ABO Blood Types
... Mendel’s Peas were ideal for learning about inheritance, but they do not represent the norm… • Traits in pea plants are determined by just two alleles • In peas, one allele is clearly dominant & the other is clearly recessive • However, things aren’t always this clearcut and simple in the world of g ...
... Mendel’s Peas were ideal for learning about inheritance, but they do not represent the norm… • Traits in pea plants are determined by just two alleles • In peas, one allele is clearly dominant & the other is clearly recessive • However, things aren’t always this clearcut and simple in the world of g ...
Genetics SHOW
... 7) The recipe has the information to bring in specific AMINO ACIDS to build the needed protein. 8) When the RIBOSOME reads “stop” on the recipe (mRNA). The amino acids fold together to make the protein. The protein moves to the needed area in the body. ...
... 7) The recipe has the information to bring in specific AMINO ACIDS to build the needed protein. 8) When the RIBOSOME reads “stop” on the recipe (mRNA). The amino acids fold together to make the protein. The protein moves to the needed area in the body. ...
Reduced hybrid fertility
... Sympatric speciation can also result from the appearance of new ecological ...
... Sympatric speciation can also result from the appearance of new ecological ...
Ch. 4. Modern Genetics
... To explain how DNA fingerprinting is used To state the goal of the Human Genome Project. ...
... To explain how DNA fingerprinting is used To state the goal of the Human Genome Project. ...
Document
... a. blood from a newborn baby b. a picture of a baby before it is born c. a picture of the chromosomes in a cell d. fluid that surrounds a baby before it is born How can genetic counselors predict genetic disorders? a. by studying karyotypes and pedigree charts b. by taking pictures of the baby befor ...
... a. blood from a newborn baby b. a picture of a baby before it is born c. a picture of the chromosomes in a cell d. fluid that surrounds a baby before it is born How can genetic counselors predict genetic disorders? a. by studying karyotypes and pedigree charts b. by taking pictures of the baby befor ...
Heredity: Our Genetic Background
... •The threadlike molecules of DNA that make up chromosomes contain the codes for the development of particular traits. •Each chromosome has more than 1000 genes. •The rungs in the ladder form the genetic code that causes the organism to develop certain traits, and can be the source of some mutations ...
... •The threadlike molecules of DNA that make up chromosomes contain the codes for the development of particular traits. •Each chromosome has more than 1000 genes. •The rungs in the ladder form the genetic code that causes the organism to develop certain traits, and can be the source of some mutations ...
The scientist is not a person who gives the right answers, he`s one
... and without membranes • Membrane is same material as cell membrane ...
... and without membranes • Membrane is same material as cell membrane ...
Name Date ______ Lab: Sexually Reproducing Organisms (Meiosis
... If these were pictures of human chromosomes, how many would there be? __________ In human males, one set of chromosomes don’t match. This is the twenty-third or sex chromosomes. In females they match. Which human parent determines the sex of the child? ...
... If these were pictures of human chromosomes, how many would there be? __________ In human males, one set of chromosomes don’t match. This is the twenty-third or sex chromosomes. In females they match. Which human parent determines the sex of the child? ...
Practice Exam 4, Biology 211, Fall 2007
... b. The evolutionary record considered over long periods of time. c. The creation of reproductive barriers between related populations. d. Slow, but steady, changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time. e. The appearance in the evolutionary record of novel forms and structures. 20. Which of ...
... b. The evolutionary record considered over long periods of time. c. The creation of reproductive barriers between related populations. d. Slow, but steady, changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time. e. The appearance in the evolutionary record of novel forms and structures. 20. Which of ...
Biology Chapter 11-5 - Wayne County Public Schools
... Morgan and his friends found that the fruit fly had 4 linkage groups (genes that were inherited together). The linkage groups assorted independently but all the genes were inherited together. ...
... Morgan and his friends found that the fruit fly had 4 linkage groups (genes that were inherited together). The linkage groups assorted independently but all the genes were inherited together. ...
PRACTICE TEST CHAPTER 11 ______ 1. Different forms of a gene
... Which phenotypic ratio did Mendel find in his F2 Generation from the parental cross TT x tt? a. ...
... Which phenotypic ratio did Mendel find in his F2 Generation from the parental cross TT x tt? a. ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... the allele from… – Occurs during formation of gametes – Methyl groups (-CH3) added to DNA and “silence” alleles – When offspring produce own gametes, parental imprinting is erased & alleles reimprinted according to sex of offspring ...
... the allele from… – Occurs during formation of gametes – Methyl groups (-CH3) added to DNA and “silence” alleles – When offspring produce own gametes, parental imprinting is erased & alleles reimprinted according to sex of offspring ...
Science 9 Unit A 3.0
... • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
... • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
Cell Division and Genetics Test
... a) 4 diploid offspring cells b) 2 diploid offspring cells c) 4 haploid offspring cells d) 2 haploid offspring cells II. True/False Questions (EACH question is worth 4 points) Directions: After reading each statement below, decide if the state is true or false. Write in the full word TRUE or FALSE in ...
