A1986D675500002
... The originality and significance ofthe review were mainly in its comparative approach, which was enhanced by the treatment of four different genetic systems, including the newly discovered sporophytic system, in plants and three systems in fungi. It may be significant that de 9Nettancourt, in his sp ...
... The originality and significance ofthe review were mainly in its comparative approach, which was enhanced by the treatment of four different genetic systems, including the newly discovered sporophytic system, in plants and three systems in fungi. It may be significant that de 9Nettancourt, in his sp ...
Sex liked genetics worksheet
... Unfortunately these assumptions are not always valid. It is a fact that there are more male zygotes created than female zygotes (108 to 100); there are more male babies born than female (106 to 100); more male infants die before age 2 years; and men tend to die younger (old age) than women. What do ...
... Unfortunately these assumptions are not always valid. It is a fact that there are more male zygotes created than female zygotes (108 to 100); there are more male babies born than female (106 to 100); more male infants die before age 2 years; and men tend to die younger (old age) than women. What do ...
Evolution as Genetic Change
... future generations, and the allele could even disappear from the gene pool completely. ...
... future generations, and the allele could even disappear from the gene pool completely. ...
Document
... • Disease in which the body makes sickle-shaped red blood cells. Sickle-shaped cells don’t move easily through your blood vessels. They’re stiff and sticky and tend to form clumps and get stuck in the ...
... • Disease in which the body makes sickle-shaped red blood cells. Sickle-shaped cells don’t move easily through your blood vessels. They’re stiff and sticky and tend to form clumps and get stuck in the ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
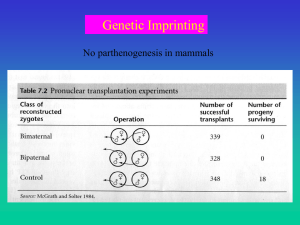
... Garfield AS…Ward A. Nature. 469(7331):534-8 (2011) Imprinted genes, defined by their preferential expression of a single parental allele, represent a subset of the mammalian genome and often have key roles in embryonic development, but also postnatal functions including energy homeostasis and behavi ...
... Garfield AS…Ward A. Nature. 469(7331):534-8 (2011) Imprinted genes, defined by their preferential expression of a single parental allele, represent a subset of the mammalian genome and often have key roles in embryonic development, but also postnatal functions including energy homeostasis and behavi ...
Y chromosome
... [we will work through the crosses on the board] These results differed from typical Mendelian results in two ways: 1. The results of reciprocal crosses were different 2. F2 progeny ratios not in quarters Remember that when Mendel performed reciprocal crosses between his various plant lines, he a ...
... [we will work through the crosses on the board] These results differed from typical Mendelian results in two ways: 1. The results of reciprocal crosses were different 2. F2 progeny ratios not in quarters Remember that when Mendel performed reciprocal crosses between his various plant lines, he a ...
The Role and Relevance of Statistics, Genetics and Epidemiology in
... (plural: statistics) is an estimate based on a sample of an unknown numerical quantity in a population, such as the mean height of men age 20. Statistics (singular) is a science that deals with the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of information that can be stated ...
... (plural: statistics) is an estimate based on a sample of an unknown numerical quantity in a population, such as the mean height of men age 20. Statistics (singular) is a science that deals with the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of information that can be stated ...
Presentation
... What is Genetics? • All body cells contain “Blueprints” with instructions as to how an animal will look or act etc. • One Gene comes from each parent (pairs) • Genes are divided into sections (Chromosomes) that carry genes • Sex chromosomes: male = XY, female = XX ...
... What is Genetics? • All body cells contain “Blueprints” with instructions as to how an animal will look or act etc. • One Gene comes from each parent (pairs) • Genes are divided into sections (Chromosomes) that carry genes • Sex chromosomes: male = XY, female = XX ...
Page 16 White Cats - Michigan Department of Education
... 12. We indicated earlier that the protein coded for by the D gene determines how much pigment is packed into each individual hair. What could be true of this type of protein? A. It regulates the rate at which the genes coding for pigmentation are expressed B. It regulates the type of pigment made C. ...
... 12. We indicated earlier that the protein coded for by the D gene determines how much pigment is packed into each individual hair. What could be true of this type of protein? A. It regulates the rate at which the genes coding for pigmentation are expressed B. It regulates the type of pigment made C. ...
ALE 8X Answer Key
... Cow A, which is horned, gives birth to a polled calf. Cow B, also horned, produces a horned calf. Cow C, which is polled, produces a horned calf. What are the genotypes of the four parents? Bull: Dd ...
