Darwin, Mendel, and Genetics
... Suppose that each genotype appears with a certain percentage in a population. If we assume that each male-female pair is equally likely to mate, then the fraction of male-female pairs with given genotypes mating is the product of the fraction of the population each mate comprises. Example: If RR Y ...
... Suppose that each genotype appears with a certain percentage in a population. If we assume that each male-female pair is equally likely to mate, then the fraction of male-female pairs with given genotypes mating is the product of the fraction of the population each mate comprises. Example: If RR Y ...
Sex Linked Inheritance
... • The inheritance is different from common dominant or recessive inheritance patterns. • A fragile area on the X chromosome tends to repeat bits of the genetic code. • The more repeats, the more likely there is to be a ...
... • The inheritance is different from common dominant or recessive inheritance patterns. • A fragile area on the X chromosome tends to repeat bits of the genetic code. • The more repeats, the more likely there is to be a ...
Lectures 15-17: Patterns of Inheritance Genotype Vs. Phenotype
... a. Dominant: trait is expressed whenever the gene is present, whether as heterozygote or homozygote b. Recessive: Trait is only expressed in the homozygote (need two copies of the gene) c. Co-dominant: effects of both alleles may be seen in the heterozygote d. You must think about whether gene is lo ...
... a. Dominant: trait is expressed whenever the gene is present, whether as heterozygote or homozygote b. Recessive: Trait is only expressed in the homozygote (need two copies of the gene) c. Co-dominant: effects of both alleles may be seen in the heterozygote d. You must think about whether gene is lo ...
chapt20_lecture
... Gametes only carry one allele, so if an individual has the genotype Ww what are the possible gametes that this individual can pass on? Answer: either a W or a w but not both Another example: ...
... Gametes only carry one allele, so if an individual has the genotype Ww what are the possible gametes that this individual can pass on? Answer: either a W or a w but not both Another example: ...
Bio 11A
... 1. Define the following terms: genetic trait, gene, locus, alleles, heterozygous, homozygous, dominant alleles, recessive alleles, phenotype, and genotype. 2. Who was Gregor Mendel and what did he contribute to our understanding of genetics? 3. Be able to analyze a monohybrid cross, using a Punnet s ...
... 1. Define the following terms: genetic trait, gene, locus, alleles, heterozygous, homozygous, dominant alleles, recessive alleles, phenotype, and genotype. 2. Who was Gregor Mendel and what did he contribute to our understanding of genetics? 3. Be able to analyze a monohybrid cross, using a Punnet s ...
Bt - Biology
... Polygenic inheritance: means that more than one gene determines the trait expressed These genes can be on multiple chromosomes ...
... Polygenic inheritance: means that more than one gene determines the trait expressed These genes can be on multiple chromosomes ...
5-Sex linked - Science-with
... • offspring can mate shortly after leaving the egg • females produce over 100 eggs • they are small and easy to take care of. • males can be easily distinguished from females. • males have smaller-rounded abdomen, females have a pointed abdomen. ...
... • offspring can mate shortly after leaving the egg • females produce over 100 eggs • they are small and easy to take care of. • males can be easily distinguished from females. • males have smaller-rounded abdomen, females have a pointed abdomen. ...
SCI 30 UA CH 2.2 Inheritance
... autosomal and sex-linked patterns of inheritance, you will also learn why some A genetics counsellor studies for many at a university to obtain a master’s diseases and characteristics are present in a particular gender more than they are years degree or PhD in medical genetics because it takes consi ...
... autosomal and sex-linked patterns of inheritance, you will also learn why some A genetics counsellor studies for many at a university to obtain a master’s diseases and characteristics are present in a particular gender more than they are years degree or PhD in medical genetics because it takes consi ...
The green dwarf parent in Cross2 is from a true
... animals (or plants) cannot produce viable offspring because either the eggs or sperm are nonfunctional, or, even if the gametes are functional, the offspring are inviable. ...
