Punnett Squares Worksheet
... Chi Square Genetics Problem 5) A student performed a genetics experiment with fruit flies. He started with red-eyed heterozygous fruit flies (white eye color is recessive). After allowing the fruit flies to mate, he documented the phenotypic traits of the offpsring. He found that 80 were red-eyed an ...
... Chi Square Genetics Problem 5) A student performed a genetics experiment with fruit flies. He started with red-eyed heterozygous fruit flies (white eye color is recessive). After allowing the fruit flies to mate, he documented the phenotypic traits of the offpsring. He found that 80 were red-eyed an ...
Genetics NOTES - Grants Pass School District 7
... C. Meiosis- copying process that makes sex cells with half the number of chromosomes (NOT the same as mitosis) 1. Chromosomes are copied once, nucleus divides twice resulting in sex cells with half the number of chromosomes 2. Only one chromosome pair from each ends up in each sex cell 3. Meiosis o ...
... C. Meiosis- copying process that makes sex cells with half the number of chromosomes (NOT the same as mitosis) 1. Chromosomes are copied once, nucleus divides twice resulting in sex cells with half the number of chromosomes 2. Only one chromosome pair from each ends up in each sex cell 3. Meiosis o ...
17.1 Genes and Variation
... • Natural selection acts directly on phenotype. • Some phenotypes are better suited to their environment than others. • **Better suited individuals produce more offspring and pass on their genes to the next generation.** ...
... • Natural selection acts directly on phenotype. • Some phenotypes are better suited to their environment than others. • **Better suited individuals produce more offspring and pass on their genes to the next generation.** ...
1 / (2Ne)
... Simplest case: If pick two random gene copies, probability that the second is the same as the first is 1 / (2Ne). This is the probability that two alleles coalesce in previous generation. It follows that 1 - 1 / (2Ne) is the probability that two sequences were derived from different sequences in the ...
... Simplest case: If pick two random gene copies, probability that the second is the same as the first is 1 / (2Ne). This is the probability that two alleles coalesce in previous generation. It follows that 1 - 1 / (2Ne) is the probability that two sequences were derived from different sequences in the ...
Document
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
C. papyracea exercise - Wesleyan College Faculty
... environment, repeat this procedure. The goal is to keep each predation event independent of all others. It is essential that exactly 50 chips are removed from the board, so both predators and helpers should count the prey as they are removed from the environment. 4. Tally Survivors and Determine All ...
... environment, repeat this procedure. The goal is to keep each predation event independent of all others. It is essential that exactly 50 chips are removed from the board, so both predators and helpers should count the prey as they are removed from the environment. 4. Tally Survivors and Determine All ...
4.3 Ch.14_Lecture_Presentation_Mendel
... product of their individual probabilities Probability in an F1 monohybrid cross can be determined using the multiplication rule Segregation in a heterozygous plant is like flipping a coin: Each gamete has a 12 chance of carrying the dominant allele and a 12 chance of carrying the recessive allel ...
... product of their individual probabilities Probability in an F1 monohybrid cross can be determined using the multiplication rule Segregation in a heterozygous plant is like flipping a coin: Each gamete has a 12 chance of carrying the dominant allele and a 12 chance of carrying the recessive allel ...
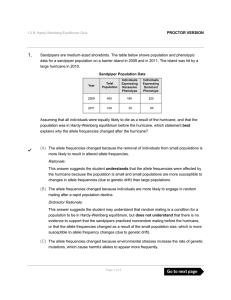
Sandpipers are medium-sized shorebirds. The table below shows
... This answer suggests the student may understand how to calculate 2pq given the percent of the population with the recessive phenotype (q2), but does not understand that the recessive genotypic frequency represents q2 and that it should be used to determine the allele frequency of q. ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand how to calculate 2pq given the percent of the population with the recessive phenotype (q2), but does not understand that the recessive genotypic frequency represents q2 and that it should be used to determine the allele frequency of q. ...
2014.10.16論文評述心得報告 環醫所博士班研究生 黃建程 Detection
... Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon by which certain genes can be expressed in a parent-of-origin-specific manner. It may also ensure transposable elements remain epigenetically silenced throughout gametogenic reprogramming to maintain genome integrity. It is an inheritance process indepe ...
... Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon by which certain genes can be expressed in a parent-of-origin-specific manner. It may also ensure transposable elements remain epigenetically silenced throughout gametogenic reprogramming to maintain genome integrity. It is an inheritance process indepe ...
mice and relative frequencies update
... 11) How many total mice are there? 12) How many mice are black? 13) What is the relative phenotype frequency of black mice? 14) How many mice are white? 15) What is the relative phenotype frequency of white mice? 16) How many total alleles for hair color are there? 17) How many black hair alleles ar ...
... 11) How many total mice are there? 12) How many mice are black? 13) What is the relative phenotype frequency of black mice? 14) How many mice are white? 15) What is the relative phenotype frequency of white mice? 16) How many total alleles for hair color are there? 17) How many black hair alleles ar ...
Natural selection of paper bugs
... that ring. Since there are only three possible genotypes, then the sum of those three frequencies must equal one. Thus we come by a biological argument to the same equation, p2 + 2pq +q2 = 1. Here a numerical example is very helpful. Say we have a population of 100 diploid individuals. Among them, t ...
