Reebop Lab - The Green Isle
... Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for certain proteins Allele: Alternate forms of the same gene. (One from mom, one from dad) Genotype: Genetic make-up or allele combination (what’s in their genes) Homozygous: dominant (AA) or recessive (aa) Heterozygous: hybrid (Aa) Phenotype: Physical expression of ...
... Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for certain proteins Allele: Alternate forms of the same gene. (One from mom, one from dad) Genotype: Genetic make-up or allele combination (what’s in their genes) Homozygous: dominant (AA) or recessive (aa) Heterozygous: hybrid (Aa) Phenotype: Physical expression of ...
EPISTASIS
... chromosomes. Setting up an epistasis problem will be much the same as a dihybrid problem. That is, you will be dealing with two sets of genes. The difference will be in interpreting the results (i.e. figuring out the phenotypes). What is epistasis? Epistasis is a term used to describe the interactio ...
... chromosomes. Setting up an epistasis problem will be much the same as a dihybrid problem. That is, you will be dealing with two sets of genes. The difference will be in interpreting the results (i.e. figuring out the phenotypes). What is epistasis? Epistasis is a term used to describe the interactio ...
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... • Sex-linked genes are genes on the sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine the gender in some species • In humans, XX is female and XY is male. • The Y chromosome is much smaller and does not contain all of the genes that the X does. • Males determine the sex of a child. • Sex-linked recessive ...
... • Sex-linked genes are genes on the sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine the gender in some species • In humans, XX is female and XY is male. • The Y chromosome is much smaller and does not contain all of the genes that the X does. • Males determine the sex of a child. • Sex-linked recessive ...
Mendelian Genetics
... TASK 2 - Patterns of inheritance II: Incomplete vs. Complete Dominance & Codominance Inheritance of traits can occur in multiple forms. So far you have considered complete dominance, where a homozygous dominant or a heterozygous individual expresses the dominant phenotype, while an individual that i ...
... TASK 2 - Patterns of inheritance II: Incomplete vs. Complete Dominance & Codominance Inheritance of traits can occur in multiple forms. So far you have considered complete dominance, where a homozygous dominant or a heterozygous individual expresses the dominant phenotype, while an individual that i ...
Chapter 5: Mendelian Traits and Behavior
... dominant to O, or in different words, allele O is recessive to B. When the phenotype of the heterozygote takes on a value somewhere between the two homozygotes, then allele action is said to be partially dominant, incompletely dominant, additive, or codominant, depending on exact value of the hetero ...
... dominant to O, or in different words, allele O is recessive to B. When the phenotype of the heterozygote takes on a value somewhere between the two homozygotes, then allele action is said to be partially dominant, incompletely dominant, additive, or codominant, depending on exact value of the hetero ...
biology - LearnCOACH
... • Occurs in the body cells (all except sex and blood cells). It is used for growth and repair ...
... • Occurs in the body cells (all except sex and blood cells). It is used for growth and repair ...
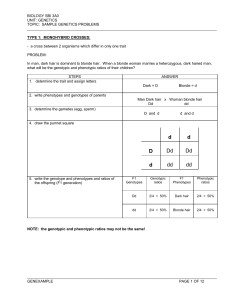
Name
... Dihybrid Cross Activity In a gamete with either chromosome from any other pair of homologous chromosomes the genes that are located on non-homologous also assort independently as you can see in the following diagram: Chromosome 1 allele 1 Chromosome 2 allele 2 ...
... Dihybrid Cross Activity In a gamete with either chromosome from any other pair of homologous chromosomes the genes that are located on non-homologous also assort independently as you can see in the following diagram: Chromosome 1 allele 1 Chromosome 2 allele 2 ...
Genetics - TeacherWeb
... Carried out the first experiments on heredity using pea plants. Carefully controlled his experiments, studying only one trait at a time and analyzed data mathematically. Was the first to succeed in predicting how traits are transferred from generation to generation. Heredity-Passing on of characteri ...
... Carried out the first experiments on heredity using pea plants. Carefully controlled his experiments, studying only one trait at a time and analyzed data mathematically. Was the first to succeed in predicting how traits are transferred from generation to generation. Heredity-Passing on of characteri ...
section 11-2 Probability and Punnett squares (pases 267-26e)
... 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Homozygous organisms are true-breeding for a particular trait. 12. Is the following sentence true or false? Plants with the same phenotype always have the same genotype. ...
... 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Homozygous organisms are true-breeding for a particular trait. 12. Is the following sentence true or false? Plants with the same phenotype always have the same genotype. ...
Flintstones Sex Linked - Kenwood Academy Freshmen Biology
... Sex-linked Traits with The Flintstones Directions: Analyze Figure 1 to complete Figure 2. ...
... Sex-linked Traits with The Flintstones Directions: Analyze Figure 1 to complete Figure 2. ...
ppt
... Case-control test for association (continued) Question: Is the Gm haplotype actually associated with risk of Type 2 diabetes??? The real story: Stratify by American Indian heritage 0 = little or no indian heritage; ...
... Case-control test for association (continued) Question: Is the Gm haplotype actually associated with risk of Type 2 diabetes??? The real story: Stratify by American Indian heritage 0 = little or no indian heritage; ...
