Captive Breeding - International Crane Foundation
... genetic material comes from our mother and half from our father. ...
... genetic material comes from our mother and half from our father. ...
Mendel`s Contributions
... Mendel Grew Generations and Generations of Garden Peas to observe inherited characteristics. Mendel picked common garden pea plants because 1. they can be grown easily in large numbers and their reproduction can be manipulated. 2. Inexpensive and many generations can be grown in short period of tim ...
... Mendel Grew Generations and Generations of Garden Peas to observe inherited characteristics. Mendel picked common garden pea plants because 1. they can be grown easily in large numbers and their reproduction can be manipulated. 2. Inexpensive and many generations can be grown in short period of tim ...
Screening for Long QT
... Family History: Using the Risk Assessment Form from SADS (www.sads.org/Materials/assmform.pdf), a parent and the child’s physician can work together to determine the family risk of these conditions. This is extremely important and should include unexplained death during swimming, death during seizur ...
... Family History: Using the Risk Assessment Form from SADS (www.sads.org/Materials/assmform.pdf), a parent and the child’s physician can work together to determine the family risk of these conditions. This is extremely important and should include unexplained death during swimming, death during seizur ...
1. Traits are controlled by particles 2. Two genes per trait 3
... b. This allows us to examine multiple traits on a single (larger) Punnett Square. This is called a dihybrid cross and predicts 2 traits at once. c. Probability II “The chances of two separate events happening at the same time equals the product of their separate probabilities” ...
... b. This allows us to examine multiple traits on a single (larger) Punnett Square. This is called a dihybrid cross and predicts 2 traits at once. c. Probability II “The chances of two separate events happening at the same time equals the product of their separate probabilities” ...
Missing Heritability
... Rare mutations in some gene might have huge effect, but in gwas, averaging across hundreds of people could dilute its effect. Solution: Need to sequence candidate genes and their surrounding regions in thousands of people – costly. Ex.: Sequencing of gene ANGPTL4, related to cholesterol and triglyce ...
... Rare mutations in some gene might have huge effect, but in gwas, averaging across hundreds of people could dilute its effect. Solution: Need to sequence candidate genes and their surrounding regions in thousands of people – costly. Ex.: Sequencing of gene ANGPTL4, related to cholesterol and triglyce ...
MUTATIONS - Valhalla High School
... • May produce a new trait or may result in a protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
... • May produce a new trait or may result in a protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... (b+ linked to vg+) (b linked to vg) If unlinked: 1:1:1:1 ratio. If linked: ratio will be altered. ...
... (b+ linked to vg+) (b linked to vg) If unlinked: 1:1:1:1 ratio. If linked: ratio will be altered. ...
PHYSMendeliangenetics
... I. Linkage A. genes for two traits carried on the same chromosome B. example: Freckles and alleles for red hair II. Mutations A. random changes in the genetic code B. may produce “unexpected” offspring that Mendel couldn’t account for. C. Ex: achondroplastic kids (Dd) usually come from two perfectly ...
... I. Linkage A. genes for two traits carried on the same chromosome B. example: Freckles and alleles for red hair II. Mutations A. random changes in the genetic code B. may produce “unexpected” offspring that Mendel couldn’t account for. C. Ex: achondroplastic kids (Dd) usually come from two perfectly ...
Chapter 12
... generation plants selfpollinate and produce new plants. He called this new generation of offspring the second filial generation or F2 generation. Notice how many of each trait was produced— what’s the deal? ...
... generation plants selfpollinate and produce new plants. He called this new generation of offspring the second filial generation or F2 generation. Notice how many of each trait was produced— what’s the deal? ...
fish frequencies
... movement into and out of a population, no mutations, and no natural selection. In some populations, these conditions may be met or nearly met for long periods of time. If, however, the conditions are not met, the genetic equilibrium will be disrupted, and the population will change (i.e., evolve). I ...
... movement into and out of a population, no mutations, and no natural selection. In some populations, these conditions may be met or nearly met for long periods of time. If, however, the conditions are not met, the genetic equilibrium will be disrupted, and the population will change (i.e., evolve). I ...
Human Genetics - Green Local Schools
... Sex Linkage Problems!!!! Use these genotypic symbols for the sex linked trait of red-green color blindness in humans to solve the problems that follow. ...
... Sex Linkage Problems!!!! Use these genotypic symbols for the sex linked trait of red-green color blindness in humans to solve the problems that follow. ...
EEB-20
... increasing morbidity and mortality in populations, the inability to cope with novel and enduring parasites can precipitate population declines and extinction. Maintaining high levels of genetic diversity at immune genes (such as the major histocompatibility complex or MHC gene family) is one way to ...
... increasing morbidity and mortality in populations, the inability to cope with novel and enduring parasites can precipitate population declines and extinction. Maintaining high levels of genetic diversity at immune genes (such as the major histocompatibility complex or MHC gene family) is one way to ...