... animals (or plants) cannot produce viable offspring because either the eggs or sperm are nonfunctional, or, even if the gametes are functional, the offspring are inviable. ...
Comparative mapping of the Oregon Wolfe Barley
... dominant dwarfing allele. • Perhaps when ZEO-1 was dominant, the plants did not survive, so the study did not see their alleles in the population. ...
... dominant dwarfing allele. • Perhaps when ZEO-1 was dominant, the plants did not survive, so the study did not see their alleles in the population. ...
introduction to genetics
... exchange of chromosomal segments between a pair of homologous chromosomes during prophase I ...
... exchange of chromosomal segments between a pair of homologous chromosomes during prophase I ...
Document
... inheritance? 3. What are the odds that III-5 is a carrier? 4. What is the relationship between I-1and III-4? 5. Which individuals are affected with cystic fibrosis? ...
... inheritance? 3. What are the odds that III-5 is a carrier? 4. What is the relationship between I-1and III-4? 5. Which individuals are affected with cystic fibrosis? ...
Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Single Gene Disorders Some
... Homozygote – an individual having identical alleles at a particular locus Heterozygote – an individual having two different alleles at a particular locus Hemizygous – having only one copy of a gene or DNA sequence in diploid cells. Males are hemizygous for most genes on sex chromosomes, having only ...
... Homozygote – an individual having identical alleles at a particular locus Heterozygote – an individual having two different alleles at a particular locus Hemizygous – having only one copy of a gene or DNA sequence in diploid cells. Males are hemizygous for most genes on sex chromosomes, having only ...
slides
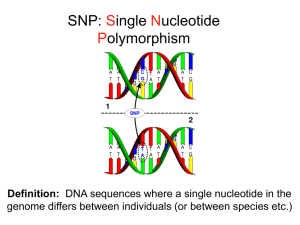
... Abundance: high frequency on the genome Posi@on: throughout the genome – coding region, intron region, promoter site Ease of genotyping (high-‐throughput genotyping) Less mutable than other forms of polymorphi ...
... Abundance: high frequency on the genome Posi@on: throughout the genome – coding region, intron region, promoter site Ease of genotyping (high-‐throughput genotyping) Less mutable than other forms of polymorphi ...
La génétique - Ms McRae`s Science
... In Canada, one in 10 000 people suffers from Huntington’s chorea, which causes neurons in the brain to decay. Patients typically have difficulty controlling their movements; eventually they become completely immobile and die. On our fourth pair of chromosomes, we all have a gene called the Huntingto ...
... In Canada, one in 10 000 people suffers from Huntington’s chorea, which causes neurons in the brain to decay. Patients typically have difficulty controlling their movements; eventually they become completely immobile and die. On our fourth pair of chromosomes, we all have a gene called the Huntingto ...
Three-factor crosses
... A. Sometimes it is difficult to determine the order of nearby loci 1. The order can be determined by using a 3-factor cross (see Brenner 74, Table 8) B. Procedure 1. Cross a double mutant (one locus is one of the problem genes, the other is a known locus) with a single mutant (the other problem gene ...
... A. Sometimes it is difficult to determine the order of nearby loci 1. The order can be determined by using a 3-factor cross (see Brenner 74, Table 8) B. Procedure 1. Cross a double mutant (one locus is one of the problem genes, the other is a known locus) with a single mutant (the other problem gene ...
File
... For example, humans have three genes responsible for color vision, all located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males ...
... For example, humans have three genes responsible for color vision, all located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males ...
PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... • Reduced penetrance: is term used to indicate that the disease some time to presenting no abnormal clinical feature • New mutation • Codominance: the presence of two alleles in heterozygous state (e.g. AB blood group) ...
... • Reduced penetrance: is term used to indicate that the disease some time to presenting no abnormal clinical feature • New mutation • Codominance: the presence of two alleles in heterozygous state (e.g. AB blood group) ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.