Chapter 23 Slides
... changes in non-coding regions Some mutations are harmful, some may be beneficial ...
... changes in non-coding regions Some mutations are harmful, some may be beneficial ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... Garden peas produce male and female sex cells called gametes. Fertilization occurs when the male and female reproductive cells join forming a zygote. The zygote becomes part of a seed. Mendel used true-breeding peas, meaning if they were allowed self self-pollinate, they would produce offspring iden ...
... Garden peas produce male and female sex cells called gametes. Fertilization occurs when the male and female reproductive cells join forming a zygote. The zygote becomes part of a seed. Mendel used true-breeding peas, meaning if they were allowed self self-pollinate, they would produce offspring iden ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 5 Notes
... Heterozygotes with one normal allele and one mutant allele would produce 50% of wild-type molecule which is sufficient to sustain normal cellular processes- life goes on. Unlike cy, most recessive lethal alleles do not have an additional dominant visible phenotype. Mutations in enzymes required for ...
... Heterozygotes with one normal allele and one mutant allele would produce 50% of wild-type molecule which is sufficient to sustain normal cellular processes- life goes on. Unlike cy, most recessive lethal alleles do not have an additional dominant visible phenotype. Mutations in enzymes required for ...
Biology Midterm Exam Review Guide
... 1. Define the following terms: mitosis meiosis heredity haploid diploid daughter cell allele gene chromosome dominant recessive homozygous heterozygous hybrid purebred zygote fertilization crossing over sex chromosomes monohybrid ...
... 1. Define the following terms: mitosis meiosis heredity haploid diploid daughter cell allele gene chromosome dominant recessive homozygous heterozygous hybrid purebred zygote fertilization crossing over sex chromosomes monohybrid ...
Chapter 11 Assessment
... Summarize what Mendel concluded from his pea plant experiments. Label these examples as one of the following heredity terms: trait, dominant allele, recessive allele, genotypes, or phenotypes. a. b. c. d. ...
... Summarize what Mendel concluded from his pea plant experiments. Label these examples as one of the following heredity terms: trait, dominant allele, recessive allele, genotypes, or phenotypes. a. b. c. d. ...
tG TG
... 31. “Father of Genetics” -- Worked with pea plants. Mendel's First Law of Genetics (Law of Segregation): A gene that can exist in more than 1 form (e.g. a gene for round or wrinkled peas) is called an allele. When gametes are produced (by meiosis) in the parent, allele pairs separate leaving eac ...
... 31. “Father of Genetics” -- Worked with pea plants. Mendel's First Law of Genetics (Law of Segregation): A gene that can exist in more than 1 form (e.g. a gene for round or wrinkled peas) is called an allele. When gametes are produced (by meiosis) in the parent, allele pairs separate leaving eac ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... 32. A population of 100 individuals has 16 that are sick with a disease known to be caused by the expression of a deleterious recessive allele in homozygous individuals. It is further known that there are three alleles at the locus, alleles a and b are co-dominant and cause no disease, but a recessi ...
... 32. A population of 100 individuals has 16 that are sick with a disease known to be caused by the expression of a deleterious recessive allele in homozygous individuals. It is further known that there are three alleles at the locus, alleles a and b are co-dominant and cause no disease, but a recessi ...
Practice Genetics Problems - mvhs
... 2. Your second case at your new job is to counsel another couple who have a son with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis is a recessive disease that affects has a high incidence in the Caucasian population (1 in every 2500 births). Individuals with cystic fibrosis produce a thick mucus in the lungs and ...
... 2. Your second case at your new job is to counsel another couple who have a son with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis is a recessive disease that affects has a high incidence in the Caucasian population (1 in every 2500 births). Individuals with cystic fibrosis produce a thick mucus in the lungs and ...
Activity 3.4.1: Family Inheritance
... and that each form of a gene present at a specific location on a specific chromosome is called an allele. When one allele in a pair of chromosomes is stronger than the other allele, the trait of the weaker allele is concealed. The stronger allele is known as the dominant gene, and the weaker allele ...
... and that each form of a gene present at a specific location on a specific chromosome is called an allele. When one allele in a pair of chromosomes is stronger than the other allele, the trait of the weaker allele is concealed. The stronger allele is known as the dominant gene, and the weaker allele ...
1. The father of genetics is_____. A. Charles Darwin B
... 45. If an individual with the dominant phenotype is crossed with an individual with the recessive phenotype and all the offspring have the dominant phenotype, it would be concluded that the individual with the dominant phenotype is _____. ___ A. homozygous dominant ...
... 45. If an individual with the dominant phenotype is crossed with an individual with the recessive phenotype and all the offspring have the dominant phenotype, it would be concluded that the individual with the dominant phenotype is _____. ___ A. homozygous dominant ...
Document
... • Counting alleles from known genotypes is the easiest way. • In simple example, there are 2 AA, 4 AB, and 2 BB genotypes (8 total individuals, 16 total alleles): ...
... • Counting alleles from known genotypes is the easiest way. • In simple example, there are 2 AA, 4 AB, and 2 BB genotypes (8 total individuals, 16 total alleles): ...
Ch. 13 - Crestwood Local Schools
... Results in hybrid offspring where the offspring may be different than the parents. ...
... Results in hybrid offspring where the offspring may be different than the parents. ...
Fun With Mendelian Genetics Introduction Charles Darwin`s and
... They did not discover how new variants, the raw material of natural selection, arose (we now know that new variants arise through a change—called a mutation—in the genetic code). Nor did they figure out how characteristics were transmitted from generation to generation. Although some of the basic pr ...
... They did not discover how new variants, the raw material of natural selection, arose (we now know that new variants arise through a change—called a mutation—in the genetic code). Nor did they figure out how characteristics were transmitted from generation to generation. Although some of the basic pr ...
Genes - Revision World
... - change might be beneficial. Offspring will flourish, doing better than others in that species. - Many more offspring will inherit this beneficial mutation and will be better suited to that environment… ...
... - change might be beneficial. Offspring will flourish, doing better than others in that species. - Many more offspring will inherit this beneficial mutation and will be better suited to that environment… ...
Genetics Practice
... 1. Sex determination in birds is different from that in humans. The sex chromosomes are called Z and W. Males have two of the same chromosome (ZZ) while females have two different chromosomes (ZW). There is a Z-linked allele in some birds that causes the death of the embryo when the normal dominant ...
... 1. Sex determination in birds is different from that in humans. The sex chromosomes are called Z and W. Males have two of the same chromosome (ZZ) while females have two different chromosomes (ZW). There is a Z-linked allele in some birds that causes the death of the embryo when the normal dominant ...
“GENE-STICKS”
... c) Each piece of tape represents the location of a _______________________, which is a section of DNA that codes for a trait. d) The letters you wrote on the tape represent ________________________, which are the different possible forms of a particular gene. Genotype: genetic makeup of an organism; ...
... c) Each piece of tape represents the location of a _______________________, which is a section of DNA that codes for a trait. d) The letters you wrote on the tape represent ________________________, which are the different possible forms of a particular gene. Genotype: genetic makeup of an organism; ...
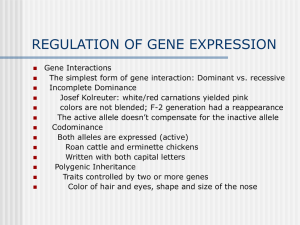
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.