GENETICS 603 EXAM III Dec. 5, 2002 NAME 5 6 7 8 1 2 4 3 I Gene
... F) One baby in 10,000 in the US is born with PKU, which until very recently was a recessive lethal condition. Does it seem likely that the population is in equilibrium with mutation balanced by selection? (Explain) This would mean a mutation rate of 1 in 10,000 which seems a bit high; there may have ...
... F) One baby in 10,000 in the US is born with PKU, which until very recently was a recessive lethal condition. Does it seem likely that the population is in equilibrium with mutation balanced by selection? (Explain) This would mean a mutation rate of 1 in 10,000 which seems a bit high; there may have ...
Homologous Chromosomes
... portions of their chromatids; result, new combo of alleles, this is a major source of _____________ w/in a species (genetic recombination) ...
... portions of their chromatids; result, new combo of alleles, this is a major source of _____________ w/in a species (genetic recombination) ...
Mitosis and Cell Division
... • Allele: A version (or flavor) of a gene; two alleles of the same gene my differ by a nucleotide or dozens of them--generally a small number • Dominant/recessive: Two alleles enter; one allele leaves (which version manifests in the organism) NOT which version is more common! • Mitosis vs Cell Divis ...
... • Allele: A version (or flavor) of a gene; two alleles of the same gene my differ by a nucleotide or dozens of them--generally a small number • Dominant/recessive: Two alleles enter; one allele leaves (which version manifests in the organism) NOT which version is more common! • Mitosis vs Cell Divis ...
Chapter 13 Presentation-Meiosis and Chromosomes
... E. coli cells. Next he gently lysed the cells and placed them onto an EM grid and exposed them to X-ray film for varying lengths of time. This showed the circular nature of the bacterial chromosomes he was working ...
... E. coli cells. Next he gently lysed the cells and placed them onto an EM grid and exposed them to X-ray film for varying lengths of time. This showed the circular nature of the bacterial chromosomes he was working ...
Modes of Inheritance
... genetic basis (carried by genes on chromosomes) • Genetic Disorders are classified in 4 categories ...
... genetic basis (carried by genes on chromosomes) • Genetic Disorders are classified in 4 categories ...
Complex Patterns of inheritance
... 3. Predict the possible offspring of a colorblind male and a normal female. 4. Predict the possible offspring of a mom with blood type IAi and a dad with Ibi. 5. What is a possible explanation for a ...
... 3. Predict the possible offspring of a colorblind male and a normal female. 4. Predict the possible offspring of a mom with blood type IAi and a dad with Ibi. 5. What is a possible explanation for a ...
Unit IIA Practice Exam (KEY) Unit_IIA_Exam_2.0_Key
... 21. Segregation of alleles does NOT occur in which of the following groups of organisms? (1994-14) a. Flowering plants b. Insects c. Flatworms d. Bacteria e. Ferns 22. In garden peas, a single gene controls stem length. The recessive allele (t) produces short stems when homozygous. The dominant alle ...
... 21. Segregation of alleles does NOT occur in which of the following groups of organisms? (1994-14) a. Flowering plants b. Insects c. Flatworms d. Bacteria e. Ferns 22. In garden peas, a single gene controls stem length. The recessive allele (t) produces short stems when homozygous. The dominant alle ...
Concepts in Biology, First Edition Sylvia Mader
... Some genetic disorders are medical conditions inherited from parents Some may be due to the inheritance of abnormal alleles on autosomal chromosomes - all the chromosomes except the sex chromosomes Carriers - those individuals that carry the abnormal allele but do not express it ...
... Some genetic disorders are medical conditions inherited from parents Some may be due to the inheritance of abnormal alleles on autosomal chromosomes - all the chromosomes except the sex chromosomes Carriers - those individuals that carry the abnormal allele but do not express it ...
Mysterious Meiosis
... Diploid: A cell with a _________ set of chromosomes (23 pairs = 46 chromosomes) Homologous Pairs: A pair of chromosomes that have the same ___________, but may have different forms of the genes (1 from _____ and one from __________) Sex Chromosomes: A special pair of chromosomes that make us girl o ...
... Diploid: A cell with a _________ set of chromosomes (23 pairs = 46 chromosomes) Homologous Pairs: A pair of chromosomes that have the same ___________, but may have different forms of the genes (1 from _____ and one from __________) Sex Chromosomes: A special pair of chromosomes that make us girl o ...
Family pedigree - people.stfx.ca
... from maternal ovum • 1 out of each pair comes from paternal sperm • 22 are matched pairs • x and y are sex chromosomes • males have 1 x and 1 y • females have 2 x’s 300/330 - appleby ...
... from maternal ovum • 1 out of each pair comes from paternal sperm • 22 are matched pairs • x and y are sex chromosomes • males have 1 x and 1 y • females have 2 x’s 300/330 - appleby ...
Genetic Mutation
... • In humans, it can be a different set of circumstances… Here’s an example: • Sickle-Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder in which there is a defect in the structure of red blood cells. This leads to fatigue and anemia when not treated. • However, it has been found that people who are carriers for Sick ...
... • In humans, it can be a different set of circumstances… Here’s an example: • Sickle-Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder in which there is a defect in the structure of red blood cells. This leads to fatigue and anemia when not treated. • However, it has been found that people who are carriers for Sick ...
No Slide Title
... Recessive Alleles -Many disorders are causes by recessive alleles and do not turn up in the population regularly due to this. The protein the gene codes for is not made in the homozygous recessive form. See examples below. PKU (Phenylketonuria) can cause mental retardation due to lack of enzyme phen ...
