Chromosomal Disorders
... genes (mostly encoding somatic function) markers, and disease-associated mutations. • The Y is small (though variable in length)…but it does have some genes ...
... genes (mostly encoding somatic function) markers, and disease-associated mutations. • The Y is small (though variable in length)…but it does have some genes ...
Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics
... • Most human traits are polygenic • Most variety of expression • There are 3 genes that contribute to skin color.. And many alleles for each gene! ...
... • Most human traits are polygenic • Most variety of expression • There are 3 genes that contribute to skin color.. And many alleles for each gene! ...
Document
... If the population size is too small, the GA is in danger of premature convergence upon a sub-optimal solution (all chromosomes will soon have identical traits). This is primarily because there may not be enough diversity in the population to allow the GA to escape local optima ...
... If the population size is too small, the GA is in danger of premature convergence upon a sub-optimal solution (all chromosomes will soon have identical traits). This is primarily because there may not be enough diversity in the population to allow the GA to escape local optima ...
Exploring the Human Genome - Cayetano Heredia University
... Instead of all mouse genes, select protein coding genes on chromosome 10. ...
... Instead of all mouse genes, select protein coding genes on chromosome 10. ...
Genes
... A newborn infected during gestation with any of the TORCH group of MOs may show microcephaly, hydrocephaly, mental retardation, or loss of hearing or sight. Congenital heart defects are common, especially with rubella. Radiation exposure may increase the risk that the child will later develop cancer ...
... A newborn infected during gestation with any of the TORCH group of MOs may show microcephaly, hydrocephaly, mental retardation, or loss of hearing or sight. Congenital heart defects are common, especially with rubella. Radiation exposure may increase the risk that the child will later develop cancer ...
SNP - HL7.org
... molecular/genetic/clinical database of several thousand primary brain tumors that is fully open and accessible to all investigators (intramural and extramural). It is envisioned to provide informatics support to molecularly characterize a large number of adult and pediatric primary brain tumors and ...
... molecular/genetic/clinical database of several thousand primary brain tumors that is fully open and accessible to all investigators (intramural and extramural). It is envisioned to provide informatics support to molecularly characterize a large number of adult and pediatric primary brain tumors and ...
Lecture 3. Complications and Crossing-Over
... independent assortment in the individual genes. • In a population we will see gradual differences, or continuous variation. ...
... independent assortment in the individual genes. • In a population we will see gradual differences, or continuous variation. ...
dragon genetics lab
... the formation of gametes. This means that traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another. Mendel’s Law of Segregatoin Mendel's law of segregation states that allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization. There are four main concept ...
... the formation of gametes. This means that traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another. Mendel’s Law of Segregatoin Mendel's law of segregation states that allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization. There are four main concept ...
Fact Sheet 56|FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLAEMIA In summary
... exercise and smoking may all lead to high cholesterol levels. In some families, there are multiple family members who have high cholesterol. This may be explained by FH. At least 1 in 500 Australians are affected by FH, although only 20% of these people would be aware they have this condition. FH is ...
... exercise and smoking may all lead to high cholesterol levels. In some families, there are multiple family members who have high cholesterol. This may be explained by FH. At least 1 in 500 Australians are affected by FH, although only 20% of these people would be aware they have this condition. FH is ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females – why? – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome. ...
... • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females – why? – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome. ...
X w
... The only two viable progeny types were XXY and X0 In this model sex is determined by the number of X chromosomes rather than the presence or absence of the Y chromosome This model makes a strong prediction -Hypothesis Genes reside on chromosome The exceptional red-eyed males should be X0 and The exc ...
... The only two viable progeny types were XXY and X0 In this model sex is determined by the number of X chromosomes rather than the presence or absence of the Y chromosome This model makes a strong prediction -Hypothesis Genes reside on chromosome The exceptional red-eyed males should be X0 and The exc ...
Honors Biology – Chapter 11 and 14
... chromosomal mutations; explain how “nondisjunction” can occur 19. Construct and interpret pedigrees using information about dominant/recessive traits passed down through ...
... chromosomal mutations; explain how “nondisjunction” can occur 19. Construct and interpret pedigrees using information about dominant/recessive traits passed down through ...
Mendelian genetics complete
... F2 generation – Offspring produced from _F1 x F1________. In F2, trait that disappeared in F1 reappeared in __1/4___ of the offspring; the other ¾ showed _dominant trait_____. C. Mendel’s Principles – After analyzing his results carefully, Mendel formed conclusions that increased understanding of ...
