Evidence for Evolution
... Changes in metabolic processes.Direct evidence of evolution: Examples – 1. Bacteria acquiring antibiotic resistance 2. Insects & weeds becoming resistant to pesticides ...
... Changes in metabolic processes.Direct evidence of evolution: Examples – 1. Bacteria acquiring antibiotic resistance 2. Insects & weeds becoming resistant to pesticides ...
Secrets of Life Video Questions
... 2. “Limbs grow and the stumps on their surface become ____________________________________.” ...
... 2. “Limbs grow and the stumps on their surface become ____________________________________.” ...
4.1 Living Things Inherit Traits in Patterns
... Control traits that show up in an organism Sections of the chromosome shown here have been coloured in. Each section is a piece of DNA called a gene. ...
... Control traits that show up in an organism Sections of the chromosome shown here have been coloured in. Each section is a piece of DNA called a gene. ...
Body Systems
... 10. Convergent evolution: Similar species with no common ancestor (Birds butterflies bats) 11. Divergent evolution: Species from a common ancestor evolving farther apart (Finches) 12. Genetic drift: A change in a population’s allele frequency due to chance 13. Homologous structures: Similar structur ...
... 10. Convergent evolution: Similar species with no common ancestor (Birds butterflies bats) 11. Divergent evolution: Species from a common ancestor evolving farther apart (Finches) 12. Genetic drift: A change in a population’s allele frequency due to chance 13. Homologous structures: Similar structur ...
CHAPTER 11 QUICK LAB
... 1. Shuffle the cards and hold the deck face down. Turn over 40 cards to represent the alleles of 20 offspring produced by random matings in the initial population. 2. Separate the 40 cards by suit. Find the allele frequencies for the offspring by calculating the percentage of each suit. 3. Suppose a ...
... 1. Shuffle the cards and hold the deck face down. Turn over 40 cards to represent the alleles of 20 offspring produced by random matings in the initial population. 2. Separate the 40 cards by suit. Find the allele frequencies for the offspring by calculating the percentage of each suit. 3. Suppose a ...
Biology: Genetic Technology questions
... world to provide more nutrition to people where meat is not common or available in the diet. Bt corn is pest resistant, requiring far less pesticide use. ...
... world to provide more nutrition to people where meat is not common or available in the diet. Bt corn is pest resistant, requiring far less pesticide use. ...
The-four-factors
... allowing it to survive the attack. Since that individual survives, it can divide and all of its "offspring" will have that same genetic mutation. Eventually all of the bacteria will be immune to the antibiotic. 9.Microevolution happens on a small scale with individual populations. Macroevolution hap ...
... allowing it to survive the attack. Since that individual survives, it can divide and all of its "offspring" will have that same genetic mutation. Eventually all of the bacteria will be immune to the antibiotic. 9.Microevolution happens on a small scale with individual populations. Macroevolution hap ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why are Okazaki fragments required on the lagging strand? 15. What is a telomere? Why do they shorten over a period of time? In what types of cells can they be lengthened? By what enzyme? Chapter 17: From Gene to P ...
... 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why are Okazaki fragments required on the lagging strand? 15. What is a telomere? Why do they shorten over a period of time? In what types of cells can they be lengthened? By what enzyme? Chapter 17: From Gene to P ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... Coined the term DNA fingerprinting and was the first to use DNA polymorphisms in paternity, immigration, and murder cases. National Center for Human Genome Research created. $3 billion dollar effort to sequence human genome. 1990 Project launched ...
... Coined the term DNA fingerprinting and was the first to use DNA polymorphisms in paternity, immigration, and murder cases. National Center for Human Genome Research created. $3 billion dollar effort to sequence human genome. 1990 Project launched ...
11-3- Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... individual units known as _____________. In organisms that reproduce sexually, genes are passed from parents to their ____________________. 2. In cases in which 2 or more forms (or _____________) of the gene for a single ___________exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others ___________ ...