... that ring. Since there are only three possible genotypes, then the sum of those three frequencies must equal one. Thus we come by a biological argument to the same equation, p2 + 2pq +q2 = 1. Here a numerical example is very helpful. Say we have a population of 100 diploid individuals. Among them, t ...
2016 - Barley World
... 40. Using a dominant molecular marker has the disadvantage that heterozygotes cannot be distinguished from recessive homozygotes a. T b. F 41. If inbred lines of maize can be developed that are good as F1 hybrids why do seed companies persist in selling F1 hybrid seed? a. It is an excellent business ...
... 40. Using a dominant molecular marker has the disadvantage that heterozygotes cannot be distinguished from recessive homozygotes a. T b. F 41. If inbred lines of maize can be developed that are good as F1 hybrids why do seed companies persist in selling F1 hybrid seed? a. It is an excellent business ...
Directional Positive Selection on an Allele of Arbitrary
... experience vivax malarial pressures (Hamblin and Di Rienzo 2000). This said, there are also anecdotal examples of dominant beneficial mutations, such as those underlying lactose tolerance ( Jobling et al. 2003). Moreover, Haldane’s sieve—the idea that a dominant allele has a greater chance of fixati ...
... experience vivax malarial pressures (Hamblin and Di Rienzo 2000). This said, there are also anecdotal examples of dominant beneficial mutations, such as those underlying lactose tolerance ( Jobling et al. 2003). Moreover, Haldane’s sieve—the idea that a dominant allele has a greater chance of fixati ...
genetics/dna jeopardy
... disease, is it a dominant or recessive disease? What are the genotypes of person 1 and 3? ...
... disease, is it a dominant or recessive disease? What are the genotypes of person 1 and 3? ...
Genetic Mapping in Drosophila melanogaster
... pioneered the use of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as a model organism in genetic studies. Drosophila has a diploid chromosome number of eight, or four pairs of homologous chromosomes numbered 1 - 4. Chromosome 1 is the X chromosome (sex chromosome) and is responsible for sex determination ...
... pioneered the use of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as a model organism in genetic studies. Drosophila has a diploid chromosome number of eight, or four pairs of homologous chromosomes numbered 1 - 4. Chromosome 1 is the X chromosome (sex chromosome) and is responsible for sex determination ...
Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human
... pairwise FST between geographic regions in a 100-kb window surrounding the SNP in the HGDP data, as well as a histogram of the null distribution calculated by finding the maximum FST in 100-kb windows surrounding each of 10,000 random SNPs. The dotted lines shows the position beyond which 5% of the ...
... pairwise FST between geographic regions in a 100-kb window surrounding the SNP in the HGDP data, as well as a histogram of the null distribution calculated by finding the maximum FST in 100-kb windows surrounding each of 10,000 random SNPs. The dotted lines shows the position beyond which 5% of the ...
Mendel explained how a dominant allele can mask the
... What is the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics? What is the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment? What are the possible offspring from a cross using a Punnett square? ...
... What is the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics? What is the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment? What are the possible offspring from a cross using a Punnett square? ...
Corn Snakes
... Corn snake color is comprised of two predominant colors Red Black Yellow, appears in varying degrees and is not the main reason ...
... Corn snake color is comprised of two predominant colors Red Black Yellow, appears in varying degrees and is not the main reason ...
Mendelian Genetics ()
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
just disorders - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... and eventually death _________________________ Inability to distinguish between the colors red and green _____________________ Colorblindness ...
... and eventually death _________________________ Inability to distinguish between the colors red and green _____________________ Colorblindness ...
How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype?
... Shotgun sequencing was one of the techniques used to sequence the human genome. Below are five DNA fragmentslabeled A, B, C, D, and E, respectivelythat were shotgun sequenced and determined to be part of the same DNA sequence. Notice that the fragments are single stranded. Determine the single-str ...
... Shotgun sequencing was one of the techniques used to sequence the human genome. Below are five DNA fragmentslabeled A, B, C, D, and E, respectivelythat were shotgun sequenced and determined to be part of the same DNA sequence. Notice that the fragments are single stranded. Determine the single-str ...
Genetics
... and color of the flies. Study the wings, noting their size, shape, and color. Notice the color of the compound eye. Examine also the legs, antennae, and balancers. You may consider the expression of traits found in the wild type of flies to be the base line, and any different expressions of these tr ...
... and color of the flies. Study the wings, noting their size, shape, and color. Notice the color of the compound eye. Examine also the legs, antennae, and balancers. You may consider the expression of traits found in the wild type of flies to be the base line, and any different expressions of these tr ...
Unit 2 - Elgin Academy
... Cohesion attracts water molecules to each other, holding them together. Adhesion attracts the water to the walls of the xylem. During the day guard cells gain water, become more turgid and open the stoma At night the guard cells lose water, become less turgid and close the stoma. Transpiration helps ...
... Cohesion attracts water molecules to each other, holding them together. Adhesion attracts the water to the walls of the xylem. During the day guard cells gain water, become more turgid and open the stoma At night the guard cells lose water, become less turgid and close the stoma. Transpiration helps ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.