Natural Selection
... • Microevolution is a change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a gene pool over time – Variation in heritable traits is a prerequisite for evolution • Population genetics studies how populations change genetically over time • The modern synthesis connects Darwin s theory with population ...
... • Microevolution is a change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a gene pool over time – Variation in heritable traits is a prerequisite for evolution • Population genetics studies how populations change genetically over time • The modern synthesis connects Darwin s theory with population ...
genetics notes
... Crossing –over during meiosis separates genes on the same chromosome onto homologous chromosomes---This gives great genetic ____________________. ...
... Crossing –over during meiosis separates genes on the same chromosome onto homologous chromosomes---This gives great genetic ____________________. ...
Honors Biology Chapter 3 – The Process of Science: Studying
... B. Dom. lethal alleles much less common than rec. lethal alleles - why? 1. for most dominant disorders, the affected person dies before producing any offspring that could inherit the allele 2. Natural mutations can return the dom. allele to the pop. thru sperm or egg cell 3. Recessive alleles often ...
... B. Dom. lethal alleles much less common than rec. lethal alleles - why? 1. for most dominant disorders, the affected person dies before producing any offspring that could inherit the allele 2. Natural mutations can return the dom. allele to the pop. thru sperm or egg cell 3. Recessive alleles often ...
Natural Selection March , 2.009 * 103
... When a significant environmental pressure arises, certain traits will be “selected” for. ...
... When a significant environmental pressure arises, certain traits will be “selected” for. ...
Evolution
... Darwin did begin using the term to replace “natural selection”, but not until the 5th edition of Origin of Species He did not mean strongest, as is sometimes assumed. Any individual that successfully reproduces is contributing to the survival of its species. Therefore, the term “fit” can be cons ...
... Darwin did begin using the term to replace “natural selection”, but not until the 5th edition of Origin of Species He did not mean strongest, as is sometimes assumed. Any individual that successfully reproduces is contributing to the survival of its species. Therefore, the term “fit” can be cons ...
What is another name for a polypeptide?
... (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that causes AIDS. UV radiation from the Sun can damage DNA. ...
... (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that causes AIDS. UV radiation from the Sun can damage DNA. ...
What are genes? Since the beginning of time, people have
... The picture above shows a make-believe, long furry animal. The animal’s head is small compared to its long body. The head has two tiny ears, a flat nose, and a mouth with broad, flat teeth. The four long, slender legs end in large, webbed feet with four bulbous toes on each foot. The long tail has a ...
... The picture above shows a make-believe, long furry animal. The animal’s head is small compared to its long body. The head has two tiny ears, a flat nose, and a mouth with broad, flat teeth. The four long, slender legs end in large, webbed feet with four bulbous toes on each foot. The long tail has a ...
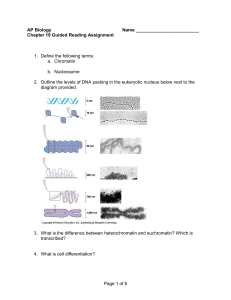
Ch. 15 Notes
... • The Hardy-Weinberg equation is used to predict genotype frequencies in a population • Frequency of the dominant (A) allele : p • Frequency of the recessive (a) allele: q • Because the sum of p and q represent 100% of the alleles for that gene in a population : p + q = 1 • Frequency of homozygous d ...
... • The Hardy-Weinberg equation is used to predict genotype frequencies in a population • Frequency of the dominant (A) allele : p • Frequency of the recessive (a) allele: q • Because the sum of p and q represent 100% of the alleles for that gene in a population : p + q = 1 • Frequency of homozygous d ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of the individual, and is composed of either two x chromosomes (female) or an x and a y chromosome (male). ...
... chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of the individual, and is composed of either two x chromosomes (female) or an x and a y chromosome (male). ...
Name: page1 of 7 pages MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO372S January
... 5. The early notion of one-gene/one-enzyme was not true because of which of the following? A. An enzyme can be composed of more than one polypeptide. B. Many genes contain the information for making polypeptides that are not enzymes. C. The end products of some genes are not polypeptides. D. An enzy ...
... 5. The early notion of one-gene/one-enzyme was not true because of which of the following? A. An enzyme can be composed of more than one polypeptide. B. Many genes contain the information for making polypeptides that are not enzymes. C. The end products of some genes are not polypeptides. D. An enzy ...
Evolution and Population Genetics
... change from one generation to the next. The frequency of individuals with better genes will increase. This process is called natural selection. Natural Selection Produces Evolutionary Change If the conditions discussed above are met, the genetic composition of the population will change from one gen ...