... Recessive Alleles -Many disorders are causes by recessive alleles and do not turn up in the population regularly due to this. The protein the gene codes for is not made in the homozygous recessive form. See examples below. PKU (Phenylketonuria) can cause mental retardation due to lack of enzyme phen ...
Chapter 11 Notes: Mendelian Genetics
... Sex Linked traits: traits that are determined by alleles that are _____________________________. a. The Y chromosome is shorter and does not _______________________ b. Females are XX and males are XY. c. ...
... Sex Linked traits: traits that are determined by alleles that are _____________________________. a. The Y chromosome is shorter and does not _______________________ b. Females are XX and males are XY. c. ...
Meiosis Review - Northern Highlands
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
Blood Type and Sex Linked Inheritance
... X (not Y) chromosome (“X-linked”) Males are affected or not, no heterozygotes… WHY, do you think? ...
... X (not Y) chromosome (“X-linked”) Males are affected or not, no heterozygotes… WHY, do you think? ...
Study Guide for Test on Chapter 11 and 14-1, 14-2
... o Describe what happens during each phase of meiosis I and meiosis II Focus on what happens to the chromosomes Know when tetrad formation and crossing-over occurs o Distinguish among the type and number of gametes formed in males vs. in females Know how many sperm, eggs, and polar bodies are f ...
... o Describe what happens during each phase of meiosis I and meiosis II Focus on what happens to the chromosomes Know when tetrad formation and crossing-over occurs o Distinguish among the type and number of gametes formed in males vs. in females Know how many sperm, eggs, and polar bodies are f ...
Biology Chapter 14 TEST (2010)
... a. only two gametes may form instead of four. b. some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes. c. the chromatids do not separate. d. it occurs during prophase. ____ 36. Nondisjunction can involve a. autosomes. b. sex chromosomes. c. homologous chromosomes. d. all of the above ____ 37. Scientist ...
... a. only two gametes may form instead of four. b. some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes. c. the chromatids do not separate. d. it occurs during prophase. ____ 36. Nondisjunction can involve a. autosomes. b. sex chromosomes. c. homologous chromosomes. d. all of the above ____ 37. Scientist ...
Mendel`s experiments: Mendel`s conclusions
... set). When the division does not occur properly, an egg (or sperm) may have both members of the chromosome resulting in trisomy! ...
... set). When the division does not occur properly, an egg (or sperm) may have both members of the chromosome resulting in trisomy! ...
Laws of Heredity -Single Gene Disorders
... set). When the division does not occur properly, an egg (or sperm) may have both members of the chromosome resulting in trisomy! ...
... set). When the division does not occur properly, an egg (or sperm) may have both members of the chromosome resulting in trisomy! ...
Mutations PP
... can examine chromosomes of human cells under the microscope to see if there are any abnormalities. They photograph them and cut out individual chromosomes from the picture and arrange them in homologous pairs. This type of arrangement of chromosomes is called a karyotype. ...
... can examine chromosomes of human cells under the microscope to see if there are any abnormalities. They photograph them and cut out individual chromosomes from the picture and arrange them in homologous pairs. This type of arrangement of chromosomes is called a karyotype. ...
Term Definition Heredity Passing of traits from parent to offspring
... Characteristics passed on to offspring through genes Organism that always produces offspring with same form of trait as parent Segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait ...
... Characteristics passed on to offspring through genes Organism that always produces offspring with same form of trait as parent Segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait ...
What is Cytogenetics?
... • Routine chromosome analysis refers to analysis of chromosomes which have been banded using trypsin (a serine proteases) followed by Giemsa, Leishmanns, or a mixture of the two. • This creates a unique banding pattern on the chromosomes. • Generally 20 cells are analyzed to rule out chromosome abno ...
... • Routine chromosome analysis refers to analysis of chromosomes which have been banded using trypsin (a serine proteases) followed by Giemsa, Leishmanns, or a mixture of the two. • This creates a unique banding pattern on the chromosomes. • Generally 20 cells are analyzed to rule out chromosome abno ...
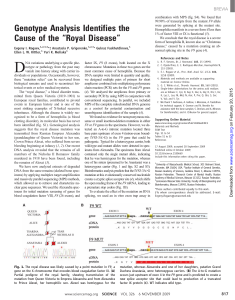
Genotype Analysis Identifies the Cause of the “Royal Disease”
... Bioinformatics analysis predicts that the IVS3-3A>G mutation at this evolutionarily conserved nucleotide creates a cryptic splice acceptor site (4), which shifts the open reading frame of the F9 mRNA, leading to a premature stop codon (Fig. 1B). To evaluate the effect of the mutation on RNA splicing ...
... Bioinformatics analysis predicts that the IVS3-3A>G mutation at this evolutionarily conserved nucleotide creates a cryptic splice acceptor site (4), which shifts the open reading frame of the F9 mRNA, leading to a premature stop codon (Fig. 1B). To evaluate the effect of the mutation on RNA splicing ...
AP Biology Practice Exam #1
... a) Down syndrome b) phenylketonuria c) neurofibromatosis d) cystic fibrosis e) hemophilia _____74. Phenylketonuria is a) caused by mutated gene on chromosome 12. b) easily detested by high levels of phenylalanine in urine or blood. c) the most common inherited disease of the nervous system. d) due t ...
... a) Down syndrome b) phenylketonuria c) neurofibromatosis d) cystic fibrosis e) hemophilia _____74. Phenylketonuria is a) caused by mutated gene on chromosome 12. b) easily detested by high levels of phenylalanine in urine or blood. c) the most common inherited disease of the nervous system. d) due t ...