CHAPs 10, 11 Rev
... a. One of the parents was homozygous for albinism. b. Both parents were heterozygous. c. One parent was homozygous for normal pigmentation. d. Both parents were albinos. e. 605 albino zygotes must have failed to develop. When the two gametes that fuse to form a zygote contain different alleles of a ...
... a. One of the parents was homozygous for albinism. b. Both parents were heterozygous. c. One parent was homozygous for normal pigmentation. d. Both parents were albinos. e. 605 albino zygotes must have failed to develop. When the two gametes that fuse to form a zygote contain different alleles of a ...
Genetics and Heredity
... For each monohybrid cross, Mendel cross-fertilized true-breeding plants that were different in just one character—in this case, flower color. He then allowed the hybrids (the F1 generation) to self-fertilize. ...
... For each monohybrid cross, Mendel cross-fertilized true-breeding plants that were different in just one character—in this case, flower color. He then allowed the hybrids (the F1 generation) to self-fertilize. ...
Notes 4
... mates independently of genotype (randomly mate), then the fractions of the genotypes of the offspring are p2, 2pq, q2, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles (p + q = 1). These are the Hardy-Weinberg (H-W) frequencies. Note that the H-W frequencies do not depend on the genotype frequen ...
... mates independently of genotype (randomly mate), then the fractions of the genotypes of the offspring are p2, 2pq, q2, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles (p + q = 1). These are the Hardy-Weinberg (H-W) frequencies. Note that the H-W frequencies do not depend on the genotype frequen ...
Lecture 3 Wednesday, March 4, 2009 Response to the Origin • Wide
... mates independently of genotype (randomly mate), then the fractions of the genotypes of the offspring are p2, 2pq, q2, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles (p + q = 1). These are the Hardy-Weinberg (H-W) frequencies. Note that the H-W frequencies do not depend on the genotype frequen ...
... mates independently of genotype (randomly mate), then the fractions of the genotypes of the offspring are p2, 2pq, q2, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles (p + q = 1). These are the Hardy-Weinberg (H-W) frequencies. Note that the H-W frequencies do not depend on the genotype frequen ...
Genetics: The Work of Gregor Mendel
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
Mendelian Genetics
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
Genetics: The Work of Gregor Mendel
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
... • Cross-pollination = one plant fertilizes another • P generation = Parent generation • F1 generation = 1st generation offspring (“filius” is Latin for “son”; offspring of P generation) • F2 generation = 2nd generation offspring (offspring of F1 generation) ...
Genetic Wheel - cloudfront.net
... fitness enable some individuals to reproduce more successfully and pass their advantageous genetic variations on to the next generation. How genetic variation arises can be complicated. Some traits are controlled by many genes that act together in a complex manner. For example, human skin color is d ...
... fitness enable some individuals to reproduce more successfully and pass their advantageous genetic variations on to the next generation. How genetic variation arises can be complicated. Some traits are controlled by many genes that act together in a complex manner. For example, human skin color is d ...
/+ +/+ +/+ +/+ a +/ b - Molecular and Cell Biology
... If we are going to want to use as a mutagen (hop into genes)… Lucky thing that M strains exist (strains with no pre-existing source of P transposase or antitransposase to interfere with our controlling non-autonomous element [transgene] mobility) ...
... If we are going to want to use as a mutagen (hop into genes)… Lucky thing that M strains exist (strains with no pre-existing source of P transposase or antitransposase to interfere with our controlling non-autonomous element [transgene] mobility) ...
description
... Your previous study has taught you that each chromosome in an autosome pair carries alleles for the same traits. For instance, located on one particular position on a chromosome may be an allele for right handedness. In the same position on the other (homologous) chromosome of that pair is an allele ...
... Your previous study has taught you that each chromosome in an autosome pair carries alleles for the same traits. For instance, located on one particular position on a chromosome may be an allele for right handedness. In the same position on the other (homologous) chromosome of that pair is an allele ...
Mendelian Genetics - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... – Genes on the same chromosome are not always linked. – Crossing-over sometimes separates linked genes to form new allele combinations. – This allows for greater genetic diversity. ...
... – Genes on the same chromosome are not always linked. – Crossing-over sometimes separates linked genes to form new allele combinations. – This allows for greater genetic diversity. ...
Heredity
... appeared to be passed down from the parent plant to the offspring. Mendel did not know about DNA or chromosomes, and he could not explain how these (8) _______________________ were passed down. His work was mostly ignored for many years. Mendel's work became the basis for the field of genetics, the ...
... appeared to be passed down from the parent plant to the offspring. Mendel did not know about DNA or chromosomes, and he could not explain how these (8) _______________________ were passed down. His work was mostly ignored for many years. Mendel's work became the basis for the field of genetics, the ...
AP Biology 1. Small Population
... Genetic Drift - Random chance events can change frequency of traits in a population ...
