electrochemistry - einstein classes
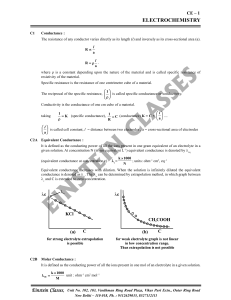
... Equivalent conductance increases with dilution. When the solution is infinitely diluted the equivalent conductance is denoted as . The can be determined by extrapolation method, in which graph between c and C is extended to zero concentration. ...
... Equivalent conductance increases with dilution. When the solution is infinitely diluted the equivalent conductance is denoted as . The can be determined by extrapolation method, in which graph between c and C is extended to zero concentration. ...
The Young Sun and Its Influence on Planetary Atmospheres 1. The
... atmosphere. Expanding atmospheres of this kind have been studied by Watson et al. (1981) for early Earth and by Kasting and Pollack (1983) for early Venus. A more recent example, in which high EUV fluxes were applied to a modern Earth-type atmosphere, has been modelled by Tian et al. (2008). Upper a ...
... atmosphere. Expanding atmospheres of this kind have been studied by Watson et al. (1981) for early Earth and by Kasting and Pollack (1983) for early Venus. A more recent example, in which high EUV fluxes were applied to a modern Earth-type atmosphere, has been modelled by Tian et al. (2008). Upper a ...
Electrochemistry - Menihek Home Page
... (does not interfere in the reaction).....it allows ions to migrate.....the ends of the salt bridge contain a porous plug.....does not let the electrolyte leak out quickly ...
... (does not interfere in the reaction).....it allows ions to migrate.....the ends of the salt bridge contain a porous plug.....does not let the electrolyte leak out quickly ...
Exam 2
... • Detach the data sheet from the centre of this book during reading time. • Write your student number in the space provided above on this page. • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provide ...
... • Detach the data sheet from the centre of this book during reading time. • Write your student number in the space provided above on this page. • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provide ...
112- Unit I -Electrochem -pdf
... Cl2 (g) + 2 e Cr2O7 2- + 14 H + + 6 e O2 (g) + 4 H + + 4 e Pb(s) Pb 2+ + 2 ea) ...
... Cl2 (g) + 2 e Cr2O7 2- + 14 H + + 6 e O2 (g) + 4 H + + 4 e Pb(s) Pb 2+ + 2 ea) ...
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FABRICATION
... factor of 5 or 10 several times to finally obtain the exact image size. The final image also must be repeated many times in a matrix array, so that many ICs will be produced in one process. The photo repeating is done with a step and repeat camera. This is an imaging device with a photographic plate ...
... factor of 5 or 10 several times to finally obtain the exact image size. The final image also must be repeated many times in a matrix array, so that many ICs will be produced in one process. The photo repeating is done with a step and repeat camera. This is an imaging device with a photographic plate ...
Diodes and Transistors HOW Theq Work
... "Valence" means the number of bonds the atom forms. For instance, the valence of silicon atoms in a crystal is four, because every atom forms four bonds. As mentioned previously, the electrons in the valence shell are called the atom's valence electrons. The rest of the atom, consisting of filled sh ...
... "Valence" means the number of bonds the atom forms. For instance, the valence of silicon atoms in a crystal is four, because every atom forms four bonds. As mentioned previously, the electrons in the valence shell are called the atom's valence electrons. The rest of the atom, consisting of filled sh ...
Hard water:
... Electromotive Force: The potential which is required to move a unit charge from one place to another place. It is also known as E.M.F It is measured in volts. Volt: The volt is defined as the value of the voltage across a conductor when a current of one ampere strength through a one ohm resistance. ...
... Electromotive Force: The potential which is required to move a unit charge from one place to another place. It is also known as E.M.F It is measured in volts. Volt: The volt is defined as the value of the voltage across a conductor when a current of one ampere strength through a one ohm resistance. ...
Class 3 updated Sep 30 2011
... Electrical breakdowm of the argon gas occurs when an electron collides with the argon atom with a kinetic energy sufficient to free an electron from the atom, thus producing a second electron and a positive ion. (ionization potential) Both free electrons reenergize creating an avalanche of ions and ...
... Electrical breakdowm of the argon gas occurs when an electron collides with the argon atom with a kinetic energy sufficient to free an electron from the atom, thus producing a second electron and a positive ion. (ionization potential) Both free electrons reenergize creating an avalanche of ions and ...
AP Electrochemistry Class Packet Unit 10
... A redox reaction is a reaction in which electrons are transferred from one element to another. The reaction involves at least two elements, one that will give up an electron, and one that will receive that electron. The term redox comes from two words, “oxidation” and “reduction.” If something is ox ...
... A redox reaction is a reaction in which electrons are transferred from one element to another. The reaction involves at least two elements, one that will give up an electron, and one that will receive that electron. The term redox comes from two words, “oxidation” and “reduction.” If something is ox ...
Slide 1
... will be some tendency for the magnesium atoms to shed electrons and go into solution as magnesium ions. The electrons will be left behind on the magnesium In a very short time, there will be a build-up of electrons on the magnesium, and it will be surrounded in the solution by a layer of positive io ...