... individual units known as _____________. In organisms that reproduce sexually, genes are passed from parents to their ____________________. 2. In cases in which 2 or more forms (or _____________) of the gene for a single ___________exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others ___________ ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes. Genetic disorders are caused by mutations, or changes in a person’s DNA. ...
... condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes. Genetic disorders are caused by mutations, or changes in a person’s DNA. ...
Genetics of Evolution - Ms. Chambers' Biology
... Evolution- change over time in the gene pools of a species If populations do not change (adapt) to their environment, they may become extinct. ...
... Evolution- change over time in the gene pools of a species If populations do not change (adapt) to their environment, they may become extinct. ...
- Google Sites
... Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive. Some offspring may be more likely than others to survive and reproduce. Characteristics that give certain individuals an advantage in surviving and reproducing might be inherited by their offspring. These characteristics would tend to becom ...
... Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive. Some offspring may be more likely than others to survive and reproduce. Characteristics that give certain individuals an advantage in surviving and reproducing might be inherited by their offspring. These characteristics would tend to becom ...
Evolution Objective Sheet
... • Generalize what biochemical (molecular) similarities tell us about evolution. • Generalize what shared anatomical structures (homologies) tell us about evolution Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences the changes in species over time. • Illustrate the role of geographic isolation in sp ...
... • Generalize what biochemical (molecular) similarities tell us about evolution. • Generalize what shared anatomical structures (homologies) tell us about evolution Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences the changes in species over time. • Illustrate the role of geographic isolation in sp ...
History of Genetics
... Despite knowing about inheritance in general, a number of incorrect ideas had to be generated and overcome before modern genetics could arise. 1. All life comes from other life. Living organisms are not spontaneously generated from non-living material. Big exception: origin of life. 2. Species conce ...
... Despite knowing about inheritance in general, a number of incorrect ideas had to be generated and overcome before modern genetics could arise. 1. All life comes from other life. Living organisms are not spontaneously generated from non-living material. Big exception: origin of life. 2. Species conce ...
Genetic variability
... in fact, each gamete contains a mixture of homologous CHm and CHp due to the process during 1st meiotic division = crossing-over and recombination thus alleles originally coming from different grandparents can appear in one chromosome ...
... in fact, each gamete contains a mixture of homologous CHm and CHp due to the process during 1st meiotic division = crossing-over and recombination thus alleles originally coming from different grandparents can appear in one chromosome ...
Structural Variations
... Sewall Wright’s Fixation index (Fst is a useful index of genetic differentiation and comparison of overall effect of population substructure. Measures reduction in heterozygosity (H) expected with non-random mating at any one level of population hierarchy relative to another more inclusive hierarchi ...
... Sewall Wright’s Fixation index (Fst is a useful index of genetic differentiation and comparison of overall effect of population substructure. Measures reduction in heterozygosity (H) expected with non-random mating at any one level of population hierarchy relative to another more inclusive hierarchi ...
Presentation
... settlers in South Africa is descended mainly from a few colonists. Today, the Afrikaner population has an unusually high frequency of the gene that causes Huntington’s disease, because those original Dutch colonists just happened to carry that gene with unusually high frequency. This effect is easy ...
... settlers in South Africa is descended mainly from a few colonists. Today, the Afrikaner population has an unusually high frequency of the gene that causes Huntington’s disease, because those original Dutch colonists just happened to carry that gene with unusually high frequency. This effect is easy ...
Practice Genetics Vocabulary Quiz
... C. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. D. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. E. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele comb ...
... C. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. D. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. E. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele comb ...
Complementation
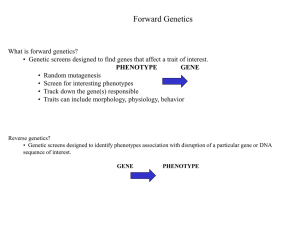
... • Large scale genetic screens that aim to create a mutation in every gene required for a trait. ...
... • Large scale genetic screens that aim to create a mutation in every gene required for a trait. ...
The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...