... Genetic Drift - Random chance events can change frequency of traits in a population ...
Chapter 7 Note taking Form
... Widow’s peak Mendel’s rules of inheritance apply to autosomal genetic ________________________. An organism's ___________________________ represents the two alleles inherited for a given trait such as CC or cc. For an organism to be a ____________________, the genotype must include one copy of a r ...
... Widow’s peak Mendel’s rules of inheritance apply to autosomal genetic ________________________. An organism's ___________________________ represents the two alleles inherited for a given trait such as CC or cc. For an organism to be a ____________________, the genotype must include one copy of a r ...
Document
... homozygous dominant----------> TT heterozygous (a hybrid--a mix)---> Tt homozygous recessive----------> tt recessive phenotypes can only be expressed (show up) when there are 2 copies of a recessive gene present at the same time...if a dominant gene was there, then that would be expressed, hiding ...
... homozygous dominant----------> TT heterozygous (a hybrid--a mix)---> Tt homozygous recessive----------> tt recessive phenotypes can only be expressed (show up) when there are 2 copies of a recessive gene present at the same time...if a dominant gene was there, then that would be expressed, hiding ...
DO NOW - Kenwood Academy High School
... the trait. Recessive traits are only seen in the offspring if both parents contribute a recessive allele. Smiley Face Baby Activity Traits are passed from parents to their offspring randomly to gametes during meiosis. Male gametes are sperm. Female gametes are eggs. Use the flip of a coin to determi ...
... the trait. Recessive traits are only seen in the offspring if both parents contribute a recessive allele. Smiley Face Baby Activity Traits are passed from parents to their offspring randomly to gametes during meiosis. Male gametes are sperm. Female gametes are eggs. Use the flip of a coin to determi ...
Unit 3- study guide Test 1
... a. Independent Assortment b. Dominant & Recessive traits c. Segregation of factors 26. Humans have ____ (2n) chromosomes in each __________(somatic) cell. 27. Humans have ____ (1n) chromosomes in each _______________ (sex cell). 28. _______________ – different forms of the same gene (flower color) 2 ...
... a. Independent Assortment b. Dominant & Recessive traits c. Segregation of factors 26. Humans have ____ (2n) chromosomes in each __________(somatic) cell. 27. Humans have ____ (1n) chromosomes in each _______________ (sex cell). 28. _______________ – different forms of the same gene (flower color) 2 ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind The
... 12. Haig, D. 2013 Kin conflict in seed development: an interdependent but fractious collective. Annu. Rev. Cell Devel. Biol. in press. ...
... 12. Haig, D. 2013 Kin conflict in seed development: an interdependent but fractious collective. Annu. Rev. Cell Devel. Biol. in press. ...
20.Human.Neanderthal.Selection
... In plots of EHH versus distance, the area under the EHH curve will usually be much greater for a selected allele than for a neutral allele. We compute the integral of the observed decay of EHH away from a specified core allele until EHH reaches 0.05. This integrated EHH (iHH) denoted iHHA or iHHD, ...
... In plots of EHH versus distance, the area under the EHH curve will usually be much greater for a selected allele than for a neutral allele. We compute the integral of the observed decay of EHH away from a specified core allele until EHH reaches 0.05. This integrated EHH (iHH) denoted iHHA or iHHD, ...
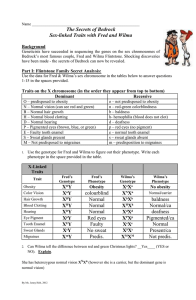
Part I: Flintstone Family Secret Analysis
... NO she does not. Her genotype is heterozygous (female offspring have 100% of inheriting a heterozygous genotype), meaning she is a carrier for baldness however she also has the dominant allele for normal hair, which means she will express normal hair ...
... NO she does not. Her genotype is heterozygous (female offspring have 100% of inheriting a heterozygous genotype), meaning she is a carrier for baldness however she also has the dominant allele for normal hair, which means she will express normal hair ...
Mendel Quiz 1. Who was Gregor Mendel? a) He was Charles
... 4. In guinea pigs, the phenotype for fur are rough hair (dominant) and straight hair (recessive). If two heterozygous guinea pigs are crossed, the largest number of any one genotype of offspring would be a) homozygous straight hair b) homozygous rough hair c) heterozygous rough hair d) intermediate ...
... 4. In guinea pigs, the phenotype for fur are rough hair (dominant) and straight hair (recessive). If two heterozygous guinea pigs are crossed, the largest number of any one genotype of offspring would be a) homozygous straight hair b) homozygous rough hair c) heterozygous rough hair d) intermediate ...
DNA
... Allele that will always affect the phenotype (as opposed to a recessive allele, whose effect will not be seen if a dominant allele is present). ...
... Allele that will always affect the phenotype (as opposed to a recessive allele, whose effect will not be seen if a dominant allele is present). ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.