Unit 8 - Genetics
... • This is possible because females have two “X” chromosomes. The normal X chromosome is dominant to the defective X C or H chromosome and masks the defective trait. • Males are more likely to get sex-linked traits because they either have the trait or they don’t. Males do not have another X chromoso ...
... • This is possible because females have two “X” chromosomes. The normal X chromosome is dominant to the defective X C or H chromosome and masks the defective trait. • Males are more likely to get sex-linked traits because they either have the trait or they don’t. Males do not have another X chromoso ...
Genetics
... POLYGENIC INHERITANCE- a trait controlled by two or more genes that may be on the same or on different chromosomes • Examples of polygenic inheritance: eye color, skin color, and blood group ...
... POLYGENIC INHERITANCE- a trait controlled by two or more genes that may be on the same or on different chromosomes • Examples of polygenic inheritance: eye color, skin color, and blood group ...
S1 Table.
... Somatic mutation. Any mutation that occurs in a cell that is not nor will become a germ cell is considered a somatic mutation. The term is commonly used to distinguish mutations that occur in tumor cells only, and not in other cells in the body. Loss of Heterozygosity. Germ line genetic variants, e. ...
... Somatic mutation. Any mutation that occurs in a cell that is not nor will become a germ cell is considered a somatic mutation. The term is commonly used to distinguish mutations that occur in tumor cells only, and not in other cells in the body. Loss of Heterozygosity. Germ line genetic variants, e. ...
BLA Biology
... • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other allele. • A heterozygous phenotype – A mixture or blending of the two ...
... • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other allele. • A heterozygous phenotype – A mixture or blending of the two ...
Mendel`s Crosses - biology-with
... alone. In the case of Mendel’s pea plants, you know that round seeds (R) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (r). a) Identify the genotypes for seed shape that you can determine by inspection alone. Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
... alone. In the case of Mendel’s pea plants, you know that round seeds (R) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (r). a) Identify the genotypes for seed shape that you can determine by inspection alone. Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
Population Genetics ppt - Liberty Union High School District
... Different combinations of alleles in a gene pool can be formed when organisms mate and have offspring. The Allele Frequency is the measure of how common a certain allele is in the population. Allele Frequency = the number of times an allele occurs the total number of alleles for that gene ...
... Different combinations of alleles in a gene pool can be formed when organisms mate and have offspring. The Allele Frequency is the measure of how common a certain allele is in the population. Allele Frequency = the number of times an allele occurs the total number of alleles for that gene ...
II. Probability and Punnett Squares
... -Organisms with 2 different alleles for the same trait (Tt) are called heterozygous, hetero = different. -Homozygous organisms are true-breeding or pure for a trait & heterozygous organisms are hybrid for a trait. ...
... -Organisms with 2 different alleles for the same trait (Tt) are called heterozygous, hetero = different. -Homozygous organisms are true-breeding or pure for a trait & heterozygous organisms are hybrid for a trait. ...
Mendelian Genetics
... appear when plants were crossed. The first generation offspring are called the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is ...
... appear when plants were crossed. The first generation offspring are called the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is ...
File
... Asexual reproduction is generally used by simple organisms, such as bacteria. In asexual reproduction, an organism produces an identical copy of itself. Only one parent is required for asexual reproduction, and the offspring and the parent are exactly the same. In general, asexual reproduction is qu ...
... Asexual reproduction is generally used by simple organisms, such as bacteria. In asexual reproduction, an organism produces an identical copy of itself. Only one parent is required for asexual reproduction, and the offspring and the parent are exactly the same. In general, asexual reproduction is qu ...
(b).
... § An organism with two for a particular trait is heterozygous. One allele is dominant, and one allele is recessive. § Aa, Ee, Tt, etc. § An organism with heterozygous alleles would express the dominant form of the trait. (the uppercase letter DOMINANTS over the lowercase letter) ...
... § An organism with two for a particular trait is heterozygous. One allele is dominant, and one allele is recessive. § Aa, Ee, Tt, etc. § An organism with heterozygous alleles would express the dominant form of the trait. (the uppercase letter DOMINANTS over the lowercase letter) ...
Unit 2 Review Sheet File
... (d) Explain how the process of meiosis accounts for Mendel’s observations and conclusions concerning factor (gene) segregation and independent assortment. 3. How many different types of gametes would each of the following parent plants be capable of producing? List the possible combinations. a. Tt b ...
