Chapter 10 Mendelian Genetics - An
... flowers and white flowers in a 3:1 ratio (Fig 14.3). Blending theory predicted that progeny should all be pale purple. Instead, F1 all had same traits as purple parent, and the white trait disappeared . o Purple is said to be DOMINANT o White is said to be RECESSIVE. Mendel observed same pattern of ...
... flowers and white flowers in a 3:1 ratio (Fig 14.3). Blending theory predicted that progeny should all be pale purple. Instead, F1 all had same traits as purple parent, and the white trait disappeared . o Purple is said to be DOMINANT o White is said to be RECESSIVE. Mendel observed same pattern of ...
biology 30•genetics worksheet 1
... Individuals afflicted with Down's syndrome typically have an extra chromosome 21, so their cells have a total of 47 chromosomes. However, in a few cases of Down's syndrome 46 chromosomes are present. Included in this total are two normal-appearing chromosomes 21, and a longer than normal chromosome ...
... Individuals afflicted with Down's syndrome typically have an extra chromosome 21, so their cells have a total of 47 chromosomes. However, in a few cases of Down's syndrome 46 chromosomes are present. Included in this total are two normal-appearing chromosomes 21, and a longer than normal chromosome ...
Bio 1 Unit Objectives Genetics
... 2. Describe the methods Mendel used in his plant-breeding experiments 3. Explain Mendel’s principle of segregation 4. Describe how probability applies to genetics 5. Contrast genotype and phenotype 6. Explain Mendel’s principle of independent assortment 7. Describe how alleles interact in intermedia ...
... 2. Describe the methods Mendel used in his plant-breeding experiments 3. Explain Mendel’s principle of segregation 4. Describe how probability applies to genetics 5. Contrast genotype and phenotype 6. Explain Mendel’s principle of independent assortment 7. Describe how alleles interact in intermedia ...
Cannus stannous: A Study of Evolution by Means of Natural Selection
... lively debate among biologists about the relative importance of natural selection in comparison with other mechanisms of evolutionary change. However, most biologists consider natural selection to be the primary mechanism of evolution. Darwin observed that no two individuals are identical, and that ...
... lively debate among biologists about the relative importance of natural selection in comparison with other mechanisms of evolutionary change. However, most biologists consider natural selection to be the primary mechanism of evolution. Darwin observed that no two individuals are identical, and that ...
Quiz 3 Thursday Answer Key
... EMS, you discover a worm on your plate which twists into right-handed helices when it moves. After isolating the gene, you sequence it to better characterize this mutation. You discover that a single-base pair change has led to an amino acid substitution of Tryptophan for Alanine (note that these tw ...
... EMS, you discover a worm on your plate which twists into right-handed helices when it moves. After isolating the gene, you sequence it to better characterize this mutation. You discover that a single-base pair change has led to an amino acid substitution of Tryptophan for Alanine (note that these tw ...
Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics
... Mendel studied seven different pea plants traits. A trait is a specific characteristic. Mendel studied crossed plants with each of the seven contrasting characters and studied their offspring. Mendel called each original pair of plants the P(parental) generation. He called the offspring the F ...
... Mendel studied seven different pea plants traits. A trait is a specific characteristic. Mendel studied crossed plants with each of the seven contrasting characters and studied their offspring. Mendel called each original pair of plants the P(parental) generation. He called the offspring the F ...
Document
... Genes that are adjacent and close to each other on the same chromosome tend to move as a unit; the probability that they will segregate as a unit is a function of the distance between them. ...
... Genes that are adjacent and close to each other on the same chromosome tend to move as a unit; the probability that they will segregate as a unit is a function of the distance between them. ...
Extending Mendel Student Notes
... length, and eye color are carried on the same chromosome. These genes are linked together on the same chromosome and will sort into the same gamete. ...
... length, and eye color are carried on the same chromosome. These genes are linked together on the same chromosome and will sort into the same gamete. ...
Press Release
... matched 699 normal individuals. They found that a 25 base pair deletion within the gene making the heart protein MYBPC was significantly more frequent in cardiac patients compared to the normal individuals. In addition, they found that if an individual had both copies of this gene defective (homozyg ...
... matched 699 normal individuals. They found that a 25 base pair deletion within the gene making the heart protein MYBPC was significantly more frequent in cardiac patients compared to the normal individuals. In addition, they found that if an individual had both copies of this gene defective (homozyg ...
Scotland - Ovarian Cancer Action
... My maternal/paternal (select one) father/brother /uncle/grandfather/ (select one) was diagnosed with/breast cancer aged (insert age). There is a possibility that they carried a BRCA1/2 gene mutation, and if they did, there is a strong possibility that the gene will have been passed onto me. While th ...
... My maternal/paternal (select one) father/brother /uncle/grandfather/ (select one) was diagnosed with/breast cancer aged (insert age). There is a possibility that they carried a BRCA1/2 gene mutation, and if they did, there is a strong possibility that the gene will have been passed onto me. While th ...
How Inheritance Works In Swine
... as black or red coat color) was determined by the order of nucleotides in a segment of the chromosome. This is the gene, the basic unit of inheritance. A chromosome, then, consists of many genes arranged end-to-end. Chromosomes occur in pairs in the nucleus, and each species of farm animals has its ...
