Answered copy of exam 3 (white)
... inbreeding Selection Sickle cell PCR Founder effect Trisomy 21 etc Mutation SSRs or STRs Mitochondrial DNA Inbreeding ...
... inbreeding Selection Sickle cell PCR Founder effect Trisomy 21 etc Mutation SSRs or STRs Mitochondrial DNA Inbreeding ...
Say 2 significant things about these terms:
... Evolution: 20. Occurs through changes in gene frequencies in a population 21. Was first explined by Darwin through descent with modification 22. Artificial selection refutes it 23. It shows patterns of transition ...
... Evolution: 20. Occurs through changes in gene frequencies in a population 21. Was first explined by Darwin through descent with modification 22. Artificial selection refutes it 23. It shows patterns of transition ...
Self Assessment: Natural Selection
... b. evolutionary processes have a final goal they are striving towards c. organisms can always find the resources they need in some way or another d. there are only so many natural resources and humans are under pressure to use them now 4. All individuals of a species that live in a defined area is c ...
... b. evolutionary processes have a final goal they are striving towards c. organisms can always find the resources they need in some way or another d. there are only so many natural resources and humans are under pressure to use them now 4. All individuals of a species that live in a defined area is c ...
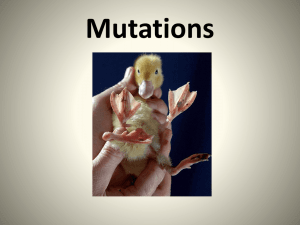
Mutations
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
Name - Animo Venice Biology
... Because members of the population interbreed, they share a common group of genes called a gene pool. ...
... Because members of the population interbreed, they share a common group of genes called a gene pool. ...
Microevolution & Macroevolution Worksheet
... 2. List two possible explanations for why drinking milk could have provided strong favorable selection for lactase persistence. __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2. List two possible explanations for why drinking milk could have provided strong favorable selection for lactase persistence. __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... a.) ____________________ is a change in the DNA of an organism b.) ____________________ is the exchange of pieces of chromosomes in meiosis which ensures that all gametes made by a sexually reproducing organism will be different c.) ___________________ is the mixing of genes in the offspring by the ...
Learning Log 4
... Examples of natural selection are not extremely difficult to find, if one looks closely enough. For example, the colobus monkey has adapted to survive in an environment where leaves are the only available food. They have large, protruding stomachs that can hold up to six pounds of leaves. Bacteria f ...
... Examples of natural selection are not extremely difficult to find, if one looks closely enough. For example, the colobus monkey has adapted to survive in an environment where leaves are the only available food. They have large, protruding stomachs that can hold up to six pounds of leaves. Bacteria f ...
BIO152 Course in Review
... What is the pattern? segregation of homologous chromosomes & independent assortment of homologous ...
... What is the pattern? segregation of homologous chromosomes & independent assortment of homologous ...
E:Med - uni-freiburg.de
... Martin Vingron’s group • Sequence alignment • Microarray gene analysis • Gene regulation and evolution: – (combinatorial) TF DNA binding prediction – Histone modification gene expression – Factors affecting mutation rates ...
... Martin Vingron’s group • Sequence alignment • Microarray gene analysis • Gene regulation and evolution: – (combinatorial) TF DNA binding prediction – Histone modification gene expression – Factors affecting mutation rates ...
Evolution Study Guide
... 9. Use your knowledge of genetics to explain how natural selection works (ex: mutation, allele frequency, etc.) 10. Explain why a population can adapt but a single individual organism cannot 11. Define genetic drift, and give an example; compare and contrast genetic drift and natural selection. 12. ...
... 9. Use your knowledge of genetics to explain how natural selection works (ex: mutation, allele frequency, etc.) 10. Explain why a population can adapt but a single individual organism cannot 11. Define genetic drift, and give an example; compare and contrast genetic drift and natural selection. 12. ...
File - hs science @ cchs
... Provide the variation that can be acted upon by natural selection. Mutations provide the raw material on which natural selection can act. Only source of additional genetic material and new alleles. Can be neutral, harmful or beneficial( give an individual a better chance for survival). Antibiotic re ...
... Provide the variation that can be acted upon by natural selection. Mutations provide the raw material on which natural selection can act. Only source of additional genetic material and new alleles. Can be neutral, harmful or beneficial( give an individual a better chance for survival). Antibiotic re ...
Genetics Challenge Name 1. The abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
Selection and Speciation
... neighbouring populations • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced t ...
... neighbouring populations • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced t ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... 1. What makes up a sequence in a DNA molecule? 2. Approximately how many genes are in the human genome? Read Your DNA makes you unique and explain how each human is unique or different if all humans have the same genes arranged in the same order. ...
... 1. What makes up a sequence in a DNA molecule? 2. Approximately how many genes are in the human genome? Read Your DNA makes you unique and explain how each human is unique or different if all humans have the same genes arranged in the same order. ...
Genetics 1
... carrier of the recessive haemophilia gene, which is sex-linked. What proportion of their offspring could have the condition? 1 in 2 ...
... carrier of the recessive haemophilia gene, which is sex-linked. What proportion of their offspring could have the condition? 1 in 2 ...
Genetic Technology
... A century ago, scientists glimpsed chromosomes through their microscopes. These cell structures control heredity. First, geneticists learned what normal chromosomes look like. They then studied abnormalities. An extra chromosome 21, for example, produces Down syndrome. This disorder negatively affec ...
... A century ago, scientists glimpsed chromosomes through their microscopes. These cell structures control heredity. First, geneticists learned what normal chromosomes look like. They then studied abnormalities. An extra chromosome 21, for example, produces Down syndrome. This disorder negatively affec ...
Genetic Drift
... A common misconception is that organisms evolve during their lifetimes Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve Consider, for example, a population of medium ground finches on Daphne Major Island During a drought, large-beaked birds were more likely to crack large s ...
... A common misconception is that organisms evolve during their lifetimes Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve Consider, for example, a population of medium ground finches on Daphne Major Island During a drought, large-beaked birds were more likely to crack large s ...
Biological Evolution
... Natural Selection 1. Variation in traits: more than one allele for a trait; one allele may be more advantageous than another 2. Differential reproduction: NOT all individuals get to reproduce to their full potential 3. Heredity: adaptations are genetic 4. End result: more advantageous trait allows ...
... Natural Selection 1. Variation in traits: more than one allele for a trait; one allele may be more advantageous than another 2. Differential reproduction: NOT all individuals get to reproduce to their full potential 3. Heredity: adaptations are genetic 4. End result: more advantageous trait allows ...