Chapter 6 Review Terms: Somatic Cell, Game - District 196 e
... 4. In pea plants, the allele for tall stems, T, is dominant to the allele for short stems, t. Draw and fill in a Punnett square that shows the cross of a heterozygous plant, Tt, with a ho ...
... 4. In pea plants, the allele for tall stems, T, is dominant to the allele for short stems, t. Draw and fill in a Punnett square that shows the cross of a heterozygous plant, Tt, with a ho ...
Review Sheet for Test #1
... have _____ in each body cell. There is a tongue fern that has _________ in each body cell! The number of chromosomes that an organism has is NOT related to the ______________ of the organism! In body cells, chromosomes come in _____________. _____________________________ are the pair of chromosomes ...
... have _____ in each body cell. There is a tongue fern that has _________ in each body cell! The number of chromosomes that an organism has is NOT related to the ______________ of the organism! In body cells, chromosomes come in _____________. _____________________________ are the pair of chromosomes ...
Name - gst boces
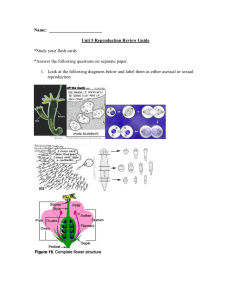
... Unit 5 Reproduction Review Guide *Study your flash cards *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
... Unit 5 Reproduction Review Guide *Study your flash cards *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
Meiosis Review Worksheet
... 18. How are DNA and chromosomes related? Chromosomes are made of DNA 19. What is the difference between a haploid, diploid, and zygote? Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes, diploid has 2 sets of chromosomes and a zygote is formed when an egg and sperm cell combine 20. Give 3 examples how meios ...
... 18. How are DNA and chromosomes related? Chromosomes are made of DNA 19. What is the difference between a haploid, diploid, and zygote? Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes, diploid has 2 sets of chromosomes and a zygote is formed when an egg and sperm cell combine 20. Give 3 examples how meios ...
Chapter 4 Cell Division - Heritage Christian School
... The mechanism: 1. Interphase – a period between cell divisions characterized by increase in size and accumulation of raw materials needed for the division process 2. Prophase – threadlike chromosomes (chromatin) shorten and thicken; centrioles separate and move to opposite ends of the cell; nuclear ...
... The mechanism: 1. Interphase – a period between cell divisions characterized by increase in size and accumulation of raw materials needed for the division process 2. Prophase – threadlike chromosomes (chromatin) shorten and thicken; centrioles separate and move to opposite ends of the cell; nuclear ...
Meiosis 1 - Learning on the Loop
... • Mitosis – produces 2 daughter cells – daughters are clones of the parent – daughter cells are diploid ...
... • Mitosis – produces 2 daughter cells – daughters are clones of the parent – daughter cells are diploid ...
Picture of man woman
... transmitted from the parents to the offspring (in your case, boy or girl) during reproduction. For example, you may inherit blonde hair from your mom or green eyes from your grand-mother or diabetes from your father, etc. Cells: a living being’s body is made of billions of cells of all types, nerve ...
... transmitted from the parents to the offspring (in your case, boy or girl) during reproduction. For example, you may inherit blonde hair from your mom or green eyes from your grand-mother or diabetes from your father, etc. Cells: a living being’s body is made of billions of cells of all types, nerve ...
Plant Life Cycles w.answers
... cycles of a) vertebrates (you - as a reference), b) early land plants (e.g. mosses as an example of a phylum with easily distinguishable alternating generations), and c) seed plants). The main goal of this excercise is for you to learn and understand what the term “alternation of generations” means, ...
... cycles of a) vertebrates (you - as a reference), b) early land plants (e.g. mosses as an example of a phylum with easily distinguishable alternating generations), and c) seed plants). The main goal of this excercise is for you to learn and understand what the term “alternation of generations” means, ...
CH 11 Review
... segregate independently during the formation of gametes. 17. Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called incomplete dominance. 18. Codominance occurs when phenotypes produced by both alleles are clearly expressed. 19. Genes that exist in several different forms are c ...
... segregate independently during the formation of gametes. 17. Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called incomplete dominance. 18. Codominance occurs when phenotypes produced by both alleles are clearly expressed. 19. Genes that exist in several different forms are c ...