... as black or red coat color) was determined by the order of nucleotides in a segment of the chromosome. This is the gene, the basic unit of inheritance. A chromosome, then, consists of many genes arranged end-to-end. Chromosomes occur in pairs in the nucleus, and each species of farm animals has its ...
Introduction Aim TE presence/absence variant discovery Abundant
... To identify TE presence/absence variants in a population of wild Arabidopsis accessions, and examine the effects of these TE variants upon genome and cellular function ...
... To identify TE presence/absence variants in a population of wild Arabidopsis accessions, and examine the effects of these TE variants upon genome and cellular function ...
Section 15.1 Summary – pages 393-403
... • Since Darwin’s time, scientists have learned a great deal about genes and modified Darwin’s ideas accordingly. • The principles of today’s modern theory of evolution are rooted in population genetics and other related fields of study and are expressed in genetic terms. ...
... • Since Darwin’s time, scientists have learned a great deal about genes and modified Darwin’s ideas accordingly. • The principles of today’s modern theory of evolution are rooted in population genetics and other related fields of study and are expressed in genetic terms. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. The 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA are good target sites for antisense oligonucleotides. 7. Diagnostic probes for pathogens are identified from a genomic library of that pathogen. 8. Trypsinization is used to cleave cell surface proteins from cells in culture. ...
... 6. The 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA are good target sites for antisense oligonucleotides. 7. Diagnostic probes for pathogens are identified from a genomic library of that pathogen. 8. Trypsinization is used to cleave cell surface proteins from cells in culture. ...
Monday, Oct - Fall Pima 100
... of you," says Wojcicki (pronounced Wo-jis-key), 35, who majored in biology and was previously a health-care investor. "It's all this information beyond what you can see in the mirror." We are at the beginning of a personal-genomics revolution that will transform not only how we take care of ourselve ...
... of you," says Wojcicki (pronounced Wo-jis-key), 35, who majored in biology and was previously a health-care investor. "It's all this information beyond what you can see in the mirror." We are at the beginning of a personal-genomics revolution that will transform not only how we take care of ourselve ...
Genetics Unit
... • 3) in the F1 generation, the tall factor was dominant (factor that is seen) • 4) In the F2 generation, the short factor or (t) produced 1 short plant So short is recessive (factor not seen) ...
... • 3) in the F1 generation, the tall factor was dominant (factor that is seen) • 4) In the F2 generation, the short factor or (t) produced 1 short plant So short is recessive (factor not seen) ...
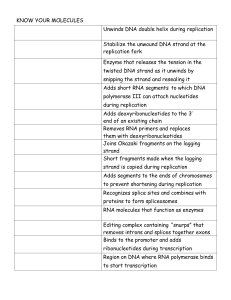
Know your molecules organizer
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
Lecture #5 PPT - College of Natural Resources
... how would you describe the pattern of spore dilution • How can you rapidly provide data to suggest an epidemic is caused by an infectious disease • What affects local adaptation between hosts and pathogens • Define “inoculum” • Describe the disease triangle, and provide a concrete example for signif ...
... how would you describe the pattern of spore dilution • How can you rapidly provide data to suggest an epidemic is caused by an infectious disease • What affects local adaptation between hosts and pathogens • Define “inoculum” • Describe the disease triangle, and provide a concrete example for signif ...
Change over Time
... a characteristic that helps an organism survive in its environment Two types of adaptations ...
... a characteristic that helps an organism survive in its environment Two types of adaptations ...
EDITORIAL Dissecting Complex Genetic Diseases: Promises and
... In contrast to the situation in single-gene defects, most susceptibility genes exert only a minor individual effect on the disease itself. Nevertheless, since multifactorial diseases are much more prevalent than single-gene diseases, the minor effects of susceptibility genes on common diseases are t ...
... In contrast to the situation in single-gene defects, most susceptibility genes exert only a minor individual effect on the disease itself. Nevertheless, since multifactorial diseases are much more prevalent than single-gene diseases, the minor effects of susceptibility genes on common diseases are t ...
Phenomena of Life and Death Based on Nonphysical Gene and
... that most of our common assumptions about genes are either too simplistic or simply incorrect. ...
... that most of our common assumptions about genes are either too simplistic or simply incorrect. ...
Inheritance of Sex and Sex-Linked or Influenced Traits
... Another form of epigenetics Gene from specific parent is silenced in each generation using attached methyl groups Methyl group are removed during meiosis and replaced once new embryo forms Most seem to control early ...
... Another form of epigenetics Gene from specific parent is silenced in each generation using attached methyl groups Methyl group are removed during meiosis and replaced once new embryo forms Most seem to control early ...
Chapter 3 Overview
... influence are also affected by environment. 2. Most environmental influences on children raised in the same home are not shared. 3. Addiction is a particularly clear example of gene–environment interaction. Some people inherit a biochemical predisposition toward alcoholism and drug addiction. Even s ...
... influence are also affected by environment. 2. Most environmental influences on children raised in the same home are not shared. 3. Addiction is a particularly clear example of gene–environment interaction. Some people inherit a biochemical predisposition toward alcoholism and drug addiction. Even s ...