Genetics of MD - Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
Lecture 12 notes
... Co‐opting structures from one function to another is known as exaptation (don’t need a new structure to arise, can simply modify an existing one) Feathers are another example—their original purpose may not have been for flight, but rather for attracting mates or thermoregulation ‐‐new studies ha ...
... Co‐opting structures from one function to another is known as exaptation (don’t need a new structure to arise, can simply modify an existing one) Feathers are another example—their original purpose may not have been for flight, but rather for attracting mates or thermoregulation ‐‐new studies ha ...
Biology B Trimester Review 6-1
... 12. What are gametes? 13. If the “n” number of a cell is 24, what would its diploid number be? 14. Be able to explain the different phases of meiosis. 15. What is crossing over, and when does it take place? 16. Identify another way to increase genetic variation in offspring? 17. Compare and contrast ...
... 12. What are gametes? 13. If the “n” number of a cell is 24, what would its diploid number be? 14. Be able to explain the different phases of meiosis. 15. What is crossing over, and when does it take place? 16. Identify another way to increase genetic variation in offspring? 17. Compare and contrast ...
AP Biology Changes in populations Bent Grass on toxic mine site
... Mean beak depth of parents (mm) ...
... Mean beak depth of parents (mm) ...
Human Genetics
... participate in protein synthesis and energy production Several diseases result from mutations in mtDNA Examples: - Mitochondrial myopathies – Weak and flaccid muscles - Leber optical atrophy – Impaired vision Ooplasmic transfer technique can enable woman to avoid transmitting a mitochondrial disorde ...
... participate in protein synthesis and energy production Several diseases result from mutations in mtDNA Examples: - Mitochondrial myopathies – Weak and flaccid muscles - Leber optical atrophy – Impaired vision Ooplasmic transfer technique can enable woman to avoid transmitting a mitochondrial disorde ...
Document
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
16.2 Evolution as Genetic Change
... 1. Directional Selection higher fitness at ONE END of the curve than at the other all phenotypes in the population shift towards HIGHER FITNESS Example bird population where food becomes scarce ...
... 1. Directional Selection higher fitness at ONE END of the curve than at the other all phenotypes in the population shift towards HIGHER FITNESS Example bird population where food becomes scarce ...
Catalyst - SharpSchool
... What forms the “rungs” of the DNA ladder? Why is the sequence of bases important? How are nitrogen base of DNA like the letters of the alphabet? ...
... What forms the “rungs” of the DNA ladder? Why is the sequence of bases important? How are nitrogen base of DNA like the letters of the alphabet? ...
Genetic Engineering
... This is a project being carried out to sequence the complete human genome – the complete nucleotide sequence of the DNA of all the genes of a human cell. This involves the collaborative work of scientists from all over the world, since there are 23 pairs of chromosomes and each contains huge numbers ...
... This is a project being carried out to sequence the complete human genome – the complete nucleotide sequence of the DNA of all the genes of a human cell. This involves the collaborative work of scientists from all over the world, since there are 23 pairs of chromosomes and each contains huge numbers ...
Evolution of mouse globin superfamily
... Review of various types and effects of mutations How larger genomes evolve through duplication and divergence Molecular archeology based on gene duplication, diversification, and selection globin gene family: an example of molecular evolution ...
... Review of various types and effects of mutations How larger genomes evolve through duplication and divergence Molecular archeology based on gene duplication, diversification, and selection globin gene family: an example of molecular evolution ...
Natural Selections
... becomes infected with AIDS, the infection usually starts with a single type of virus, but within two years the virus evolves into numerous forms. Within the last three decades, strains of tuberculosis, syphilis, and gonorrhea have evolved resistance to the antibiotics that once controlled them. The ...
... becomes infected with AIDS, the infection usually starts with a single type of virus, but within two years the virus evolves into numerous forms. Within the last three decades, strains of tuberculosis, syphilis, and gonorrhea have evolved resistance to the antibiotics that once controlled them. The ...
File
... 1) Do the offspring of two parents ever look exactly like either parent? Why not? No, because they are a combination of the genes from both parents and not from only one parent. 2) What type of organisms only reproduce asexually? Single-celled organisms. 3a) How similar are the offspring to the pare ...