... a) 4 diploid offspring cells b) 2 diploid offspring cells c) 4 haploid offspring cells d) 2 haploid offspring cells II. True/False Questions (EACH question is worth 4 points) Directions: After reading each statement below, decide if the state is true or false. Write in the full word TRUE or FALSE in ...
Chapter 10
... Meiosis Provides Variation Depending on how the chromosomes line up at the equator, four gametes with four different combinations of chromosomes can result. Genetic variation also is produced during crossing over and during fertilization, when gametes randomly combine. In Prophase I: Crossing ...
... Meiosis Provides Variation Depending on how the chromosomes line up at the equator, four gametes with four different combinations of chromosomes can result. Genetic variation also is produced during crossing over and during fertilization, when gametes randomly combine. In Prophase I: Crossing ...
Differentiation in Germline Cells
... (23pairs of homologous chromosomes). • Germline cells can divide by mitosis to produce more germline cells. • Gamete mother cells divide by meiosis to produce gametes. ...
... (23pairs of homologous chromosomes). • Germline cells can divide by mitosis to produce more germline cells. • Gamete mother cells divide by meiosis to produce gametes. ...
Genetics
... Extra X: inactivated, bar body Spots of 2 colors: female cat One color spots: male cat Non-disjunction Failure of chromosome pairs to separate during meiosis Results in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes Aneuploidy: abnormal # of a certain chromosome Polyploidy: more than 2 complete ...
... Extra X: inactivated, bar body Spots of 2 colors: female cat One color spots: male cat Non-disjunction Failure of chromosome pairs to separate during meiosis Results in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes Aneuploidy: abnormal # of a certain chromosome Polyploidy: more than 2 complete ...
Genetics Student Notes
... daughter cell or In meiosis II, the sister chromatids both go into the same gamete. The result: ___________ (3 copies of a single chromosome) or ___________ (1 copy of a single chromosome) ...
... daughter cell or In meiosis II, the sister chromatids both go into the same gamete. The result: ___________ (3 copies of a single chromosome) or ___________ (1 copy of a single chromosome) ...
Name_____________ ______ Due Date: Biology MCA Q3 Exam
... 12. In snapdragon flowers, flowers can be red, white or pink. If two flowers that are each heterozygous for pink flowers are crossed, what are the possible phenotypes and genotype ratios? Show the Punnett square. ...
... 12. In snapdragon flowers, flowers can be red, white or pink. If two flowers that are each heterozygous for pink flowers are crossed, what are the possible phenotypes and genotype ratios? Show the Punnett square. ...
Barron`s Ch 7 ppt Heredity
... Genomic Imprinting + Extranuclear Genes - Two inheritance patterns that are exceptions to Mendelian inheritance - genomic imprinting + extranuclear genes Genomic imprinting: a variation in phenotype depending on whether a trait is inherited from mother or father. - Occurs during gamete formation - ...
... Genomic Imprinting + Extranuclear Genes - Two inheritance patterns that are exceptions to Mendelian inheritance - genomic imprinting + extranuclear genes Genomic imprinting: a variation in phenotype depending on whether a trait is inherited from mother or father. - Occurs during gamete formation - ...
Chromosomal Abnormalities
... Growth hormone therapy to increase height Hormone replacement therapy to trigger menstruation and the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as breasts Regular monitoring to check hormone levels Regular follow-up and management of medical conditions Treatment for the management of comp ...
... Growth hormone therapy to increase height Hormone replacement therapy to trigger menstruation and the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as breasts Regular monitoring to check hormone levels Regular follow-up and management of medical conditions Treatment for the management of comp ...
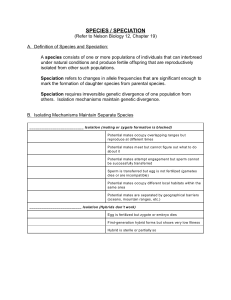
species / speciation
... A species consists of one or more populations of individuals that can interbreed under natural conditions and produce fertile offspring that are reproductively isolated from other such populations. Speciation refers to changes in allele frequencies that are significant enough to mark the formation o ...
... A species consists of one or more populations of individuals that can interbreed under natural conditions and produce fertile offspring that are reproductively isolated from other such populations. Speciation refers to changes in allele frequencies that are significant enough to mark the formation o ...
Heredity Part 2 - Pima Community College
... Sickle cell disease, multiple effects of a single human gene ...
... Sickle cell disease, multiple effects of a single human gene ...
a Sample - Rainbow Resource
... The notes say that the species is diploid, with a chromosome number of 17. Is this the haploid or diploid number? If this is the haploid number, give the diploid number. If this is the diploid number, give the corresponding haploid number. ...
... The notes say that the species is diploid, with a chromosome number of 17. Is this the haploid or diploid number? If this is the haploid number, give the diploid number. If this is the diploid number, give the corresponding haploid number. ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.