... Cow A, which is horned, gives birth to a polled calf. Cow B, also horned, produces a horned calf. Cow C, which is polled, produces a horned calf. What are the genotypes of the four parents? Bull: Dd ...
Big_Idea_1.A.1 Natural Selection
... the colors of Strawfish. We will also look “underneath the skin” and measure how these natural selection factors also affect the inheritance of the genes that code for the color of Strawfish. In Strawfish, there are three scale/skin colors (phenotypes)— blue, yellow, green. These three colors are co ...
... the colors of Strawfish. We will also look “underneath the skin” and measure how these natural selection factors also affect the inheritance of the genes that code for the color of Strawfish. In Strawfish, there are three scale/skin colors (phenotypes)— blue, yellow, green. These three colors are co ...
Genetic Alterations
... (DNA sequence) within a cell or organism to produce a desired result. a change in the genetic makeup of an ...
... (DNA sequence) within a cell or organism to produce a desired result. a change in the genetic makeup of an ...
Mutations
... -thalassemia interference with -chain production Etiology: -chain gene deletion, 1 – 4 6.5 A survey of adaptive (health) significance of Hb mutations Majority of point mutations are rare, from neutral to grossly pathologic In non-malaric regions: a single „normal“ Hb - HbA1 (possibly HbA2 with ...
... -thalassemia interference with -chain production Etiology: -chain gene deletion, 1 – 4 6.5 A survey of adaptive (health) significance of Hb mutations Majority of point mutations are rare, from neutral to grossly pathologic In non-malaric regions: a single „normal“ Hb - HbA1 (possibly HbA2 with ...
Question
... generation, whereas the species is diploid during the ___________________ generation. ...
... generation, whereas the species is diploid during the ___________________ generation. ...
pedigrees poweropint 2015
... 7. Which members of the family above are afflicted with sickle cell anemia? 8. How are individuals III-4 and III-5 related? 9. How are individuals I-1 and I-2 related? 10. How are individuals II-7 and III-2 related? 11. How are individuals I-2 and III-5 related? 12. How many children did individuals ...
... 7. Which members of the family above are afflicted with sickle cell anemia? 8. How are individuals III-4 and III-5 related? 9. How are individuals I-1 and I-2 related? 10. How are individuals II-7 and III-2 related? 11. How are individuals I-2 and III-5 related? 12. How many children did individuals ...
Human Traits Lab
... a dominant phenotypic trait, but you need two copies of a recessive gene in order to see a recessive phenotypic trait. • A dominant phenotypic trait is represented capitol letter like B for brown eyes • A recessive phenotypic trait is represented lower case letter like b for blue (or light color ...
... a dominant phenotypic trait, but you need two copies of a recessive gene in order to see a recessive phenotypic trait. • A dominant phenotypic trait is represented capitol letter like B for brown eyes • A recessive phenotypic trait is represented lower case letter like b for blue (or light color ...
Unit D Key Terms D54-Investigating Human Traits
... of itself; results in two genetically identical offspring from ONE parent ...
... of itself; results in two genetically identical offspring from ONE parent ...
Unit A - Topic 3.0 Notes
... Genes are located on the chromosomes. Each chromosome has many genes. Genes come in pairs (one from each parent). Both genes in a pair carry instructions for the same trait (eg. hair color, height . . .) Gene pairs occupy matching locations on the two chromosomes. DNA code may not be exactly the sam ...
... Genes are located on the chromosomes. Each chromosome has many genes. Genes come in pairs (one from each parent). Both genes in a pair carry instructions for the same trait (eg. hair color, height . . .) Gene pairs occupy matching locations on the two chromosomes. DNA code may not be exactly the sam ...
Document
... seeds acquired a gene associated with smoothness from either the male or female gamete, and it will bear wrinkled peas only if its seed acquired a gene associated with wrinkledness from both gametes. The phenomenon of an individual demonstrating the form of a characteristic associated with one form ...
... seeds acquired a gene associated with smoothness from either the male or female gamete, and it will bear wrinkled peas only if its seed acquired a gene associated with wrinkledness from both gametes. The phenomenon of an individual demonstrating the form of a characteristic associated with one form ...
1 Natural Selection 2 Mutation
... Consider a locus where there are 2 alleles possible A and B. Suppose the mutation rate (per replication cycle per locus) for mutating A → B is u. Let v be the rate from B → A. Let pA (t) be the frequency of allele A in the tth generation. In the next generation, type A alleles will arise by faithful ...
... Consider a locus where there are 2 alleles possible A and B. Suppose the mutation rate (per replication cycle per locus) for mutating A → B is u. Let v be the rate from B → A. Let pA (t) be the frequency of allele A in the tth generation. In the next generation, type A alleles will arise by faithful ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.