1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with 1. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. 2. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. 3. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with 1. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. 2. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. 3. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
Control of Gene Express in Prokaryotes
... • Structural gene-gene that codes for a polypeptide • Promoter region-controls access to the structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycis ...
... • Structural gene-gene that codes for a polypeptide • Promoter region-controls access to the structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycis ...
Gregor Mendel Mendel`s 7 Pea Plant Traits
... Eg. The Purple Pigment Protein which give a flower its purple color are “encoded” by a specific set of genes. ...
... Eg. The Purple Pigment Protein which give a flower its purple color are “encoded” by a specific set of genes. ...
Genetics Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes
... Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. Genetics concerns the process of trait inheritance from parents to offspring, including the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior in the context of a cell or organism (e.g. dom ...
... Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. Genetics concerns the process of trait inheritance from parents to offspring, including the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior in the context of a cell or organism (e.g. dom ...
Plant DNA mini
... these organisms are likely to be novel and of significant biological interest. Additionally, their identification may have practical benefits, contributing to our understanding of human disease genes and providing useful tools for agricultural bioengineering. ...
... these organisms are likely to be novel and of significant biological interest. Additionally, their identification may have practical benefits, contributing to our understanding of human disease genes and providing useful tools for agricultural bioengineering. ...
TM Review Genetics
... Since males have just one X chromosome, all X-linked alleles are expressed in males. Girls need ...
... Since males have just one X chromosome, all X-linked alleles are expressed in males. Girls need ...
Epigenetics - Hospital Melaka Department of Medicine Haematology
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
Course Outline
... the difference between genes and chromosomes, outlining the number of chromosomes in autosomal and sex cells (autosomal = 46, sex cells = 23) • Compare and contrast Mitosis and Meiosis (Function, chromosome number, number of cells and stages ie interphase, prophase, metaphase (I & II), anaphase (I & ...
... the difference between genes and chromosomes, outlining the number of chromosomes in autosomal and sex cells (autosomal = 46, sex cells = 23) • Compare and contrast Mitosis and Meiosis (Function, chromosome number, number of cells and stages ie interphase, prophase, metaphase (I & II), anaphase (I & ...
Genes and Genetic Disease
... Homozygous – loci on a pair of chromosomes have identical genes Example: O blood type (OO) Heterozygous – loci on a pair of chromosomes have different genes Example: AB blood type (A & B genes on a pair of loci) ...
... Homozygous – loci on a pair of chromosomes have identical genes Example: O blood type (OO) Heterozygous – loci on a pair of chromosomes have different genes Example: AB blood type (A & B genes on a pair of loci) ...
Name: Date: Period:______ Genetics Vocabulary Note
... Groups of atoms __________ together. An animal’s or human’s young, children. A quality or _______________ which makes one thing different from another. Differences between things of the same type, _________________. The kinds of genes (alleles) an individual carries The ___________________ expressio ...
... Groups of atoms __________ together. An animal’s or human’s young, children. A quality or _______________ which makes one thing different from another. Differences between things of the same type, _________________. The kinds of genes (alleles) an individual carries The ___________________ expressio ...
13. Testing for cancer gene susceptibility
... Mutations, or changes to the structure of DNA, can make us more susceptible to some diseases or disabilities. Even if you have the mutation, it may not mean you get the disease, but are just more likely to get it. The link between having the mutation and the possibility of getting the disease is not ...
... Mutations, or changes to the structure of DNA, can make us more susceptible to some diseases or disabilities. Even if you have the mutation, it may not mean you get the disease, but are just more likely to get it. The link between having the mutation and the possibility of getting the disease is not ...
BI0 10-3 P0WERPOINT
... these roses become too hardy and that the gardeners are unable to get rid of them using herbicides. This problem is an example of the unpredictable nature of genetically modifying plants and other organisms. Scientists do not always fully understand how genetically modifying a particular organism wi ...
... these roses become too hardy and that the gardeners are unable to get rid of them using herbicides. This problem is an example of the unpredictable nature of genetically modifying plants and other organisms. Scientists do not always fully understand how genetically modifying a particular organism wi ...
Genetics Review
... What are the sides of a DNA molecule made up of? During which phase does the copying of DNA occur? What are the middle “rungs” of the DNA ladder made up of? What are the 4 bases that are found in DNA? Adenine pairs with Guanine pairs with Cytosine pairs with Thymine pairs with What is another name f ...