Chromosome Number Mutations
... Mutation / accident during cell division Homologous chromosomes fail to separate in meiosis I Sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis II or mitosis Results in extra or missing chromosomes ...
... Mutation / accident during cell division Homologous chromosomes fail to separate in meiosis I Sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis II or mitosis Results in extra or missing chromosomes ...
Mitosis/Meiosis Modeling Lab Analysis Questions – Answer Key
... How does Independent Assortment relate to meiosis? When the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate during Meiosis I, they do so independently of other pairs. How can you calculate the possible number of different kinds of gametes? Because of independent assortment, the number ...
... How does Independent Assortment relate to meiosis? When the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate during Meiosis I, they do so independently of other pairs. How can you calculate the possible number of different kinds of gametes? Because of independent assortment, the number ...
Cloze passage 3
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
Meiosis ppt
... each pair in a diploid cell • each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex parent ...
... each pair in a diploid cell • each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex parent ...
Biology Study Guide/Test Review CH 11
... The # of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol ___________. The # of chromsomes in a body cell is represented by the symbol __________. Define gamete. Define allele. Gametes have _______________ allele for each gene. Define CROSSING OVER and be sure you understand the diagram of cross ...
... The # of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol ___________. The # of chromsomes in a body cell is represented by the symbol __________. Define gamete. Define allele. Gametes have _______________ allele for each gene. Define CROSSING OVER and be sure you understand the diagram of cross ...
Document
... examined). A greater number of irregular c o n f i g u r a t i o n s was observed during the meiotic division, analyzed during microsporogenosis. Polyvalents, multivalent chromosome associations, chromosome bridges, metaphase II with an unequal number of chromosomes in the equatorial plates, chromos ...
... examined). A greater number of irregular c o n f i g u r a t i o n s was observed during the meiotic division, analyzed during microsporogenosis. Polyvalents, multivalent chromosome associations, chromosome bridges, metaphase II with an unequal number of chromosomes in the equatorial plates, chromos ...
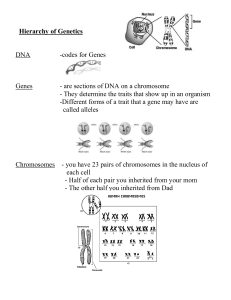
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
******ANSWER KEY*****SI Worksheet #14 (Chapter 13) BY 123
... independently of the other pairs at metaphase I, the first meiotic division results in each pair sorting its maternal and paternal homologs into daughter cells independently of every other pair….. 2n possibilities 2) Crossing Over: production of recombinant chromosomes in prophase I of meiosis 3) Ra ...
... independently of the other pairs at metaphase I, the first meiotic division results in each pair sorting its maternal and paternal homologs into daughter cells independently of every other pair….. 2n possibilities 2) Crossing Over: production of recombinant chromosomes in prophase I of meiosis 3) Ra ...
chapter 6 vocabulary card sort
... chromosome piece reattaches to the original chromosome but in a reverse ...
... chromosome piece reattaches to the original chromosome but in a reverse ...
Meiosis Student Notes • Organisms have tens of thousands of
... _____________________ – A different type of cell division where gametes have half the number of chromosomes as the parents. ...
... _____________________ – A different type of cell division where gametes have half the number of chromosomes as the parents. ...
Ploidy
Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell. Usually a gamete (sperm or egg, which fuse into a single cell during the fertilization phase of sexual reproduction) carries a full set of chromosomes that includes a single copy of each chromosome, as aneuploidy generally leads to severe genetic disease in the offspring. The gametic or haploid number (n) is the number of chromosomes in a gamete. Two gametes form a diploid zygote with twice this number (2n, the zygotic or diploid number) i.e. two copies of autosomal chromosomes. For humans, a diploid species, n = 23. A typical human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes: 2 complete haploid sets, which make up 23 homologous chromosome pairs.Because chromosome number is generally reduced only by the specialized process of meiosis, the somatic cells of the body inherit and maintain the chromosome number of the zygote. However, in many situations somatic cells double their copy number by means of endoreduplication as an aspect of cellular differentiation. For example, the hearts of two-year-old children contain 85% diploid and 15% tetraploid nuclei, but by 12 years of age the proportions become approximately equal, and adults examined contained 27% diploid, 71% tetraploid and 2% octaploid nuclei.Cells are described according to the number of sets present (the ploidy level): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is frequently used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes (triploid or higher ploidy).