(Students with questions should see the appropriate Professor)
... 1) Using either G (Giemsa) or R (reverse) banding, the 23 pairs of human chromosomes can be identified in interphase cells obtained from normal human cells. 2) In human, only the trisomy of either human chromosome 13, 18 and 21 can produce viable individuals. 3) Endomitosis has never been detected i ...
... 1) Using either G (Giemsa) or R (reverse) banding, the 23 pairs of human chromosomes can be identified in interphase cells obtained from normal human cells. 2) In human, only the trisomy of either human chromosome 13, 18 and 21 can produce viable individuals. 3) Endomitosis has never been detected i ...
The Mechanism of X inactivation
... The Mechanism of X inactivation (formation of Barr bodies) • Randomly, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated by the DNA becoming highly compacted – Most genes on the inactivated X cannot be expressed • When this inactivated X is replicated during cell division – Both copies remain highly comp ...
... The Mechanism of X inactivation (formation of Barr bodies) • Randomly, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated by the DNA becoming highly compacted – Most genes on the inactivated X cannot be expressed • When this inactivated X is replicated during cell division – Both copies remain highly comp ...
(Students with questions should see the appropriate Professor)
... 1) Using either G (Giemsa) or R (reverse) banding, the 23 pairs of human chromosomes can be identified in interphase cells obtained from normal human cells. 2) In human, only the trisomy of either human chromosome 13, 18 and 21 can produce viable individuals. 3) Endomitosis has never been detected i ...
... 1) Using either G (Giemsa) or R (reverse) banding, the 23 pairs of human chromosomes can be identified in interphase cells obtained from normal human cells. 2) In human, only the trisomy of either human chromosome 13, 18 and 21 can produce viable individuals. 3) Endomitosis has never been detected i ...
CILJANA MUTAGENEZA I GENETSKI MARKERI U SELEKCIJI SVINJA
... percentage, and with the regression of basal-plasma-GH concentration on age and weight it was detected polymorphism as a double-strand conformation and was assumed to be caused by an adenine being swapped with a timine in the TATA box in the GH promotor, as a quantitative trait loci for growth rate ...
... percentage, and with the regression of basal-plasma-GH concentration on age and weight it was detected polymorphism as a double-strand conformation and was assumed to be caused by an adenine being swapped with a timine in the TATA box in the GH promotor, as a quantitative trait loci for growth rate ...
my talk - David Rasnick, PhD
... Equation (solid line) fitted to data from Armitage & Doll (1954) Br J Cancer 8:1-12. Broken lines are for best-fit 7-gene mutation model. ...
... Equation (solid line) fitted to data from Armitage & Doll (1954) Br J Cancer 8:1-12. Broken lines are for best-fit 7-gene mutation model. ...
Genetic Disorders
... Genetics Disorders • Many disorders in humans are genetic in origin and follow Mendel’s laws of inheritance. • These genetic disorders are often controlled by a single pair of alleles. ...
... Genetics Disorders • Many disorders in humans are genetic in origin and follow Mendel’s laws of inheritance. • These genetic disorders are often controlled by a single pair of alleles. ...
Mendel and Heredity
... What does segregation imply? This happens with your chromosomes We have 2 copies for each chromosome but can only give 1 copy to the gametes So the 2 copies you have separate or segregate when they move to the gametes ...
... What does segregation imply? This happens with your chromosomes We have 2 copies for each chromosome but can only give 1 copy to the gametes So the 2 copies you have separate or segregate when they move to the gametes ...
Chapter 9: Patterns of Inheritance
... Variations on Mendel’s Laws A) Describe the inheritance patterns of incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, codominance, pleiotropy, and polygenic inheritance. Provide an example of each. B) Explain how the sickle-cell allele can be adaptive. C) Explain why human skin coloration is not sufficiently ...
... Variations on Mendel’s Laws A) Describe the inheritance patterns of incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, codominance, pleiotropy, and polygenic inheritance. Provide an example of each. B) Explain how the sickle-cell allele can be adaptive. C) Explain why human skin coloration is not sufficiently ...
Advanced Molecular and Cell Biology (Dorn, Holton)
... In this half of the semester we will begin by reviewing DNA and chromosomal structure before moving on to the mechanisms cells use to regulate gene expression. This topic of regulating gene expression is perhaps the most rapidly advancing and fascinating fields of genetics research today. In large ...
... In this half of the semester we will begin by reviewing DNA and chromosomal structure before moving on to the mechanisms cells use to regulate gene expression. This topic of regulating gene expression is perhaps the most rapidly advancing and fascinating fields of genetics research today. In large ...
Human Inheritance
... 1. Nondisjunction - Abnormal numbers of chromosomes in _gametes___________ result in genetic disorders called _number disorders___________. This most often is a result of _nondisjunction________, which means _”not coming apart”_____. Nondisjunction may occur in: ...
... 1. Nondisjunction - Abnormal numbers of chromosomes in _gametes___________ result in genetic disorders called _number disorders___________. This most often is a result of _nondisjunction________, which means _”not coming apart”_____. Nondisjunction may occur in: ...
Name - Animo Venice Biology
... • Natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in any of three ways: ___________________ ...
... • Natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in any of three ways: ___________________ ...
Unit 7: Genetics
... 1. Be able to define and utilize the following key terms of genetics: a. gene: a section of DNA that carries a trait. b. allele: a form of a gene c. dominant: a trait that when present will be expressed (seen). d. recessive: a trait that will only be seen when it is the only one present. e. genotype ...
... 1. Be able to define and utilize the following key terms of genetics: a. gene: a section of DNA that carries a trait. b. allele: a form of a gene c. dominant: a trait that when present will be expressed (seen). d. recessive: a trait that will only be seen when it is the only one present. e. genotype ...
Let`s talk about sex... chromosomes Examples of well known human
... It involves the production of noncoding RNAs from a region on the X chromosome called the Xic (X inactivation center) Both X chromosomes initially produce both Xist and Tsix, but eventually a “choice” is made (it’s not clear what breaks the symmetry between the two Xs). After this tipping point, onl ...
... It involves the production of noncoding RNAs from a region on the X chromosome called the Xic (X inactivation center) Both X chromosomes initially produce both Xist and Tsix, but eventually a “choice” is made (it’s not clear what breaks the symmetry between the two Xs). After this tipping point, onl ...
Sex chromosomes, dosage compensation, and aneuploidy
... In future lectures, we will discuss how mosaicism can be a useful experimental tool in fruit flies and worms, and how also how it can be an indicator of elevated rates of chromosome loss in yeast. A much rarer kind of mosaicism, chimerism results from the fusion of two fertilized eggs very early in ...
... In future lectures, we will discuss how mosaicism can be a useful experimental tool in fruit flies and worms, and how also how it can be an indicator of elevated rates of chromosome loss in yeast. A much rarer kind of mosaicism, chimerism results from the fusion of two fertilized eggs very early in ...
BIOL 321 Lecture 7_pwpt
... (genes do not function: they have mutations) and phenotypically white 3. The L3 cells are genetically and phenotypically green (green genes are functional) ...
... (genes do not function: they have mutations) and phenotypically white 3. The L3 cells are genetically and phenotypically green (green genes are functional) ...
Polyploid Speciation
... What is the frequency of auto- vs allopolyploid speciation? Hard to assess - autopolyploids often cryptic and undescribed - 8 – 9 % of plant species contain multiple cytotypes Bioinformatic analysis suggests 86% of polyploids are allopolyploids ...
... What is the frequency of auto- vs allopolyploid speciation? Hard to assess - autopolyploids often cryptic and undescribed - 8 – 9 % of plant species contain multiple cytotypes Bioinformatic analysis suggests 86% of polyploids are allopolyploids ...
embryonic stem cells
... As shown on the following page, let’s say the sequence GGATCC happens to be found near the beginning and end on the insulin gene in human cells; and it’s also found in a particular bacteria cell’s DNA. If you add the restriction enzyme that cuts at GGATCC to test tubes with human and bacterial chrom ...
... As shown on the following page, let’s say the sequence GGATCC happens to be found near the beginning and end on the insulin gene in human cells; and it’s also found in a particular bacteria cell’s DNA. If you add the restriction enzyme that cuts at GGATCC to test tubes with human and bacterial chrom ...
Document
... GENE = unit of inheritance encodes one protein (structural gene) or tRNA and rRNA Allele = concrete form of gene How many alleles can have gene? Locus (plural loci) = fixed position of gene on chromosome GENOTYPE - the genetic (allelic) constitution of organism with respect to trait Homozygous - ...
... GENE = unit of inheritance encodes one protein (structural gene) or tRNA and rRNA Allele = concrete form of gene How many alleles can have gene? Locus (plural loci) = fixed position of gene on chromosome GENOTYPE - the genetic (allelic) constitution of organism with respect to trait Homozygous - ...
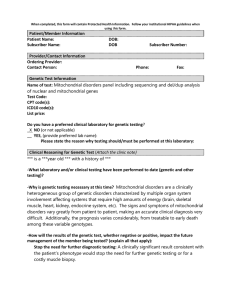
When completed, this form will contain Protected Health Information
... indicate which clinical features increase the probability that this test will provide a diagnosis. Our patient’s clinical features are highly suspicious of a mitochondrial disorder including ***. The likelihood this test will be positive is unknown. -If this is a request is for a gene panel, then pl ...
... indicate which clinical features increase the probability that this test will provide a diagnosis. Our patient’s clinical features are highly suspicious of a mitochondrial disorder including ***. The likelihood this test will be positive is unknown. -If this is a request is for a gene panel, then pl ...
MUTATIONS - MsWalshMosher
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
CHAPTER 16 Advanced Gene Mapping in Eukaryotes
... Caused by Mitotic Recombination 1. Retinoblastoma is the most common childhood eye cancer, occurring from birth to 4 years of age. Two types are known: a. The sporadic (nonhereditary) form occurs in an individual with no family history of the disease, and affects only one eye (unilateral). b. The he ...
... Caused by Mitotic Recombination 1. Retinoblastoma is the most common childhood eye cancer, occurring from birth to 4 years of age. Two types are known: a. The sporadic (nonhereditary) form occurs in an individual with no family history of the disease, and affects only one eye (unilateral). b. The he ...