Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... did her father. Which of her parents underwent nondisjunction during meiosis, giving rise to the gamete responsible for the syndrome? 1. her mother 2. her father 3. both parents 4. technically speaking, there is not enough information to tell ...
... did her father. Which of her parents underwent nondisjunction during meiosis, giving rise to the gamete responsible for the syndrome? 1. her mother 2. her father 3. both parents 4. technically speaking, there is not enough information to tell ...
Deletions, Duplications and Inversions ppt
... With each additional inversion the probability of viable gametes in a hybrid between a normal by an inversion genotype decreases while fertility of individuals having two normal or two inversion parents stays at 100% ...
... With each additional inversion the probability of viable gametes in a hybrid between a normal by an inversion genotype decreases while fertility of individuals having two normal or two inversion parents stays at 100% ...
Mendel/Punnet/pedigrees powerpoint mendel.punnett
... monk living in the 1800’s Interested in the causes of variation in plants – used peas to study inheritance Why Peas? • Short generation time • Large number of ...
... monk living in the 1800’s Interested in the causes of variation in plants – used peas to study inheritance Why Peas? • Short generation time • Large number of ...
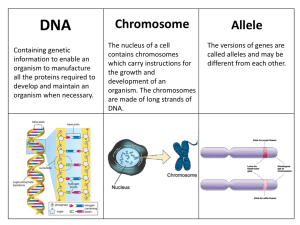
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
Course Outline - Roper Mountain Science Center!
... H.B.1: The student will use the science and engineering practices, including the processes and skills of scientific inquiry, to develop understandings of science content. H.B.1A. Conceptual Understanding: The practices of science and engineering support the development of science concepts, develop t ...
... H.B.1: The student will use the science and engineering practices, including the processes and skills of scientific inquiry, to develop understandings of science content. H.B.1A. Conceptual Understanding: The practices of science and engineering support the development of science concepts, develop t ...
Teratogenicity
... -During this stage : toxic chemical can kill some of the cells in the blastocyst, resulting in the death of the embryo the embryo (embryolethality), or have no effect at all. b.Post-implantation (stage of organogenesis ) from the 3rd to the 8th week of gestation . 6-7 days after gestation ,implantat ...
... -During this stage : toxic chemical can kill some of the cells in the blastocyst, resulting in the death of the embryo the embryo (embryolethality), or have no effect at all. b.Post-implantation (stage of organogenesis ) from the 3rd to the 8th week of gestation . 6-7 days after gestation ,implantat ...
When hybrids are fertile - Revista Pesquisa Fapesp
... within cells that contain genes. This difference can prevent the normal development of the embryo, as each chromosome that came from the male parent must be aligned with an equivalent chromosome from the female parent when the fertilized cell divides for the first time. Without this proper alignment ...
... within cells that contain genes. This difference can prevent the normal development of the embryo, as each chromosome that came from the male parent must be aligned with an equivalent chromosome from the female parent when the fertilized cell divides for the first time. Without this proper alignment ...
DNA 101 intro
... sample for DNA analysis, the results of which will be recorded in a computer chip on a wallet-sized plastic card. This card will contain specific aspects of your genetic makeup that can be identified as needed. The genetic information contained there may be used in several ways: • To predict your ri ...
... sample for DNA analysis, the results of which will be recorded in a computer chip on a wallet-sized plastic card. This card will contain specific aspects of your genetic makeup that can be identified as needed. The genetic information contained there may be used in several ways: • To predict your ri ...
Syllabus
... or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 18, 20. The 4th edition of Alberts is also available on line at pub med. You can search the text using t ...
... or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 18, 20. The 4th edition of Alberts is also available on line at pub med. You can search the text using t ...
3.14 C: Genetic Disorders Quiz PROCTOR VERSION
... This answer suggests the student may understand that sex-linked, recessive traits are mostly expressed in males, but does not understand that these traits cannot be observed in a daughter with a father who does not express the condition, as seen in the affected daughter in generation III, because th ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that sex-linked, recessive traits are mostly expressed in males, but does not understand that these traits cannot be observed in a daughter with a father who does not express the condition, as seen in the affected daughter in generation III, because th ...
1 4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION 4.1 Sex
... not true, and the genetic information in a portion of certain chromosomes is inactivated when inherited from one sex parent but not when inherited from the other. In these so-called imprinted regions, only one copy of the genes is transcribed, the other remaining genetically silent (at least in soma ...
... not true, and the genetic information in a portion of certain chromosomes is inactivated when inherited from one sex parent but not when inherited from the other. In these so-called imprinted regions, only one copy of the genes is transcribed, the other remaining genetically silent (at least in soma ...
Blueprint of Life by Arthur Huang
... It occurs due to natural selection pressure from a changing environment, which causes a particular trait/characteristic to be advantageous for survival. Within a population, individuals are characterized by a variety of different traits. Individuals with the advantageous traits will survive, breed a ...
... It occurs due to natural selection pressure from a changing environment, which causes a particular trait/characteristic to be advantageous for survival. Within a population, individuals are characterized by a variety of different traits. Individuals with the advantageous traits will survive, breed a ...
b2 6 mark question challenge
... Stem cells can be taken from spare embryos from IVF, created from adult cells or extracted from the umbilical cord blood of new born babies. Evaluate the usefulness of each type of stem cell and discuss the ethical implications of their use. ...
