
Sex-linked traits
... Incomplete dominance Codominance Multiple gene inheritance Sex-Linked traits ...
... Incomplete dominance Codominance Multiple gene inheritance Sex-Linked traits ...
Population
... and Weinberg went on to develop an equation that can be used to discover the probable genotype frequencies in a population and to track their changes from one generation to another. The equation is: p2+2pq+q2 = 1 p= frequency of the dominant allele q = frequency of the recessive allele See handout ...
... and Weinberg went on to develop an equation that can be used to discover the probable genotype frequencies in a population and to track their changes from one generation to another. The equation is: p2+2pq+q2 = 1 p= frequency of the dominant allele q = frequency of the recessive allele See handout ...
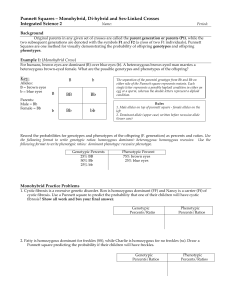
Punnett Squares – Monohybrid, Di-hybrid and Sex
... The normal female condition is a result of the chromosomal pairing XX, while the normal male condition is XY. Certain genes located on the X chromosome, not associated with female sex characteristics, cause sex-linked recessive traits. As a result, females must receive two recessive alleles to exhib ...
... The normal female condition is a result of the chromosomal pairing XX, while the normal male condition is XY. Certain genes located on the X chromosome, not associated with female sex characteristics, cause sex-linked recessive traits. As a result, females must receive two recessive alleles to exhib ...
Human Pedigree
... I 1 ________ 2 ________ 3 ________ 4 ________ II 1 ________ 2 ________ 3 ________ 4 ________ 5 ________ 6 ________ 7 ________ 8 ________ III 1 ________ 2 ________ 7 ________ 7 ________ ...
... I 1 ________ 2 ________ 3 ________ 4 ________ II 1 ________ 2 ________ 3 ________ 4 ________ 5 ________ 6 ________ 7 ________ 8 ________ III 1 ________ 2 ________ 7 ________ 7 ________ ...
Genetics final exam honors 2010
... ______________________________ 3. The process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA. ______________________________ 4. The building blocks of a protein. ______________________________ 5. One form of a gene. ______________________________ 6. An organism’s genetic makeup or the letters used to repre ...
... ______________________________ 3. The process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA. ______________________________ 4. The building blocks of a protein. ______________________________ 5. One form of a gene. ______________________________ 6. An organism’s genetic makeup or the letters used to repre ...
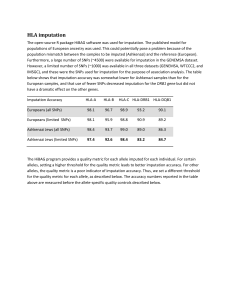
HLA imputation - BioMed Central
... population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a limited number of SNPs (~1000) was available in all three datasets (GENEMSA, WTCCC2, and IMSGC) ...
... population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a limited number of SNPs (~1000) was available in all three datasets (GENEMSA, WTCCC2, and IMSGC) ...
New Title - Pepperell Middle School
... Hemophilia is a genetic disorder in which the blood clots very slowly or not at all. People with the disorder do not produce one of the proteins needed for normal blood clotting. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome. Because it is a sex-linked disorder, it occurs more often ...
... Hemophilia is a genetic disorder in which the blood clots very slowly or not at all. People with the disorder do not produce one of the proteins needed for normal blood clotting. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome. Because it is a sex-linked disorder, it occurs more often ...
Principles of Inheritance and Variation.pmd
... that the genotype of the dwarfs was homozygous – tt. What do you think he would have got had he self-pollinated a tall F2 plant? From the preceeding paragraphs it is clear that though the genotypic ratios can be calculated using mathematical probability, by simply looking at the phenotype of a domin ...
... that the genotype of the dwarfs was homozygous – tt. What do you think he would have got had he self-pollinated a tall F2 plant? From the preceeding paragraphs it is clear that though the genotypic ratios can be calculated using mathematical probability, by simply looking at the phenotype of a domin ...
Part II: Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change
... The purpose of this case study is to help you develop an intuition about how selection and mutation cause evolution. You will use a software simulation of an evolving population to analyze the examples discussed in Chapter 5, and to answer a variety questions concerning changes in the frequencies of ...
... The purpose of this case study is to help you develop an intuition about how selection and mutation cause evolution. You will use a software simulation of an evolving population to analyze the examples discussed in Chapter 5, and to answer a variety questions concerning changes in the frequencies of ...
Conclusions from Hardy
... zygote formation. Assortment of alleles simply means what occurs during meiosis when only one copy of each pair of alleles enters any given gamete (remember each gamete only contains half the DNA of a body cell). ...
... zygote formation. Assortment of alleles simply means what occurs during meiosis when only one copy of each pair of alleles enters any given gamete (remember each gamete only contains half the DNA of a body cell). ...
Plant Genetics
... No dominance, incomplete dominance Important for phenotype, phenotype ratios change Genotypic ratios stay the same F1 phenotype is intermediate of both parents F2 phenotypic ratios same as genotypic ratios 1Red:2Pink:1White ...