... What are the sides of a DNA molecule made up of? During which phase does the copying of DNA occur? What are the middle “rungs” of the DNA ladder made up of? What are the 4 bases that are found in DNA? Adenine pairs with Guanine pairs with Cytosine pairs with Thymine pairs with What is another name f ...
Pedigree link
... diseases. They can be caused by a number of unrelated processes. Single gene mutations, cause a~terations in the specific base sequences of the DNA, Othem work a~t a toucan larger sca.te, ca.using pieces of chromosome to be moved or IosL ...
... diseases. They can be caused by a number of unrelated processes. Single gene mutations, cause a~terations in the specific base sequences of the DNA, Othem work a~t a toucan larger sca.te, ca.using pieces of chromosome to be moved or IosL ...
Lecture 10
... the aggression that maintains lower population density where the species are native. • High genetic diversity • In invasions, usually the product of repeated introductions • Higher diversity within populations than between them. This contrast to native range where individual populations are ...
... the aggression that maintains lower population density where the species are native. • High genetic diversity • In invasions, usually the product of repeated introductions • Higher diversity within populations than between them. This contrast to native range where individual populations are ...
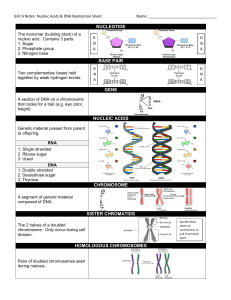
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
How are we different? …at the RNA level.
... • Genome... the dynamic complement of heritable genetic material, • Transcriptome... mRNA component in an individual, • Proteome... the protein component of an individual, ...
... • Genome... the dynamic complement of heritable genetic material, • Transcriptome... mRNA component in an individual, • Proteome... the protein component of an individual, ...
Genetics
... TAGCCTGAT is a part of DNA that codes for blue eye color. Replicate the DNA and tell or show how the new DNA is the same as the original. ...
... TAGCCTGAT is a part of DNA that codes for blue eye color. Replicate the DNA and tell or show how the new DNA is the same as the original. ...
DNA Chips
... • Inject genetically modified ES cells into blastocyststage embryos & implant in surrogate mother. • Resulting adult mice should be somatic chimeras & some should also be germ line chimeras. • Do genetic crosses & use PCR to screen for progeny that are heterozygous for the targeted mutation. • Cross ...
... • Inject genetically modified ES cells into blastocyststage embryos & implant in surrogate mother. • Resulting adult mice should be somatic chimeras & some should also be germ line chimeras. • Do genetic crosses & use PCR to screen for progeny that are heterozygous for the targeted mutation. • Cross ...
ch 20 study guide: dna technology
... Liga - = bound, tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme essential for DNA replication) Electro - = electricity (electroporation: a technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by applying a breif electrical pulse to a solution containing cells) Poly - = many; morph - = form (Single nucleotide polymo ...
... Liga - = bound, tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme essential for DNA replication) Electro - = electricity (electroporation: a technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by applying a breif electrical pulse to a solution containing cells) Poly - = many; morph - = form (Single nucleotide polymo ...
An Introduction to DNA and Genetics Directions: As you watch the
... • All humans have the same ______________ arranged in the same _____________. What percent of our DNA sequence is the same? _____% On average, a human gene will have _______ - _______ bases that differ from person to person. These differences can change the _____________ and ____________________ of ...
... • All humans have the same ______________ arranged in the same _____________. What percent of our DNA sequence is the same? _____% On average, a human gene will have _______ - _______ bases that differ from person to person. These differences can change the _____________ and ____________________ of ...
1. Genetics
... • Learn the genotype of a (nonhuman) organism • Cross organism with homozygous recessive organism (aa) • If all offspring are Aa, parent was probably AA • If some of the offspring have the dominant trait and some have the recessive trait, parent was Aa ...
... • Learn the genotype of a (nonhuman) organism • Cross organism with homozygous recessive organism (aa) • If all offspring are Aa, parent was probably AA • If some of the offspring have the dominant trait and some have the recessive trait, parent was Aa ...
A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to
... What are organisms that get energy by breaking down the remains of dead organisms called? Engineers use what to determine solutions to problems? Engineers follow a _________ approach of the EDP to create multiple possible solutions to problems. What is the first step of the Engineering Design Proces ...
... What are organisms that get energy by breaking down the remains of dead organisms called? Engineers use what to determine solutions to problems? Engineers follow a _________ approach of the EDP to create multiple possible solutions to problems. What is the first step of the Engineering Design Proces ...