... (d) Explain how the process of meiosis accounts for Mendel’s observations and conclusions concerning factor (gene) segregation and independent assortment. 3. How many different types of gametes would each of the following parent plants be capable of producing? List the possible combinations. a. Tt b ...
Meiosis II
... dominant or recessive. The alleles you have are your genotype; the observable characteristics that come from your genotype are your ...
... dominant or recessive. The alleles you have are your genotype; the observable characteristics that come from your genotype are your ...
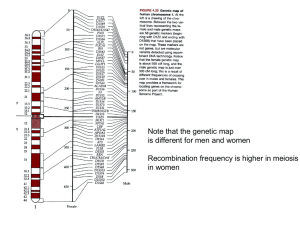
Recombination between homologous chromosomes
... - In independent assortment, each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologues into daughter cells independently of the other pairs - For humans (n = 23), there are more than 8 million possible combinations of chromosomes ...
... - In independent assortment, each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologues into daughter cells independently of the other pairs - For humans (n = 23), there are more than 8 million possible combinations of chromosomes ...
Ch. 14 parts 1 & 2
... “What is the probability that an F2 plant from a monohybrid cross will be heterozygous?” - there are 2 ways that this can occur: * the dominant allele can come from the ovum and the recessive from the sperm, or vice versa - to find the probability that an event can occur in 2 or more different ways, ...
... “What is the probability that an F2 plant from a monohybrid cross will be heterozygous?” - there are 2 ways that this can occur: * the dominant allele can come from the ovum and the recessive from the sperm, or vice versa - to find the probability that an event can occur in 2 or more different ways, ...
Mendelian Genetics
... using two traits, each one should have 4 alleles, 2 for each trait. Each gamete produced by the P1 generations will contain 2 alleles, one for each trait. ...
... using two traits, each one should have 4 alleles, 2 for each trait. Each gamete produced by the P1 generations will contain 2 alleles, one for each trait. ...
Hardy-Weinberg Principle and Equations The Hardy
... Total # of alleles in a population p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (TT) 2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Tt) q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (tt) -Can be counted in a population based on phenotype. Note: the frequency of heterozygotes i ...
... Total # of alleles in a population p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (TT) 2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Tt) q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (tt) -Can be counted in a population based on phenotype. Note: the frequency of heterozygotes i ...
Word
... Total # of alleles in a population p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (TT) 2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Tt) q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (tt) -Can be counted in a population based on phenotype. Note: the frequency of heterozygotes i ...
... Total # of alleles in a population p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (TT) 2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Tt) q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (tt) -Can be counted in a population based on phenotype. Note: the frequency of heterozygotes i ...
Evolution Essay Questions
... 1. Explain how the ratio of dominant to recessive alleles within a population can tell you if a population is evolving. In your explanation list the conditions that need to be in place for evolution not to happen, why we are concerned about alleles vs phenotypes, and an example of how each of the fi ...
... 1. Explain how the ratio of dominant to recessive alleles within a population can tell you if a population is evolving. In your explanation list the conditions that need to be in place for evolution not to happen, why we are concerned about alleles vs phenotypes, and an example of how each of the fi ...
solutions
... GM foods can help solve world hunger, improve the production of food, make better versions of what nature has provided GM foods are not ‘natural’, may do more harm than good, we cannot see the long term effects of changing the species. 19. What is meant by the term ‘genetic screening’ and how could ...
... GM foods can help solve world hunger, improve the production of food, make better versions of what nature has provided GM foods are not ‘natural’, may do more harm than good, we cannot see the long term effects of changing the species. 19. What is meant by the term ‘genetic screening’ and how could ...
Lecture 3 Human Genetics
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
Chapter 11 ~ GENETICS
... Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles 10. Some alleles are neither dominant nor _________________________, and many traits are controlled by _______________________ alleles or by multiple genes. 11. In the F1 generation of Mirabilis plants, a red flower crossed with a white flower will produce ____ ...
... Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles 10. Some alleles are neither dominant nor _________________________, and many traits are controlled by _______________________ alleles or by multiple genes. 11. In the F1 generation of Mirabilis plants, a red flower crossed with a white flower will produce ____ ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.