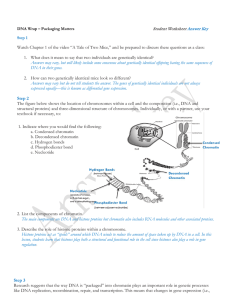
Answer Key
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
www.dps61.org
... of parent populations. • Can occur in a single generation. • In sympatric speciation, speciation takes place in geographically overlapping populations ...
... of parent populations. • Can occur in a single generation. • In sympatric speciation, speciation takes place in geographically overlapping populations ...
Mutations - The Super Heroes of Biology
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
Brainpop Genetics questions Weinmann ANSWERS
... 9. Curly hair is dominant, and straight hair is recessive. If a curly-hairs man has a baby with a straight-haired woman, what will happen? - C. the baby will PROBABLY have curly hair 10. Which of the following is completely determined by your genes? - B. your bone structure Where are the chromosomes ...
... 9. Curly hair is dominant, and straight hair is recessive. If a curly-hairs man has a baby with a straight-haired woman, what will happen? - C. the baby will PROBABLY have curly hair 10. Which of the following is completely determined by your genes? - B. your bone structure Where are the chromosomes ...
Human Genome Project
... • Many fewer genes than expected (half): – Only 35,000-45,000 genes vs. previously predicted 100,000. – Only twice the amount of a nematode or a fruit fly. – Does not correlate to twice as complex. – Alternative splicing: Invertebrate genes are more innovative in their assembly of genes. – Protein d ...
... • Many fewer genes than expected (half): – Only 35,000-45,000 genes vs. previously predicted 100,000. – Only twice the amount of a nematode or a fruit fly. – Does not correlate to twice as complex. – Alternative splicing: Invertebrate genes are more innovative in their assembly of genes. – Protein d ...
Chapter 11 - Jamestown Public Schools
... Genetic Engineering Basic Steps of Genetic Engineering continued •Cutting DNA and Making Recombinant DNA Restriction enzymes are used to generate sticky ends. Sticky ends allow DNA fragments from different organisms to join together to form recombinant DNA. •Cloning, Selecting, and Screening Cells R ...
... Genetic Engineering Basic Steps of Genetic Engineering continued •Cutting DNA and Making Recombinant DNA Restriction enzymes are used to generate sticky ends. Sticky ends allow DNA fragments from different organisms to join together to form recombinant DNA. •Cloning, Selecting, and Screening Cells R ...
Understanding Genetics
... threadlike structures in the nucleus or central portion, of each human cell ...
... threadlike structures in the nucleus or central portion, of each human cell ...
Lecture#3 Genes encode Proteins Readings: Problems: Concepts
... Note: the entire model was inferred from the properties of the mutants (phenotype) - later the presence of defective enzymes was demonstrated by independent biochemical analysis History - first insight into the function of genes and how they worked (remember it wasn't until 1944 that DNA was shown t ...
... Note: the entire model was inferred from the properties of the mutants (phenotype) - later the presence of defective enzymes was demonstrated by independent biochemical analysis History - first insight into the function of genes and how they worked (remember it wasn't until 1944 that DNA was shown t ...
Genetic Interactions and Linkage
... • A lot of plants (and a small number of animals) can tolerate having multiple copies of the chromosome set therefore are = 3n, 4n, 6n ...
... • A lot of plants (and a small number of animals) can tolerate having multiple copies of the chromosome set therefore are = 3n, 4n, 6n ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... a. process in which one strain of bacteria changes into another one b. process in which DNA makes a copy of itself c. protein that DNA wraps around in eukaryotic chromosomes d. virus that infects bacteria e. region of DNA that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make RNA f. a change in the genet ...
... a. process in which one strain of bacteria changes into another one b. process in which DNA makes a copy of itself c. protein that DNA wraps around in eukaryotic chromosomes d. virus that infects bacteria e. region of DNA that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make RNA f. a change in the genet ...
Mutation
... A mutation is a spontaneous change in the genetic material. Generally it occurs either when DNA is copied or when cells divide. Only if mutations happen in the germ cells (those that produce the gametes) can they be passed on to the next generation. If they happen in somatic or body cells, mutations ...