221_exam_3_2003
... _____ Based on what you have learned about the elements that control synthesis of the enzymes for tryptophan synthesis, what effect on enzyme activity would you expect under the following conditions: a mutation in the trpR gene, encoding TrpR the tryptophan repressor, such that TrpR can bind DNA wit ...
... _____ Based on what you have learned about the elements that control synthesis of the enzymes for tryptophan synthesis, what effect on enzyme activity would you expect under the following conditions: a mutation in the trpR gene, encoding TrpR the tryptophan repressor, such that TrpR can bind DNA wit ...
Test Corrections for Genetics Test B Test corrections are available to
... Test Corrections for Genetics Test B Test corrections are available to those that completed the study guide. Each question will receive ½ credit toward the test grade. Missed any of 1-3, 5 or 6. Use the information in the question to write a summary of the why Protein synthesis is called the central ...
... Test Corrections for Genetics Test B Test corrections are available to those that completed the study guide. Each question will receive ½ credit toward the test grade. Missed any of 1-3, 5 or 6. Use the information in the question to write a summary of the why Protein synthesis is called the central ...
CHAPTER 2 - MENDELIAN ANALYSIS I. MENDEL`S LIFE A. Born
... At first, the F2 ratios seemed really confusing; however, Mendel carefully analyzed each trait separately and found that color was 3:1 and shape was 3:1. This is the same phenotypic ratio Mendel saw for the monohybrid crosses! So Mendel proposed the his 2nd law or the Law of Independent Assortment: ...
... At first, the F2 ratios seemed really confusing; however, Mendel carefully analyzed each trait separately and found that color was 3:1 and shape was 3:1. This is the same phenotypic ratio Mendel saw for the monohybrid crosses! So Mendel proposed the his 2nd law or the Law of Independent Assortment: ...
Genetic Breast Cancer Testing Article
... BCRA1 mutation have a 55%-65% chance of developing breast cancer by the time they are 70 years old, and those with the BCRA2 mutation have a 45% chance. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes occur naturally in the human body, they are responsible for creating protein which helps repair DNA. However, when these ...
... BCRA1 mutation have a 55%-65% chance of developing breast cancer by the time they are 70 years old, and those with the BCRA2 mutation have a 45% chance. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes occur naturally in the human body, they are responsible for creating protein which helps repair DNA. However, when these ...
Document
... • Tay-Sachs Disease- is a disease that affects those who are mostly of Jewish decent. It affects children at an early age by preventing them from breaking down fat. As a result fat gathers in the child’s brain and causes death at an early age. ...
... • Tay-Sachs Disease- is a disease that affects those who are mostly of Jewish decent. It affects children at an early age by preventing them from breaking down fat. As a result fat gathers in the child’s brain and causes death at an early age. ...
CAPT Review Strand V Genetics Evolution Biodiversity revised
... chromosomes, 46 in a normal body cell Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on each of the homologous chromosomes in the cell nucleus. Crossing over: Chromosomes swap genetic material from one chromosome to another Random process: unique gametes with different combinations of chrom ...
... chromosomes, 46 in a normal body cell Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on each of the homologous chromosomes in the cell nucleus. Crossing over: Chromosomes swap genetic material from one chromosome to another Random process: unique gametes with different combinations of chrom ...
Science 9 - Unit A - Lesson 8
... in a way that a student in grade 4 could easily understand it. ...
... in a way that a student in grade 4 could easily understand it. ...
MetaQuant : a new platform dealing with DNA samples
... In contact with the 1st pool of immune cells and the 2nd pool of neural cells of the body ...
... In contact with the 1st pool of immune cells and the 2nd pool of neural cells of the body ...
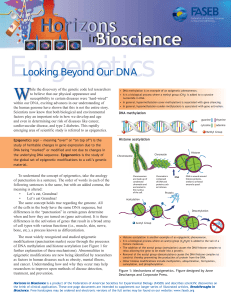
Looking Beyond Our DNA - Federation of American Societies for
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
Supplemental File S6. You and Your Oral Microflora
... 2. (1 point) One difference between replicating DNA by PCR and cellular DNA replication is a. PCR uses enzymes to separate DNA strands. b. PCR makes many copies of all the DNA in the test tube. c. PCR uses a polymerase to copy DNA d. PCR makes many copies of only a targeted portion of the DNA in the ...
... 2. (1 point) One difference between replicating DNA by PCR and cellular DNA replication is a. PCR uses enzymes to separate DNA strands. b. PCR makes many copies of all the DNA in the test tube. c. PCR uses a polymerase to copy DNA d. PCR makes many copies of only a targeted portion of the DNA in the ...
Molecular_genetics_revision_checklist
... promoter, operator, structural gene. The role of the inhibitor in blocking the pathway of RNA polymerase needs to be explained. In eukaryotes - control of metabolic pathways by gene expression includes enhancers and transcription factors. Students should understand the role of control elements, inc ...
... promoter, operator, structural gene. The role of the inhibitor in blocking the pathway of RNA polymerase needs to be explained. In eukaryotes - control of metabolic pathways by gene expression includes enhancers and transcription factors. Students should understand the role of control elements, inc ...