... Stem cells can be taken from spare embryos from IVF, created from adult cells or extracted from the umbilical cord blood of new born babies. Evaluate the usefulness of each type of stem cell and discuss the ethical implications of their use. ...
Selective Breeding
... Drugs that prevent the separation of chromosomes during meiosis are very useful in plant breeding. These drugs can produce cells that have many times the normal number of chromosomes. Plants grown from these cells are called polyploid because they have many sets of chromosomes. Polyploidy is usually ...
... Drugs that prevent the separation of chromosomes during meiosis are very useful in plant breeding. These drugs can produce cells that have many times the normal number of chromosomes. Plants grown from these cells are called polyploid because they have many sets of chromosomes. Polyploidy is usually ...
Genetics and genomics
... • The technology used is termed gene expression profiling, and identifying the sets of proteins in a cell is proteomics • DNA microarrays or DNA chips profile gene expression • This is valuable in anatomy and physiology when it allows medical researchers see ...
... • The technology used is termed gene expression profiling, and identifying the sets of proteins in a cell is proteomics • DNA microarrays or DNA chips profile gene expression • This is valuable in anatomy and physiology when it allows medical researchers see ...
Genetics Powerpoint
... sequence of DNA) • Can be : Harmful mutations – organism less able to survive: genetic disorders, cancer, death Beneficial mutations – allows organism to better survive: provides genetic variation Neutral mutations – neither harmful nor helpful to organism • Mutations can occur in 2 ways: chromosoma ...
... sequence of DNA) • Can be : Harmful mutations – organism less able to survive: genetic disorders, cancer, death Beneficial mutations – allows organism to better survive: provides genetic variation Neutral mutations – neither harmful nor helpful to organism • Mutations can occur in 2 ways: chromosoma ...
Genetics Unit: 1. Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to young
... Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to young Genetics- branch of Biology that studies heredity Genes- factors that control traits Genotype- genetic makeup (ex. TT, Tt or tt) Genotypic Ratio- the proportion of genotypes for a particular parental cross Traits- specific characteristics that var ...
... Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to young Genetics- branch of Biology that studies heredity Genes- factors that control traits Genotype- genetic makeup (ex. TT, Tt or tt) Genotypic Ratio- the proportion of genotypes for a particular parental cross Traits- specific characteristics that var ...
Powerpoint notes for chapter 14
... forms thick, condensed structures called chromosomes. A chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids which are held together by a structure called a centromere Each sister chromatid contains an identical copy of the genetic information or DNA. Other events which occur during this stage are: ...
... forms thick, condensed structures called chromosomes. A chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids which are held together by a structure called a centromere Each sister chromatid contains an identical copy of the genetic information or DNA. Other events which occur during this stage are: ...
Genetics, II
... • Ability of a gene to affect an organism in multiple ways • Examples: – 40% of cats with white fur and blue eyes are deaf – Phenylketonuria in humans (PKU) • Lack of an enzyme that converts Phe ...
... • Ability of a gene to affect an organism in multiple ways • Examples: – 40% of cats with white fur and blue eyes are deaf – Phenylketonuria in humans (PKU) • Lack of an enzyme that converts Phe ...
Slides review lecture
... - Mating combines haploid genomes to diploid genomes us: female & male produce egg & sperm yeast: mating types “a” and “alpha” produce spores (“dauer state”) that produce haploid cells (active state) - our (human) haploids are short-lived gamets but yeast haploids are free living organisms that are ...
... - Mating combines haploid genomes to diploid genomes us: female & male produce egg & sperm yeast: mating types “a” and “alpha” produce spores (“dauer state”) that produce haploid cells (active state) - our (human) haploids are short-lived gamets but yeast haploids are free living organisms that are ...
Bio 309F
... 29. Why have geneticists been able to identify several genes linked to the X chromosome in humans? A. the X chromosome is much easier to identify than the other chromosomes. B. the X chromosome is one of the smaller chromosomes, therefore easier to study C. only dominant genes are localized on the X ...
... 29. Why have geneticists been able to identify several genes linked to the X chromosome in humans? A. the X chromosome is much easier to identify than the other chromosomes. B. the X chromosome is one of the smaller chromosomes, therefore easier to study C. only dominant genes are localized on the X ...
Learning Target #1: Know vocabulary that builds the
... c. Both A and B 23. The following process precedes (comes before) both mitosis and meiosis, and ensures that the resulting cells are identical. a. DNA duplication b. Metaphase c. Cytokinesis d. DNA replication Learning Target #4: Describe how hereditary information is passed from parents to offsprin ...
... c. Both A and B 23. The following process precedes (comes before) both mitosis and meiosis, and ensures that the resulting cells are identical. a. DNA duplication b. Metaphase c. Cytokinesis d. DNA replication Learning Target #4: Describe how hereditary information is passed from parents to offsprin ...
5 Evolution and biodiversity
... Natural selection can occur if the individuals in a species show variation in their characteristics. Organisms produce many more progeny than survive – numbers in local populations remain more or less constant. Some variations among progeny are especially advantageous, making these individuals bette ...
... Natural selection can occur if the individuals in a species show variation in their characteristics. Organisms produce many more progeny than survive – numbers in local populations remain more or less constant. Some variations among progeny are especially advantageous, making these individuals bette ...
Practice Genetics Vocabulary Quiz
... C. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. D. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. E. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele comb ...
... C. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. D. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. E. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele comb ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.