File
... • A very important tool for studying human inherited diseases – Allow inferences concerning genotypes in a family or population – Allows predictions concerning phenotypes of offspring inheriting a genetic disease (genetic counseling) ...
... • A very important tool for studying human inherited diseases – Allow inferences concerning genotypes in a family or population – Allows predictions concerning phenotypes of offspring inheriting a genetic disease (genetic counseling) ...
Cross over frequency and gene mapping Notes
... Crossing over – homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I, they may exchange pieces of chromosome Linked genes do not always stay together in gamete formation Crossing over results in new combinations of genes Crossing over occurs during meiosis and cause linked genes to separate. ...
... Crossing over – homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I, they may exchange pieces of chromosome Linked genes do not always stay together in gamete formation Crossing over results in new combinations of genes Crossing over occurs during meiosis and cause linked genes to separate. ...
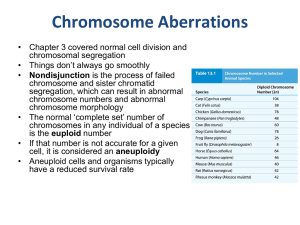
Chromosome Aberrations
... Chromosome Aberrations • Uniparental disomy - when both chromosomes of a pair in the offspring were derived from a single parent • Scenario 1 - rare • Nondisjunction for the same chromosome occurs in sperm and egg • One gamete with neither copy unites with the other gamete with both copies • Scenar ...
... Chromosome Aberrations • Uniparental disomy - when both chromosomes of a pair in the offspring were derived from a single parent • Scenario 1 - rare • Nondisjunction for the same chromosome occurs in sperm and egg • One gamete with neither copy unites with the other gamete with both copies • Scenar ...
Review L12 Inheritance L13 Chromosomal
... 17. What are the two laws that Mendel proposed? 18. What is a testcross and why is it used? Do testcrosses always provide you with the information you are looking for? Why or why not? 19. Provide a brief definition of incomplete dominance and codominance that clearly distinguishes between the two te ...
... 17. What are the two laws that Mendel proposed? 18. What is a testcross and why is it used? Do testcrosses always provide you with the information you are looking for? Why or why not? 19. Provide a brief definition of incomplete dominance and codominance that clearly distinguishes between the two te ...
Untitled - Pearson
... will yield Ly + br and + Sb + as phenotypes. Inspection shows that these categories (5 and 6) are actually single crossovers, not double crossovers. Therefore, the sequence is incorrect as written. Only two other sequences are possible: The br gene is either to the left of Ly (Case A), or it is betw ...
... will yield Ly + br and + Sb + as phenotypes. Inspection shows that these categories (5 and 6) are actually single crossovers, not double crossovers. Therefore, the sequence is incorrect as written. Only two other sequences are possible: The br gene is either to the left of Ly (Case A), or it is betw ...
Why the
... ork completed in the past five years has filled in many of the gaps. For instance, in 1999 one of us (Lahn) and David C. Page of the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Cambridge, Mass., showed that the Y lost the ability to swap DNA with the X in an unexpected, stepwise fashion— first in ...
... ork completed in the past five years has filled in many of the gaps. For instance, in 1999 one of us (Lahn) and David C. Page of the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Cambridge, Mass., showed that the Y lost the ability to swap DNA with the X in an unexpected, stepwise fashion— first in ...
UNIT 3 - OCCC.edu
... Alterations of Chromosome Number or Structure Cause Some Genetic Disorders Large-scale chromosomal alterations in humans and other mammals often lead to spontaneous _____________________ (miscarriages) or cause a variety of developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better than ani ...
... Alterations of Chromosome Number or Structure Cause Some Genetic Disorders Large-scale chromosomal alterations in humans and other mammals often lead to spontaneous _____________________ (miscarriages) or cause a variety of developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better than ani ...
Assigned Study Questions Due on Monday, April 9, 2007
... 21) Which of the following is true regarding linkage maps? They A) always have a total of 100 map units. B) can be used to pinpoint the precise physical position of a gene on a chromosome. C) are a genetic map based on recombination frequencies. D) require preparation of karyotypes. E) reflect the f ...
... 21) Which of the following is true regarding linkage maps? They A) always have a total of 100 map units. B) can be used to pinpoint the precise physical position of a gene on a chromosome. C) are a genetic map based on recombination frequencies. D) require preparation of karyotypes. E) reflect the f ...
Crossing-over and Independent Assortment
... called independent assortment. In humans, there are over 8 million ways in which the chromosomes can line up during metaphase I of meiosis. This independent assortment, in which the chromosome inherited from either the father or mother can sort into any gamete, produces the potential for tremendous ...
... called independent assortment. In humans, there are over 8 million ways in which the chromosomes can line up during metaphase I of meiosis. This independent assortment, in which the chromosome inherited from either the father or mother can sort into any gamete, produces the potential for tremendous ...
CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE
... example of a disorder seen in newborn babies that is due to an extra copy of an autosome is called Down syndrome. In 1866, a physician named John Langdon Down who worked with people with intellectual disabilities, observed that a number of his patients were so similar in appearance that they might e ...
... example of a disorder seen in newborn babies that is due to an extra copy of an autosome is called Down syndrome. In 1866, a physician named John Langdon Down who worked with people with intellectual disabilities, observed that a number of his patients were so similar in appearance that they might e ...
flipperiuabstract
... experiments: deletion, backcross, and recombinant inbred. The latter can be any generation from F2 onward. The mapper can process any experiment that can be phrased in terms of deletion from a parental monoploid genotype with one allele per locus. This condition is not as restrictive as it looks: A ...
... experiments: deletion, backcross, and recombinant inbred. The latter can be any generation from F2 onward. The mapper can process any experiment that can be phrased in terms of deletion from a parental monoploid genotype with one allele per locus. This condition is not as restrictive as it looks: A ...
