Long hair is dominant for Abyssinian guinea pigs. If you mate a male
... At a murder scene, the victim has been determined to have Type A blood. Another blood source at the crime scene has been determined to be Type O blood. There is a potential person of interest in the crime however, his whereabouts are unknown. The person of interest’s father has been recently determ ...
... At a murder scene, the victim has been determined to have Type A blood. Another blood source at the crime scene has been determined to be Type O blood. There is a potential person of interest in the crime however, his whereabouts are unknown. The person of interest’s father has been recently determ ...
Lecture on Population Genetics
... genetics and molecular biology. This has all been in preparation for the remainder of the course which will focus on the science that Discovery Manager supports—the discovery of disease genes. To this point we have focused on the fate of genes in a single cell and the biochemical processes involved ...
... genetics and molecular biology. This has all been in preparation for the remainder of the course which will focus on the science that Discovery Manager supports—the discovery of disease genes. To this point we have focused on the fate of genes in a single cell and the biochemical processes involved ...
Heredity and Environment
... In mitotic cell division, if a viable mutation occurs early in development, it will then be passed along to all cells replicated. In meiotic cell division, mutation only affects the ensuing gametes and stops there, Unless a mutated gamete happens to be involved in producing offspring – in which case ...
... In mitotic cell division, if a viable mutation occurs early in development, it will then be passed along to all cells replicated. In meiotic cell division, mutation only affects the ensuing gametes and stops there, Unless a mutated gamete happens to be involved in producing offspring – in which case ...
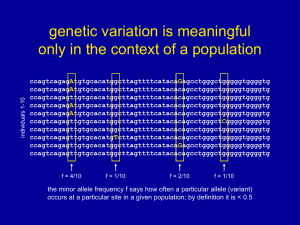
Making Sense of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium One of the more
... Problem 4. A more sophisticated version of this problem (Trout, 2012) states that sickle-cell disease affects approximately 9% of the African population and then asks the students to use the Hardy-Weinberg equations to calculate the predicted genotype frequencies. The students are then asked, ‘Based ...
... Problem 4. A more sophisticated version of this problem (Trout, 2012) states that sickle-cell disease affects approximately 9% of the African population and then asks the students to use the Hardy-Weinberg equations to calculate the predicted genotype frequencies. The students are then asked, ‘Based ...
Document
... Mechanisms of Epigenetic Inheritance Epigenetic: The term that refers to any factor that can affect gene function without change in the genotype. ...
... Mechanisms of Epigenetic Inheritance Epigenetic: The term that refers to any factor that can affect gene function without change in the genotype. ...
Dragon Genetics
... In this activity you will study the patterns of inheritance of multiple genes in (imaginary) dragons. These dragons have two pairs of homologous chromosomes in each cell. You will see that, since genes are carried on chromosomes, the patterns of inheritance are determined by the behavior of chromoso ...
... In this activity you will study the patterns of inheritance of multiple genes in (imaginary) dragons. These dragons have two pairs of homologous chromosomes in each cell. You will see that, since genes are carried on chromosomes, the patterns of inheritance are determined by the behavior of chromoso ...
Mathematical Modelling - Mathematical Association
... cells genes occur in pairs and appear on paired chromosomes. A particular gene with two alleles R and r. The genes of an offspring result from the pairing of two genes, one from each parent. There are three possible genotypes of the organism relative to this gene: ...
... cells genes occur in pairs and appear on paired chromosomes. A particular gene with two alleles R and r. The genes of an offspring result from the pairing of two genes, one from each parent. There are three possible genotypes of the organism relative to this gene: ...
HLA - KNMP
... The genotype is the hereditary information about a specific characteristic of an individual. This information is located in the genes, in the DNA that consists of nucleotides. The piece of the DNA that carries information for one specific hereditary characteristic is called a gene. The DNA is divide ...
... The genotype is the hereditary information about a specific characteristic of an individual. This information is located in the genes, in the DNA that consists of nucleotides. The piece of the DNA that carries information for one specific hereditary characteristic is called a gene. The DNA is divide ...
Mendel - Spring Branch ISD
... (a) The three alleles for the ABO blood groups and their carbohydrates IA ...
... (a) The three alleles for the ABO blood groups and their carbohydrates IA ...
Caspi et al 5HTT.
... birthday and before the 26th birthday were assessed with a life-history calendar • These events included employment, financial, housing, health and relationship stressors • There was no significant difference between the genotype groups in the number of life events they experienced (suggesting that ...
... birthday and before the 26th birthday were assessed with a life-history calendar • These events included employment, financial, housing, health and relationship stressors • There was no significant difference between the genotype groups in the number of life events they experienced (suggesting that ...
Mechanisms of Heredity Sex
... (B = black and b = yellow) that combine to give Bb = calico. This trait is also sex-linked, which means that the genes for this trait appear only on the X chromosome. Females may have the genotype Bb and show the calico phenotype, but males only have one X chromosome, so their genotype is either B ( ...