Ch 23 – Evolution of Populations
... Concept 23.3: Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter a population’s genetic composition • Three major factors alter allele frequencies and bring about most evolutionary change – Natural selection – Genetic drift – Gene flow ...
... Concept 23.3: Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter a population’s genetic composition • Three major factors alter allele frequencies and bring about most evolutionary change – Natural selection – Genetic drift – Gene flow ...
Review for ch 16 and 17
... 10. Large scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time are called ______________ 11. The process by which unrelated organisms come to resemble each other is called _______________ 12. A species or small group of species evolves into many new species during __________________ ...
... 10. Large scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time are called ______________ 11. The process by which unrelated organisms come to resemble each other is called _______________ 12. A species or small group of species evolves into many new species during __________________ ...
Name: AP Biology - Unit 6: Patterns of Inheritance Mendelian
... 11. DNA fingerprinting is a method used to identify individuals by locating unique base sequences in their DNA molecules. Before researchers refined the method, attorneys often relied on ABO blood-typing to settle disputes over paternity. Suppose that you, as a geneticist, are asked to testify duri ...
... 11. DNA fingerprinting is a method used to identify individuals by locating unique base sequences in their DNA molecules. Before researchers refined the method, attorneys often relied on ABO blood-typing to settle disputes over paternity. Suppose that you, as a geneticist, are asked to testify duri ...
Oxford Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency care pathway for routine referrals
... requesting phenotype confirmation Letter (1C) to Patient (Enclose information & management guidelines) ...
... requesting phenotype confirmation Letter (1C) to Patient (Enclose information & management guidelines) ...
Chapter 2- Genetics
... These diseases are genetic; the mutation is present in every cell of the offspring. In most cases a parent is a carrier and the mutated gene is ______________ to the healthy gene of the other parent. ___ chance of having disease, ½ of carrier and ¼ healthy. d) Genetic Diseases Each disease o ...
... These diseases are genetic; the mutation is present in every cell of the offspring. In most cases a parent is a carrier and the mutated gene is ______________ to the healthy gene of the other parent. ___ chance of having disease, ½ of carrier and ¼ healthy. d) Genetic Diseases Each disease o ...
PINK
... CODOMINANCE = both alleles are dominant and therefore BOTH are expressed completely when present I the heterozygous state. NO blending of traits; instead, both traits appear eg. Codominance ...
... CODOMINANCE = both alleles are dominant and therefore BOTH are expressed completely when present I the heterozygous state. NO blending of traits; instead, both traits appear eg. Codominance ...
Biology 321 Spring 2013 Assignment Set #4 Problems sorted by type
... Three true-breeding white lines of snapdragons that do not produce anthocyanin have been established. The mutation in each of these lines is recessive. Line C was developed by plant breeders in California, Line H in Holland and Line W in Washington. When petals from Lines H and C lines are ground up ...
... Three true-breeding white lines of snapdragons that do not produce anthocyanin have been established. The mutation in each of these lines is recessive. Line C was developed by plant breeders in California, Line H in Holland and Line W in Washington. When petals from Lines H and C lines are ground up ...
Biology (056) (E) CHAPTER
... Rr, RR, Yy, YY 6. If two opposite alleles come together, one finding morphological expression masking the other, the fact is described as law of (A) Inheritance (B) Dominance (C) Limiting factor (D) Segregation 7. Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozy ...
... Rr, RR, Yy, YY 6. If two opposite alleles come together, one finding morphological expression masking the other, the fact is described as law of (A) Inheritance (B) Dominance (C) Limiting factor (D) Segregation 7. Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozy ...
Assignment 1: Genetic Counseling
... What have you learned from this assignment? A genetic counselor characterizes an inheritance pattern by tracking a phenotype. In this example, you established that the most probable inheritance pattern was autosomal dominant. This leads to the conclusion that hearing adults carry two normal alleles ...
... What have you learned from this assignment? A genetic counselor characterizes an inheritance pattern by tracking a phenotype. In this example, you established that the most probable inheritance pattern was autosomal dominant. This leads to the conclusion that hearing adults carry two normal alleles ...
Examples of connected symbols:
... chickens, a dominant gene (F) on the X chromosome results in silver feathers. Its recessive allele (f) results in gold feathers. What are the 2 possible F1 generations that would result from a cross between a golden rooster and a silver hen? (Hint: 2 possible genotypes for a silver hen) ...
... chickens, a dominant gene (F) on the X chromosome results in silver feathers. Its recessive allele (f) results in gold feathers. What are the 2 possible F1 generations that would result from a cross between a golden rooster and a silver hen? (Hint: 2 possible genotypes for a silver hen) ...
Chapter 7 – Linkage, Recombination, and
... • Separate during meiosis – only one gamete enters each gamete ...
... • Separate during meiosis – only one gamete enters each gamete ...
Unit 3
... 16. Give an example of incomplete dominance and explain why it is not evidence for the blending theory of inheritance. - an example of incomplete dominance would be the crossing of a red and white flower and the emergence of its pink progeny (not one or the other, but both). 17. Explain how the phen ...
... 16. Give an example of incomplete dominance and explain why it is not evidence for the blending theory of inheritance. - an example of incomplete dominance would be the crossing of a red and white flower and the emergence of its pink progeny (not one or the other, but both). 17. Explain how the phen ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.