... 1) Do the offspring of two parents ever look exactly like either parent? Why not? No, because they are a combination of the genes from both parents and not from only one parent. 2) What type of organisms only reproduce asexually? Single-celled organisms. 3a) How similar are the offspring to the pare ...
2 Sex chromosomes
... • How many autosomes do humans have? How many sex chromosomes? • 44 autosomes (22 pairs) • 2 Sex chromosomes (1 pair) ...
... • How many autosomes do humans have? How many sex chromosomes? • 44 autosomes (22 pairs) • 2 Sex chromosomes (1 pair) ...
Restriction Enzymes, Vectors, and Genetic Libraries
... contains all the genetic information of an individual = genomic library - gene bank Chromosomes, set of genes of single cell type etc. ...
... contains all the genetic information of an individual = genomic library - gene bank Chromosomes, set of genes of single cell type etc. ...
Genetic Notes
... B. Meiosis: is the formation of sex cells or gametes. 1. Eggs are produced in the female sex organ the ovaries, sperm is produced in the male sex organ the testes. 2. Meiosis produces sex cells with only one set of chromosomes these cells are monoploid. 3. In meiosis the chromosomes separate twice ...
... B. Meiosis: is the formation of sex cells or gametes. 1. Eggs are produced in the female sex organ the ovaries, sperm is produced in the male sex organ the testes. 2. Meiosis produces sex cells with only one set of chromosomes these cells are monoploid. 3. In meiosis the chromosomes separate twice ...
DNA, RNA, PROTEINS STARTS WITH
... _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A ...
... _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A ...
The Evolution of Populations AP Biology Notes I. Overview: The Sma
... D. The Hardy-‐Weinberg Theorem: measures properties of gene pools that are not evolving(preserves genetic variation from one generation to the next in populations that are not evolving)(provides the opportunity ...
... D. The Hardy-‐Weinberg Theorem: measures properties of gene pools that are not evolving(preserves genetic variation from one generation to the next in populations that are not evolving)(provides the opportunity ...
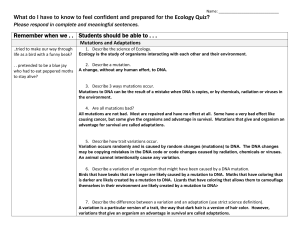
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
Name Period Chapter 12 Genetics Lesson 1: The Genetic Code
... 1. Walter Sutton studied grasshoppers to discover how sex cells (eggs and sperm) form. 2. He hypothesized that chromosomes are the key to understanding how offspring have traits similar to those of their parents. 3. He discovered that grasshopper sex cells have ½ of the number of chromosomes found i ...
... 1. Walter Sutton studied grasshoppers to discover how sex cells (eggs and sperm) form. 2. He hypothesized that chromosomes are the key to understanding how offspring have traits similar to those of their parents. 3. He discovered that grasshopper sex cells have ½ of the number of chromosomes found i ...
A1978FE76900002
... geneticist R.A. Emerson in the 1930's, I recall his futile attempts to interest plant physiologists and biochemists in making use of genetic traits in corn known to be concerned with the synthesis of chlorophyll and its role in photosynthesis. "As a National Research Council Fellow at the California ...
... geneticist R.A. Emerson in the 1930's, I recall his futile attempts to interest plant physiologists and biochemists in making use of genetic traits in corn known to be concerned with the synthesis of chlorophyll and its role in photosynthesis. "As a National Research Council Fellow at the California ...
Genetics Vocabulary Week 3
... number is placed into two daughter cells (Ex: Body Cells – hair, skin, etc…) Karyotype - the chromosomes of a cell, usually displayed as a systematized arrangement of chromosome pairs in descending order of size (a picture of chromosomes) Mutation - a change in a gene or chromosome Genetic Disorder ...
... number is placed into two daughter cells (Ex: Body Cells – hair, skin, etc…) Karyotype - the chromosomes of a cell, usually displayed as a systematized arrangement of chromosome pairs in descending order of size (a picture of chromosomes) Mutation - a change in a gene or chromosome Genetic Disorder ...
Chapter 19
... master genes Some master genes called homeotic genes are responsible for shaping the developing ...
... master genes Some master genes called homeotic genes are responsible for shaping the developing ...