more severe cases of osteogenesis (types II, III, and IV) ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.