... F2 generation – Offspring produced from _F1 x F1________. In F2, trait that disappeared in F1 reappeared in __1/4___ of the offspring; the other ¾ showed _dominant trait_____. C. Mendel’s Principles – After analyzing his results carefully, Mendel formed conclusions that increased understanding of ...
genetics keystone review
... • Part B: Describe how chromosome separation in meiosis is different from chromosome separation in mitosis. • Part C: Compare the effects of a disorder caused by chromosomes failing to separate during meiosis, such as Patau syndrome, to the effects of chromosomes failing to separate during mitosis. ...
... • Part B: Describe how chromosome separation in meiosis is different from chromosome separation in mitosis. • Part C: Compare the effects of a disorder caused by chromosomes failing to separate during meiosis, such as Patau syndrome, to the effects of chromosomes failing to separate during mitosis. ...
Genetic Inheritance Type Review
... expressed as long as one copy is present. We only see the recessive trait (shown as a lower case letter) when both copies of the gene are the recessive allele. Gregor Mendel discovered this type of inheritance using pea plants. He stated that genes separate from their pair during meiosis and then re ...
... expressed as long as one copy is present. We only see the recessive trait (shown as a lower case letter) when both copies of the gene are the recessive allele. Gregor Mendel discovered this type of inheritance using pea plants. He stated that genes separate from their pair during meiosis and then re ...
Neoplasia & Hereditary Diseases Lecture Notes Page
... – Missing enzyme prevents metabolization phenylalanine – Causes CNS damage to the newborn ...
... – Missing enzyme prevents metabolization phenylalanine – Causes CNS damage to the newborn ...
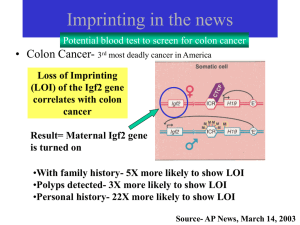
Imprinting
... •None or minimal use of words •Receptive and non-verbal communication skills higher than verbal ones •Movement or balance disorder, usually ataxia of gait •Behavioral uniqueness: any combination of frequent laughter/smiling; apparent happy demeanor ...
... •None or minimal use of words •Receptive and non-verbal communication skills higher than verbal ones •Movement or balance disorder, usually ataxia of gait •Behavioral uniqueness: any combination of frequent laughter/smiling; apparent happy demeanor ...
Genetics Fact Sheet - Barth Syndrome Foundation
... alterations in the structure and function of Tafazzin protein or in the amount of protein produced. Although we do not know all of the functions of Tafazzin protein, it is clear that mutations that alter the Tafazzin protein can cause Barth syndrome. Inheritance The inheritance of Barth syndrome fol ...
... alterations in the structure and function of Tafazzin protein or in the amount of protein produced. Although we do not know all of the functions of Tafazzin protein, it is clear that mutations that alter the Tafazzin protein can cause Barth syndrome. Inheritance The inheritance of Barth syndrome fol ...
Genetics - sciencegeek
... • Many genetic disorders are linked to the X Chromosome • Much more common phenotypically in males • Females are typically carriers • These traits become evident after puberty due to the chemical production in the body ...
... • Many genetic disorders are linked to the X Chromosome • Much more common phenotypically in males • Females are typically carriers • These traits become evident after puberty due to the chemical production in the body ...
unit 5 study guide (ch 13-15)
... 1 a) If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes will be present in somatic cells? b) If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes will be found in the gametes? c) If n = 18, how many chromosomes will be found in diploid somatic cells? d) If n = 18, how many pairs of homologous chromosomes will be found in gametes? e) If ...
... 1 a) If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes will be present in somatic cells? b) If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes will be found in the gametes? c) If n = 18, how many chromosomes will be found in diploid somatic cells? d) If n = 18, how many pairs of homologous chromosomes will be found in gametes? e) If ...
Non-linear conversion between genetic and
... by local installations. Motivation: Genetic linkage maps and radiation hybrid (RH) maps are based on the rate of uncoupling between linked genetic markers. These are usually measured in centiMorgan (cM) when uncoupling is originated by natural recombination or in centiRay (cR) for chromosomes that a ...
... by local installations. Motivation: Genetic linkage maps and radiation hybrid (RH) maps are based on the rate of uncoupling between linked genetic markers. These are usually measured in centiMorgan (cM) when uncoupling is originated by natural recombination or in centiRay (cR) for chromosomes that a ...
EOC Review Part 5
... the bad gene? Males only have one copy of the X chromosome so if a gene is mutated, it will be expressed. Males inherit their X chromosome from their mother because they must inherit the Y chromosome from their father. If the father passes on his X chromosome, the child will be female. Describe the ...
... the bad gene? Males only have one copy of the X chromosome so if a gene is mutated, it will be expressed. Males inherit their X chromosome from their mother because they must inherit the Y chromosome from their father. If the father passes on his X chromosome, the child will be female. Describe the ...