Keystone Bio Practice Test
... processes. Single-celled organisms do not have organ systems and yet they are able to carry out life processes. This is because (1) human organ systems lack the organelles found in single-celled organisms (2) a human cell is more efficient than the cell of a single-celled organism (3) it is not nece ...
... processes. Single-celled organisms do not have organ systems and yet they are able to carry out life processes. This is because (1) human organ systems lack the organelles found in single-celled organisms (2) a human cell is more efficient than the cell of a single-celled organism (3) it is not nece ...
unnatural selection or artificial selection or selective breeding
... Reproductive success is defined as the passing of genes into the next generation in a way that they too can pass on these genes. Organisms compete for food, water, space, and territory, sexual mates, (sexual selection) e.g. peacocks vs horned animals. They also compete in their resistance to disease ...
... Reproductive success is defined as the passing of genes into the next generation in a way that they too can pass on these genes. Organisms compete for food, water, space, and territory, sexual mates, (sexual selection) e.g. peacocks vs horned animals. They also compete in their resistance to disease ...
Lecture 11 Speciation
... The role of natural selection in speciation. Prezygotic vs. postzygotic reproductive isolation. The genetic mechanisms responsible for reproductive isolation. ...
... The role of natural selection in speciation. Prezygotic vs. postzygotic reproductive isolation. The genetic mechanisms responsible for reproductive isolation. ...
41) A Closer Look at Natural Selection
... • Alleles have evolved in some populations that confer insecticide resistance to these mosquitoes • The flow of insecticide resistance alleles into a population can cause an increase in fitness ...
... • Alleles have evolved in some populations that confer insecticide resistance to these mosquitoes • The flow of insecticide resistance alleles into a population can cause an increase in fitness ...
3.1 Teacher Notes
... a. Operons are segments of DNA where a transcription factor (a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA) can bind b. The operon regulates gene expression! Control of Gene expression a. How a gene expr ...
... a. Operons are segments of DNA where a transcription factor (a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA) can bind b. The operon regulates gene expression! Control of Gene expression a. How a gene expr ...
Lecture 19 Basics: Beyond simple dominance
... Sixteen alleles are known to exist for a given gene in a diploid organism. This means that any given individual of that species can have: A. Up to 16 chromosomes with that gene B. Up to 16 genes for that trait C. A haploid number of 8 chromosomes D. Up to 16 different traits E. At most, 2 alleles fo ...
... Sixteen alleles are known to exist for a given gene in a diploid organism. This means that any given individual of that species can have: A. Up to 16 chromosomes with that gene B. Up to 16 genes for that trait C. A haploid number of 8 chromosomes D. Up to 16 different traits E. At most, 2 alleles fo ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
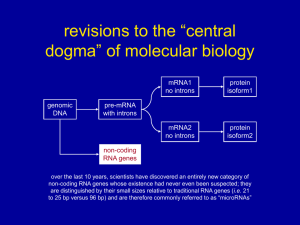
... over the last 10 years, scientists have discovered an entirely new category of non-coding RNA genes whose existence had never even been suspected; they are distinguished by their small sizes relative to traditional RNA genes (i.e. 21 to 25 bp versus 96 bp) and are therefore commonly referred to as “ ...
... over the last 10 years, scientists have discovered an entirely new category of non-coding RNA genes whose existence had never even been suspected; they are distinguished by their small sizes relative to traditional RNA genes (i.e. 21 to 25 bp versus 96 bp) and are therefore commonly referred to as “ ...
What are genomes and how are they studied
... Segmental duplications: Closely related sequence blocks at different genomic loci Transfer of 1-200kb blocks of genomic sequence Segmental duplications can occur on homologous chromosomes (intrachromosomal) or non homologous chromosomes (interchromosomal) Not always tandemly arranged Relat ...
... Segmental duplications: Closely related sequence blocks at different genomic loci Transfer of 1-200kb blocks of genomic sequence Segmental duplications can occur on homologous chromosomes (intrachromosomal) or non homologous chromosomes (interchromosomal) Not always tandemly arranged Relat ...
CP Biology Cumulative Final Exam Study Guide write all answers on
... 69. How do vaccines work? 70. What are the major differences between bacteria and viruses? 71. Describe the causes, symptoms, and treatments for HIV and AIDS. 72. How do feedback loops in the body systems help maintain homeostasis? 73. Describe the body’s immune response to a pathogen. (discuss B ce ...
... 69. How do vaccines work? 70. What are the major differences between bacteria and viruses? 71. Describe the causes, symptoms, and treatments for HIV and AIDS. 72. How do feedback loops in the body systems help maintain homeostasis? 73. Describe the body’s immune response to a pathogen. (discuss B ce ...