Baby Lab Instructions 1. Choosing Your Donor Bring a color
... There is a possibility that genetic disorders run in previous generations. You will need to draw one slip of paper from one container for your possible disorder and one slip of paper from another container for possible disorder of your donor. There are also slips of papers that indicate no disorders ...
... There is a possibility that genetic disorders run in previous generations. You will need to draw one slip of paper from one container for your possible disorder and one slip of paper from another container for possible disorder of your donor. There are also slips of papers that indicate no disorders ...
Multiple Alleles
... You have performed Mendel’s dihybrid cross using the traits for seed shape and seed color. In the F2 generation you obtain plants with round, yellow seeds. You decide to determine the genotype of ONE of these plants. In your cross, you obtain progeny with the following phenotypes. 25% produce round ...
... You have performed Mendel’s dihybrid cross using the traits for seed shape and seed color. In the F2 generation you obtain plants with round, yellow seeds. You decide to determine the genotype of ONE of these plants. In your cross, you obtain progeny with the following phenotypes. 25% produce round ...
File
... Dominant and recessive • An allele is said to be dominant if it is always expressed in the appearance of an organism • E.g. the allele, T, for tall plants in pea is dominant to that for short plant, t. • Hence, with the pair of alleles, TT or Tt, the plants will always be tall. This shows the domi ...
... Dominant and recessive • An allele is said to be dominant if it is always expressed in the appearance of an organism • E.g. the allele, T, for tall plants in pea is dominant to that for short plant, t. • Hence, with the pair of alleles, TT or Tt, the plants will always be tall. This shows the domi ...
CHAPTER 9 Patterns of Inheritance
... Many genes have more than two alleles in the population • In a population, multiple alleles often exist for a characteristic – The three alleles for ABO blood type in humans is an example ...
... Many genes have more than two alleles in the population • In a population, multiple alleles often exist for a characteristic – The three alleles for ABO blood type in humans is an example ...
1 1 The diagram shows a maize (corn) cob with purple and yellow
... 4 A man who was blood group A and a woman who was blood group B had four children, each with a different blood group A, B, AB and O. Which type of variation does this demonstrate? A continuous, environmental and genetic B continuous and genetic only C discontinuous, environmental and genetic D disco ...
... 4 A man who was blood group A and a woman who was blood group B had four children, each with a different blood group A, B, AB and O. Which type of variation does this demonstrate? A continuous, environmental and genetic B continuous and genetic only C discontinuous, environmental and genetic D disco ...
Biology Ch. 9 notes “Genetics” Mendel’s Laws
... the inheritance of a single characteristic. A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited character because allele pairs separate (segregate) from each other during the production of gametes. This explains how a trait can disappear in one generation and reappear in the next generation. B ...
... the inheritance of a single characteristic. A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited character because allele pairs separate (segregate) from each other during the production of gametes. This explains how a trait can disappear in one generation and reappear in the next generation. B ...
Pedigrees
... – In Sex-linked the females can be unaffected, affected or carriers and marked with a dot. (XCXc) 4. Assign remaining genotypes to unaffected individuals . – In Sex-linked the unshaded males will not carry the gene (XCY) and be unaffected. ...
... – In Sex-linked the females can be unaffected, affected or carriers and marked with a dot. (XCXc) 4. Assign remaining genotypes to unaffected individuals . – In Sex-linked the unshaded males will not carry the gene (XCY) and be unaffected. ...
Alleles and Genotypes in Populations that Mate at Random Three
... whereas those (heterozygotes) which received from their two parents genes of different kinds. . . (Fisher, 1930, p. 8) ...
... whereas those (heterozygotes) which received from their two parents genes of different kinds. . . (Fisher, 1930, p. 8) ...
Section11.3OtherInheritance
... trait. Each trait only has two alleles, but in a population there may exist more than two alleles for a trait. 2. Where do new alleles come from? New alleles are often the result of a spontaneous mutation in which one nitrogenous base is changed in the ...
... trait. Each trait only has two alleles, but in a population there may exist more than two alleles for a trait. 2. Where do new alleles come from? New alleles are often the result of a spontaneous mutation in which one nitrogenous base is changed in the ...
Mode of Inheritance
... A lysosomal enzyme is missing, which results in improper lipid metabolism in cells, particularly those of the nervous system Between four and six months of age, an affected infant shows neurological impairment. The child gradually becomes blind, helpless, and paralyzed, and usually dies by age four. ...
... A lysosomal enzyme is missing, which results in improper lipid metabolism in cells, particularly those of the nervous system Between four and six months of age, an affected infant shows neurological impairment. The child gradually becomes blind, helpless, and paralyzed, and usually dies by age four. ...
Inheritance, Genes, and Chromosomes
... Different traits arise from different forms of a gene (now called alleles). •An organism that is homozygous for a gene has two alleles that are the same •An organism that is heterozygous for a gene has two different alleles. One may be dominant, (e.g., round [R]), and the other recessive, (e.g., wri ...
... Different traits arise from different forms of a gene (now called alleles). •An organism that is homozygous for a gene has two alleles that are the same •An organism that is heterozygous for a gene has two different alleles. One may be dominant, (e.g., round [R]), and the other recessive, (e.g., wri ...
Chapter_16_Review_Game
... A male is heterozygous for the trait that produces freckles on the skin, and he has freckles. If he marries a woman who is also heterozygous for freckles, ______ percent of their children will be freckled and __________ percent of their children will 38% ...
... A male is heterozygous for the trait that produces freckles on the skin, and he has freckles. If he marries a woman who is also heterozygous for freckles, ______ percent of their children will be freckled and __________ percent of their children will 38% ...