... (B = black and b = yellow) that combine to give Bb = calico. This trait is also sex-linked, which means that the genes for this trait appear only on the X chromosome. Females may have the genotype Bb and show the calico phenotype, but males only have one X chromosome, so their genotype is either B ( ...
homologous recombination
... this information, it is possible to replace any gene with a DNA construct of your choosing. ...
... this information, it is possible to replace any gene with a DNA construct of your choosing. ...
MYP Assessment Task Coversheet Teacher/Profesor Trevor Lafferty
... 1. In humans brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. What type of offspring would you expect if you crossed a heterozygous brown eyed person to a heterozygous brown eyed person? 2. In humans premature gray hair is dominant over normal hair coloring. Cross a homozygous premature gray haired person to ...
... 1. In humans brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. What type of offspring would you expect if you crossed a heterozygous brown eyed person to a heterozygous brown eyed person? 2. In humans premature gray hair is dominant over normal hair coloring. Cross a homozygous premature gray haired person to ...
I-1 to I-7
... (4) Magnitude of the difference in allele frequencies in sexes decreases by 1/2 each generation: – Some biological consequences of sex linkage: If the frequency of allele A is the same in both sexes, i.e., , then among the offspring: ...
... (4) Magnitude of the difference in allele frequencies in sexes decreases by 1/2 each generation: – Some biological consequences of sex linkage: If the frequency of allele A is the same in both sexes, i.e., , then among the offspring: ...
lecture26_Polymorphi..
... training, is familial and may have a genetic component, but that genetic influence does not manifest in the absence of early musical training. The difference is primarily environmental. (b) Phenylthiocarbamide tasting gene (PTC) on chromosome 7 is polymorphic in European populations, with the low-se ...
... training, is familial and may have a genetic component, but that genetic influence does not manifest in the absence of early musical training. The difference is primarily environmental. (b) Phenylthiocarbamide tasting gene (PTC) on chromosome 7 is polymorphic in European populations, with the low-se ...
Genetics-HEREDITY Unit Overview
... Two children have second toes that are shorter than the big toe. What are the most likely genotypes of the parents? Ratio of 3 long to 1 short indicates typical phenotypic ratios that result from two heterozygous parents: Ll and Ll ...
... Two children have second toes that are shorter than the big toe. What are the most likely genotypes of the parents? Ratio of 3 long to 1 short indicates typical phenotypic ratios that result from two heterozygous parents: Ll and Ll ...
Name
... 17. Imagine that there is a dominant gene that protects against sun-burning (T) and a recessive gene that increases intolerance to the sun and causes sun-burning (t). If this trait has a simple inheritance pattern, what is the probability that parents would have sunintolerant children if they are b ...
... 17. Imagine that there is a dominant gene that protects against sun-burning (T) and a recessive gene that increases intolerance to the sun and causes sun-burning (t). If this trait has a simple inheritance pattern, what is the probability that parents would have sunintolerant children if they are b ...
LECTURE #30: Sex Linkage
... Inheritance of SexLinked Genes sex chromosomes Have genes for many characters unrelated to sex (especially the X chromosome) A gene located on either sex chromosome Is called a sex-linked gene The ...
... Inheritance of SexLinked Genes sex chromosomes Have genes for many characters unrelated to sex (especially the X chromosome) A gene located on either sex chromosome Is called a sex-linked gene The ...
Presentation
... 3. Genetic Drift- is the phenomenon by which allele frequencies in a population change as a result of random events or chance. In a small population, a particular allele may disappear completely over a few generations (about 45) If we assume that we started with two alleles for a trait, then only o ...
... 3. Genetic Drift- is the phenomenon by which allele frequencies in a population change as a result of random events or chance. In a small population, a particular allele may disappear completely over a few generations (about 45) If we assume that we started with two alleles for a trait, then only o ...
fact file: genetic diversity
... A gene is a section of a DNA that contains coded information for making polypeptides. All members of the same species have same genes. However it’s just the allele that differs. Therefore the combination of the different alleles results individuals to be different from others also known as random fe ...
... A gene is a section of a DNA that contains coded information for making polypeptides. All members of the same species have same genes. However it’s just the allele that differs. Therefore the combination of the different alleles results individuals to be different from others also known as random fe ...
AP Chap 14 pp
... Extending Mendelian Genetics for a Single Gene • Inheritance of characters by a single gene may deviate from simple Mendelian patterns in the following situations: – When alleles are not completely dominant or recessive – When a gene has more than two alleles ...
... Extending Mendelian Genetics for a Single Gene • Inheritance of characters by a single gene may deviate from simple Mendelian patterns in the following situations: – When alleles are not completely dominant or recessive – When a gene has more than two alleles ...
10.3
... A, B, & C are tall alleles X, Y, & Z are short alleles Parents each give 3 alleles each AABBCC would be a tall individual AXBBCC would be a little shorter AXBYCC would be even shorter, and so on . . . until XXYYZZ would be the shortest individual The potential combinations of alleles (and phenotypes ...
... A, B, & C are tall alleles X, Y, & Z are short alleles Parents each give 3 alleles each AABBCC would be a tall individual AXBBCC would be a little shorter AXBYCC would be even shorter, and so on . . . until XXYYZZ would be the shortest individual The potential combinations of alleles (and phenotypes ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.