... No dominance, incomplete dominance Important for phenotype, phenotype ratios change Genotypic ratios stay the same F1 phenotype is intermediate of both parents F2 phenotypic ratios same as genotypic ratios 1Red:2Pink:1White ...
IS IT GENETIC? How do genes, environment and chance interact to
... A variant gene (a variant allele or polymorphism) carried by about 40% of the population sharply increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, researchers here have reported. The link between the gene TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7-like 2 gene) and diabetes was found by analyzing genetic records of Iceland ...
... A variant gene (a variant allele or polymorphism) carried by about 40% of the population sharply increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, researchers here have reported. The link between the gene TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7-like 2 gene) and diabetes was found by analyzing genetic records of Iceland ...
What is DNA? - Livingstone High School
... Why is DNA Interesting? • DNA is a nonliving molecule. • There are 6 feet of it in every cell. • The human body can have as many as ten thousand trillion cells, and almost every one of them has 6 feet of densely compacted DNA. • DNA is unique for every individual • DNA controls all the activities i ...
... Why is DNA Interesting? • DNA is a nonliving molecule. • There are 6 feet of it in every cell. • The human body can have as many as ten thousand trillion cells, and almost every one of them has 6 feet of densely compacted DNA. • DNA is unique for every individual • DNA controls all the activities i ...
Quantitative genetics
... Demonstrated that bean seed weight is partly heritable and partly environmental. ...
... Demonstrated that bean seed weight is partly heritable and partly environmental. ...
dragon genetics lab
... 1. You will work with the partner that you are sitting with. You and your “spouse” will create one dragon. Each of you will fill out a sheet and draw your baby. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color o ...
... 1. You will work with the partner that you are sitting with. You and your “spouse” will create one dragon. Each of you will fill out a sheet and draw your baby. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color o ...
mendel111
... ________each trait and that __________ one factor must be able to _______ HIDE the other. ...
... ________each trait and that __________ one factor must be able to _______ HIDE the other. ...
Pedigrees – Important Points are in BLUE
... • X-linked dominant diseases are extremely unusual • Often, they are lethal (before birth) in males and only seen in females ex. incontinentia pigmenti (skin lesions) ...
... • X-linked dominant diseases are extremely unusual • Often, they are lethal (before birth) in males and only seen in females ex. incontinentia pigmenti (skin lesions) ...
Using uniformat and Gene[rate] to analyse data with ambiguities in
... Diploid systems are characterised by genotypes with two alleles at each locus, one inherited from the mother, the other from the father. The typing technologies used to determine these alleles do not always reveal exactly two alleles; sometimes only one is seen and sometimes more than two seem to be ...
... Diploid systems are characterised by genotypes with two alleles at each locus, one inherited from the mother, the other from the father. The typing technologies used to determine these alleles do not always reveal exactly two alleles; sometimes only one is seen and sometimes more than two seem to be ...
Genetic Inheritance - leavingcertbiology.net
... • Incomplete dominance: incomplete dominance is where two homologous alleles are equally expressed and neither allele is dominant over or recessive to the other – The heterozygous genotype produces a phenotype intermediate between those produced by the two homozygous genotypes – An example is flower ...
... • Incomplete dominance: incomplete dominance is where two homologous alleles are equally expressed and neither allele is dominant over or recessive to the other – The heterozygous genotype produces a phenotype intermediate between those produced by the two homozygous genotypes – An example is flower ...
HW 1
... A white flowered, small flowered individual is crossed with a red flowered individual having large flowers and gives rise to offspring that are pink flowered and produce intermediate sized flowers. Given that AA and aa refers to the homozygous conditions of white and red, respectively and BB and bb ...
... A white flowered, small flowered individual is crossed with a red flowered individual having large flowers and gives rise to offspring that are pink flowered and produce intermediate sized flowers. Given that AA and aa refers to the homozygous conditions of white and red, respectively and BB and bb ...
Genetic Drift and Gene Flow Illustration
... that gene flow is the exchange of genes between populations. Unless the two populations have exactly the same frequencies of a particular gene the overall composition of the resulting population will be altered. Remembering that the evolution is defined as a change in gene frequencies over time we s ...
... that gene flow is the exchange of genes between populations. Unless the two populations have exactly the same frequencies of a particular gene the overall composition of the resulting population will be altered. Remembering that the evolution is defined as a change in gene frequencies over time we s ...
Genetic Drift and Gene Flow Activities
... that gene flow is the exchange of genes between populations. Unless the two populations have exactly the same frequencies of a particular gene the overall composition of the resulting population will be altered. Remembering that the evolution is defined as a change in gene frequencies over time we s ...
... that gene flow is the exchange of genes between populations. Unless the two populations have exactly the same frequencies of a particular gene the overall composition of the resulting population will be altered. Remembering that the evolution is defined as a change in gene frequencies over time we s ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.
















![Using uniformat and Gene[rate] to analyse data with ambiguities in](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003111231_1-701ba56eac6c2ce171209330d44b2e19-300x300.png)