... change from one generation to the next. The frequency of individuals with better genes will increase. This process is called natural selection. Natural Selection Produces Evolutionary Change If the conditions discussed above are met, the genetic composition of the population will change from one gen ...
genetic variation
... The directly method to test the genetic variation is using molecular markers, but the adaptive traits are not correlation to the results, which depend on the testing level (Hall et al., 2007). Genetic variation among tree populations is routinely studied with provenance trials (e.g. Hamann et al., 2 ...
... The directly method to test the genetic variation is using molecular markers, but the adaptive traits are not correlation to the results, which depend on the testing level (Hall et al., 2007). Genetic variation among tree populations is routinely studied with provenance trials (e.g. Hamann et al., 2 ...
MedlinePlus genetic disorders
... Many factors contribute to the transmittance of diseases – lifestyle, inheritance, and environment. When people make key lifestyle choices, they are in essence running the risk of developing disease. Smoking and obesity are ranked as the two highest factors in preventable deaths. Therefore, choosing ...
... Many factors contribute to the transmittance of diseases – lifestyle, inheritance, and environment. When people make key lifestyle choices, they are in essence running the risk of developing disease. Smoking and obesity are ranked as the two highest factors in preventable deaths. Therefore, choosing ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
X-linked Inheritance - Great Ormond Street Hospital
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
BASIC CONCEPTS IN GENETICS
... • PKU is a human hereditary disease resulting from inability of the body to process the chemical phenylalanine (contained in protein that we eat). • It is caused by a recessive allele with simple Mendelian inheritance. • Some couple wants to have children. The man has a sister with PKU and the woman ...
... • PKU is a human hereditary disease resulting from inability of the body to process the chemical phenylalanine (contained in protein that we eat). • It is caused by a recessive allele with simple Mendelian inheritance. • Some couple wants to have children. The man has a sister with PKU and the woman ...
Topic 2 & 3: Genetics Review
... Identifying individuals who died long ago. Identifying animals that migrate in order to estimate population size. 5. Identifying animal parts (distinguish from common species vs. endangered species). Contamination of samples by even a single cell would totally throw off results. ...
... Identifying individuals who died long ago. Identifying animals that migrate in order to estimate population size. 5. Identifying animal parts (distinguish from common species vs. endangered species). Contamination of samples by even a single cell would totally throw off results. ...
Module 5 Homework Assignment
... frequency or a microevolution. The change could also be on a larger scale where larger changes are made over a period of time to create a new species, or macroevolution. 2. Why has Lamarck’s theory been rejected? Lamarck’s theory was rejected because it was based on acquired characteristics or trait ...
... frequency or a microevolution. The change could also be on a larger scale where larger changes are made over a period of time to create a new species, or macroevolution. 2. Why has Lamarck’s theory been rejected? Lamarck’s theory was rejected because it was based on acquired characteristics or trait ...
CHAPTER 1 – INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS I. SYLLABUS A
... organisms are composed of basic units called cells which are derived from preexisting cells) c) Charles Darwin: The theory of natural selection (those organisms with heritable traits that better adapt them to their environment are better able to survive and reproduce; therefore, over a long period o ...
... organisms are composed of basic units called cells which are derived from preexisting cells) c) Charles Darwin: The theory of natural selection (those organisms with heritable traits that better adapt them to their environment are better able to survive and reproduce; therefore, over a long period o ...
Chapter 9 answers
... contain all instructions, but most cells don’t need but a certain selection of the instructions. For instance a cell near your ear does not need to make the molecules that help your stomach with digestion. It would be terribly wasteful in terms of space, energy, and materials. That is why most genes ...
... contain all instructions, but most cells don’t need but a certain selection of the instructions. For instance a cell near your ear does not need to make the molecules that help your stomach with digestion. It would be terribly wasteful in terms of space, energy, and materials. That is why most genes ...
Lecture Notes
... recessive allele for this gene Detached earlobes: either one or two copies of the dominant allele ...
... recessive allele for this gene Detached earlobes: either one or two copies of the dominant allele ...
Summary of sixth lesson - UC Berkeley College of Natural
... Measurable differential: size of structures Gene-for-gene defense model Sympatric speciation: Heterobasidion, Armillaria, Sphaeropsis, Phellinus, Fusarium ...
... Measurable differential: size of structures Gene-for-gene defense model Sympatric speciation: Heterobasidion, Armillaria, Sphaeropsis, Phellinus, Fusarium ...
Themes in the Development of DNA Science
... Linus Pauling uses X-ray crystallography to deduce the structure of ...
... Linus Pauling uses X-ray crystallography to deduce the structure of ...