Genetic Inheritance Teacher Information Sheet
... There are several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. ...
... There are several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. ...
Bio 220 MiniQuiz 1
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Notes: Applications of Recombinant DNA
... a) Normally tomatoes are picked when the are unripe so that they will not bruise during transit. Prior to marketing ethylene is provided which initiates the ripening process; however, although the tomatoes appear to ripen, the flavor is poorer than vine-ripened tomatoes. Thus, researchers at Calgene ...
... a) Normally tomatoes are picked when the are unripe so that they will not bruise during transit. Prior to marketing ethylene is provided which initiates the ripening process; however, although the tomatoes appear to ripen, the flavor is poorer than vine-ripened tomatoes. Thus, researchers at Calgene ...
ESR173U7LecA
... The Theory of Biological Evolution • Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by means of natural selection explains the unity and diversity of life as “descent with modification” – Parents pass traits to their offspring (heredity) – Individuals within a population vary in those traits (variation) – So ...
... The Theory of Biological Evolution • Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by means of natural selection explains the unity and diversity of life as “descent with modification” – Parents pass traits to their offspring (heredity) – Individuals within a population vary in those traits (variation) – So ...
DISEASES AND TREES - UC Berkeley College of Natural Resources
... • Scale of dispersal (implicitely correlated to metapopulation structure)--- ...
... • Scale of dispersal (implicitely correlated to metapopulation structure)--- ...
Positive assortative mating
... parameters other than the number of breeding individuals in the population. These include: •Variation in offspring number among individuals •A sex ratio other than 1:1 •Natural selection •Inbreeding (reduces the number of different copies of a gene passed to the next generation) •Fluctuations in pop ...
... parameters other than the number of breeding individuals in the population. These include: •Variation in offspring number among individuals •A sex ratio other than 1:1 •Natural selection •Inbreeding (reduces the number of different copies of a gene passed to the next generation) •Fluctuations in pop ...
9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics
... 9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics • The Human Genome Project has sequenced all of the DNA base pairs of human chromosomes. – analyzed DNA from a few people – still working to identify and map human genes ...
... 9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics • The Human Genome Project has sequenced all of the DNA base pairs of human chromosomes. – analyzed DNA from a few people – still working to identify and map human genes ...
9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics KEY CONCEPT Entire genomes are sequenced, studied, and compared.
... 9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics Technology allows the study and comparison of both genes and proteins. • Bioinformatics is the use of computer databases to organize and analyze biological data. • DNA microarrays are used to study the expression of many genes at once. ...
... 9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics Technology allows the study and comparison of both genes and proteins. • Bioinformatics is the use of computer databases to organize and analyze biological data. • DNA microarrays are used to study the expression of many genes at once. ...
Control of Metabolic Pathways
... • If one enzyme is absent, the pathway comes to a halt Gene(s) ...
... • If one enzyme is absent, the pathway comes to a halt Gene(s) ...
Mendel`s Investigations
... fertilization of his pea plants by removing the male parts, or stamens. ...
... fertilization of his pea plants by removing the male parts, or stamens. ...
Ch. 15 Chromosomal Inheritance
... Leads to aneuploidy: • Aneuploidy is the condition of having less than or more than the normal diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
... Leads to aneuploidy: • Aneuploidy is the condition of having less than or more than the normal diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
Human Genetics - Cloudfront.net
... ○ Fetal cells, cells from bone marrow, skin, or blood are cultured and then treated with colchicine (arrests the cell in metaphase) ...
... ○ Fetal cells, cells from bone marrow, skin, or blood are cultured and then treated with colchicine (arrests the cell in metaphase) ...
Week 10 Pre-Lecture Slides
... • After this class, you should be able to: – Express antibiotics as a temporary and limited means of controlling rapidly evolving bacteria – Describe multiple differences between similar individuals in terms of their microbiota – Hypothesize causes or potential treatments for human diseases based on ...
... • After this class, you should be able to: – Express antibiotics as a temporary and limited means of controlling rapidly evolving bacteria – Describe multiple differences between similar individuals in terms of their microbiota – Hypothesize causes or potential treatments for human diseases based on ...
ppt
... individual (i.e., its genome – it’s full complement of genes and the two alleles that comprise each locus), or a subset of an individual’s genes ...
... individual (i.e., its genome – it’s full complement of genes and the two alleles that comprise each locus), or a subset of an individual’s genes ...
3 - Goshen Community Schools
... individual (i.e., its genome – it’s full complement of genes and the two alleles that comprise each locus), or a subset of an individual’s genes ...
... individual (i.e., its genome – it’s full complement of genes and the two alleles that comprise each locus), or a subset of an individual’s genes ...