Quick Vocabulary Lesson 1 Lesson 2 dominant trait
... the offspring’s phenotype is a blend of the parents’ phenotypes ...
... the offspring’s phenotype is a blend of the parents’ phenotypes ...
Heredity (1)
... • During meiosis, the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to 4 different cells. The resulting sex cells have only half as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. ...
... • During meiosis, the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to 4 different cells. The resulting sex cells have only half as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. ...
21.1 Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Are Eukaryotic
... a. They have genes with many introns. b. They contain more genes than derived genomes ...
... a. They have genes with many introns. b. They contain more genes than derived genomes ...
Document
... (Evolutions “dead-mans” switch) • Mobile genetic elements = Transposons • Present in all organisms (yes - even Humans!!) ...
... (Evolutions “dead-mans” switch) • Mobile genetic elements = Transposons • Present in all organisms (yes - even Humans!!) ...
Pre-AP Biology 2009
... 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an exon and an intron? 8. What is the purpose of transcription? What is the role of RNA in this process? ...
... 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an exon and an intron? 8. What is the purpose of transcription? What is the role of RNA in this process? ...
Learning objectives: • Define the terms `Gene` and `Chromosome
... What is a Chromosome? ! ! All our genetic information is held within the DNA. ! Genes are sections of DNA that code for specific ...
... What is a Chromosome? ! ! All our genetic information is held within the DNA. ! Genes are sections of DNA that code for specific ...
Autosomal & Chromosomal Disorders
... Autosomal Disorders Autosomal disorders involve dominant, recessive, or other types of traits that can produce multiple abnormalities. These traits are found on chromosomes 1-22. Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell, and Huntington’s disease are just a few examples of autosomal disorders. ...
... Autosomal Disorders Autosomal disorders involve dominant, recessive, or other types of traits that can produce multiple abnormalities. These traits are found on chromosomes 1-22. Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell, and Huntington’s disease are just a few examples of autosomal disorders. ...
Dear-Family-Member-HBOC
... recommend that my children, siblings, and aunts, uncles and cousins on my (mother/father) side of the family consider the following information. Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome is an inherited condition meaning that it is passed down from one generation to the next. Lynch syndrome is k ...
... recommend that my children, siblings, and aunts, uncles and cousins on my (mother/father) side of the family consider the following information. Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome is an inherited condition meaning that it is passed down from one generation to the next. Lynch syndrome is k ...
Mutations and other genetic problems
... Cystic fibrosis—excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver; increased susceptibility to infections; often die young ...
... Cystic fibrosis—excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver; increased susceptibility to infections; often die young ...
5.2 Human Genetic Disorders File
... chromosomal mutations POINT > Describe examples of genetic diseases caused by single gene mutations POINT > Identify human diseases caused by chromosomal mutations POINT > Explain Pedigree analysis ...
... chromosomal mutations POINT > Describe examples of genetic diseases caused by single gene mutations POINT > Identify human diseases caused by chromosomal mutations POINT > Explain Pedigree analysis ...
Mutations and other genetic problems
... Cystic fibrosis—excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver; increased susceptibility to infections; often die young ...
... Cystic fibrosis—excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver; increased susceptibility to infections; often die young ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...
Unit 7 Review – DNA Replication, Gene Expression, and Gene
... sure you describe the actors involved in the process (e.g. donor gene, chromosome, vector, restriction enzyme, DNA ligase, target organism, cloning, etc.) ...
... sure you describe the actors involved in the process (e.g. donor gene, chromosome, vector, restriction enzyme, DNA ligase, target organism, cloning, etc.) ...
Document
... S1.Zickler was the first person to demonstrate gene conversion by observing unusual ratios in Neurospora octads. At first, it was difficult for geneticists to believe these results because they seemed to contradict the Mendelian concept that alleles do not physically interact with each other. Howeve ...
... S1.Zickler was the first person to demonstrate gene conversion by observing unusual ratios in Neurospora octads. At first, it was difficult for geneticists to believe these results because they seemed to contradict the Mendelian concept that alleles do not physically interact with each other. Howeve ...
same genes, different fates final evaluation assignment
... You have been hired as a science writer for the Discovery Channel. The company is introducing a new line of children’s educational products in different areas of biology. Your job is to create a product that will teach children (about 10 years of age) about stem cells and differential gene expressio ...
... You have been hired as a science writer for the Discovery Channel. The company is introducing a new line of children’s educational products in different areas of biology. Your job is to create a product that will teach children (about 10 years of age) about stem cells and differential gene expressio ...
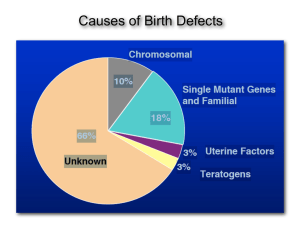
Causes of Birth Defects
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
GeneticsJeopardy-1415
... An autosomal genetic disorder (caused by a mutation on pair #7) that causes a protein malformation. This results in thick mucus in the lining of the lungs and intestines and frequent (and resistant) bacterial infections. ...
... An autosomal genetic disorder (caused by a mutation on pair #7) that causes a protein malformation. This results in thick mucus in the lining of the lungs and intestines and frequent (and resistant) bacterial infections. ...
Case Study 3: Hutchinson-Gilford’s Progeria Syndrome
... What mechanisms control the proliferation of cells? What governs the life span of an organism? Cell death as a necessary and important part of development: Apoptosis (programmed cell death, pcd) ...
... What mechanisms control the proliferation of cells? What governs the life span of an organism? Cell death as a necessary and important part of development: Apoptosis (programmed cell death, pcd) ...
Autosomal & Chromosomal Disorders
... Autosomal Disorders Autosomal disorders involve dominant, recessive, or other types of traits that can produce multiple abnormalities. These traits are found on chromosomes 1-22. Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell, and Huntington’s disease are just a few examples of autosomal disorders. ...
... Autosomal Disorders Autosomal disorders involve dominant, recessive, or other types of traits that can produce multiple abnormalities. These traits are found on chromosomes 1-22. Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell, and Huntington’s disease are just a few examples of autosomal disorders. ...
GENETICS & HEREDITY
... Patterning can occur in identical twins. This is where some body details are on the right side of one twin may be on the left side of the other twin. ...
... Patterning can occur in identical twins. This is where some body details are on the right side of one twin may be on the left side of the other twin. ...
Chapter 15 Study Questions
... *condensed, inactive “X” (sex) chromosome (most genes are not expressed); condenses during embryonic development How many Barr bodies are there in each female somatic cell? ...
... *condensed, inactive “X” (sex) chromosome (most genes are not expressed); condenses during embryonic development How many Barr bodies are there in each female somatic cell? ...
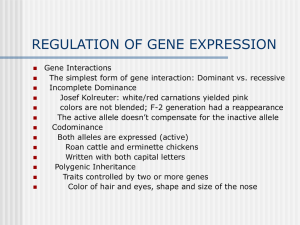
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
Document
... 10. If you see a white cat with orange and black spots, is it most likely a male or a female? Female. In cells in some parts of the body one X chromosome that has allele for orange spots is switched off, whereas in other parts of the body, the other X chromosome with the allele for black spots is s ...
... 10. If you see a white cat with orange and black spots, is it most likely a male or a female? Female. In cells in some parts of the body one X chromosome that has allele for orange spots is switched off, whereas in other parts of the body, the other X chromosome with the allele for black spots is s ...