... A mutation is a spontaneous change in the genetic material. Generally it occurs either when DNA is copied or when cells divide. Only if mutations happen in the germ cells (those that produce the gametes) can they be passed on to the next generation. If they happen in somatic or body cells, mutations ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – Macroevolution
... 1. There are two types of evolution based on their scale of action. Microevolution refers to change in the genetic makeup of a population from generation to generation. It refers to adaptations that are confined to a single gene pool (within one species). Macroevolution refers to evolutionary change ...
... 1. There are two types of evolution based on their scale of action. Microevolution refers to change in the genetic makeup of a population from generation to generation. It refers to adaptations that are confined to a single gene pool (within one species). Macroevolution refers to evolutionary change ...
finding the gene to go into the plasmid
... Once we insert the plasmid into the bacteria how do we know its in the bacteria and has the the right gene in it? ...
... Once we insert the plasmid into the bacteria how do we know its in the bacteria and has the the right gene in it? ...
Hemochromatosis gene nomenclature
... One is that there is a strong HLA community who have strict criteria for accepting a “new” HLA gene and this gene does not satisfy these [WHO, 1976]. The other is that there was already an HLA-H pseudogene (Genbank ID: AF116214), which is well characterised [Geraghty et al., 1992] and only four mega ...
... One is that there is a strong HLA community who have strict criteria for accepting a “new” HLA gene and this gene does not satisfy these [WHO, 1976]. The other is that there was already an HLA-H pseudogene (Genbank ID: AF116214), which is well characterised [Geraghty et al., 1992] and only four mega ...
File
... mRNA copies the code from DNA in the nucleus mRNA carries the code out of the nucleus, through the cytoplasm to a ribosome ...
... mRNA copies the code from DNA in the nucleus mRNA carries the code out of the nucleus, through the cytoplasm to a ribosome ...
Introduction to Genomics, Bioinformatics - UNC
... • Retrieve/compare gene sequences • Predict function of unknown genes/proteins • Search for previously known functions of a gene ...
... • Retrieve/compare gene sequences • Predict function of unknown genes/proteins • Search for previously known functions of a gene ...
Heredity
... Recessive allele – a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring – an organism can carry the recessive trait and not show it is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present represented with a lowercase letter Hybrid Organism – has two different alleles ...
... Recessive allele – a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring – an organism can carry the recessive trait and not show it is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present represented with a lowercase letter Hybrid Organism – has two different alleles ...
Lab #8 Pop genetics
... 1 in 5 in Central Africans = HbHs unusual for allele with severe detrimental effects in homozygotes 1 in 100 = HsHs usually die before reproductive age Why is the Hs allele maintained at such high levels in African populations? ...
... 1 in 5 in Central Africans = HbHs unusual for allele with severe detrimental effects in homozygotes 1 in 100 = HsHs usually die before reproductive age Why is the Hs allele maintained at such high levels in African populations? ...
Presentation - Anil Jegga - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital Medical
... 1. Gene Ontology: GO and NCBI Entrez Gene 2. Mouse Phenotype: MGI (used for the first time for human disease gene prioritization) ...
... 1. Gene Ontology: GO and NCBI Entrez Gene 2. Mouse Phenotype: MGI (used for the first time for human disease gene prioritization) ...
Answer all the questions Time allowed : 49 minutes 1. State two
... Mutation may occur spontaneously, or be induced by chemicals (e.g. colchicines ), radiations (e.g. X-rays and UV) and biological factors (e.g. viruses).
Mutation may involve
change in the number of chromosomes, e.g. polyploidy
changes in chromosome structure,
changes in DNA structure
Sub-tot ...
... Mutation may occur spontaneously, or be induced by chemicals (e.g. colchicines ), radiations (e.g. X-rays and UV) and biological factors (e.g. viruses).
Lecture 13: May 24, 2004
... of the parents and offspring for the following families. When two alternative genotypes are possible, list both. (A) Two non albino (normal) parents have five children, four normal and one albino. (B) A normal male and an albino female have six ...
... of the parents and offspring for the following families. When two alternative genotypes are possible, list both. (A) Two non albino (normal) parents have five children, four normal and one albino. (B) A normal male and an albino female have six ...