... will be some tendency for the magnesium atoms to shed electrons and go into solution as magnesium ions. The electrons will be left behind on the magnesium In a very short time, there will be a build-up of electrons on the magnesium, and it will be surrounded in the solution by a layer of positive io ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
Chemistry B2A Chapter 18 Oxidation
... 5. In binary compounds, the element with the greater electronegativity is assigned a negative oxidation state equal to its charge as an anion in its ionic compounds. It means, the most electronegative atom controls or possesses the charge electrons. For example, in SO2 oxygen has a higher electrone ...
... 5. In binary compounds, the element with the greater electronegativity is assigned a negative oxidation state equal to its charge as an anion in its ionic compounds. It means, the most electronegative atom controls or possesses the charge electrons. For example, in SO2 oxygen has a higher electrone ...
Electrochemistry
... - we added H+ to balance the equation. The [H+] in a basic solution is very small. The [OH-] is much greater. For this reason, we will add enough OH- ions to both sides of the equation to neutralize the H+ in the overall reaction. The hydrogen and hydroxide ions will combine to make water, and you m ...
... - we added H+ to balance the equation. The [H+] in a basic solution is very small. The [OH-] is much greater. For this reason, we will add enough OH- ions to both sides of the equation to neutralize the H+ in the overall reaction. The hydrogen and hydroxide ions will combine to make water, and you m ...
Powerpoint
... of the first half-reaction is larger. Copper metal, rather than OH-, gives out electrons. In principle, if platinum electrode is used, platinum may also give out electrons to form platinum ion. But in practice, it seldom happens due to the very negative value of Eo for this process: Pt(s) Pt2+(aq) ...
... of the first half-reaction is larger. Copper metal, rather than OH-, gives out electrons. In principle, if platinum electrode is used, platinum may also give out electrons to form platinum ion. But in practice, it seldom happens due to the very negative value of Eo for this process: Pt(s) Pt2+(aq) ...
Tutorial 7
... By the end of this session, the student should be able to: To calculate potential of a cell when current passes. Differentiate between electrogravimetry, coulometry. Correlate concentration to the electrochemical phenomena measured. ...
... By the end of this session, the student should be able to: To calculate potential of a cell when current passes. Differentiate between electrogravimetry, coulometry. Correlate concentration to the electrochemical phenomena measured. ...
ch19 MSJ jlm
... The Ag|Ag+ half-cell has a higher reduction potential than the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell. This means that the Ag/Ag+ half-cell will more readily undergo reduction when compared to the Cu/Cu2+ halfcell, and the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell will undergo oxidation. The Ag|Ag+ standard reduction potential is Eored = +0.8 ...
... The Ag|Ag+ half-cell has a higher reduction potential than the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell. This means that the Ag/Ag+ half-cell will more readily undergo reduction when compared to the Cu/Cu2+ halfcell, and the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell will undergo oxidation. The Ag|Ag+ standard reduction potential is Eored = +0.8 ...
half-reactions - Clayton State University
... Nonspontaneous Process - Requires something to be applied in order for it to occur (usually in the form of energy) ...
... Nonspontaneous Process - Requires something to be applied in order for it to occur (usually in the form of energy) ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
Exam 3 Review Key
... d) Oxidizing agent: Ag+; reducing agent: O3 Pt(s)|O3(g), O2(g)|OH-(aq)|| Ag+(aq)|Ag(s); -0.44V (this is for basic conditions, used because this is how the reaction is given in the Standard Potentials Table in the book’s appendix. In acid, the cell would have the same set-up, only there would be H+ ...
... d) Oxidizing agent: Ag+; reducing agent: O3 Pt(s)|O3(g), O2(g)|OH-(aq)|| Ag+(aq)|Ag(s); -0.44V (this is for basic conditions, used because this is how the reaction is given in the Standard Potentials Table in the book’s appendix. In acid, the cell would have the same set-up, only there would be H+ ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The result then is the production of Cl2(g) and Cu(s). anode, oxidation: Cl2(g) + 2e– 2Cl–(aq) E° = +1.358 V • cathode, reduction: Cu2+(aq) + 2e– Cu(s) E° = +0.337 V • overall: CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + Cl2(g) E = –1.021 V ...
... • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The result then is the production of Cl2(g) and Cu(s). anode, oxidation: Cl2(g) + 2e– 2Cl–(aq) E° = +1.358 V • cathode, reduction: Cu2+(aq) + 2e– Cu(s) E° = +0.337 V • overall: CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + Cl2(g) E = –1.021 V ...
Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H SO ? A)
... 67) The diagram below represents the electroplating of a metal fork with Ag(s). ...
... 67) The diagram below represents the electroplating of a metal fork with Ag(s). ...
Chapter 20: Electrochemistry
... V = 0 when two charged objects are separated by infinity We are interested in DV between Anode and Cathode ...
... V = 0 when two charged objects are separated by infinity We are interested in DV between Anode and Cathode ...
LATENT HEAT AND ELECTRODE POTENTIAL
... described the influence of temperature and of the state of the metallic electrodes on the electromotive force (emf) of a voltaic cell (1). In the copper-zinc Daniell cell he had found that sheet, electrodeposited, and other types of copper, combined with various types of zinc, produced essentially t ...
... described the influence of temperature and of the state of the metallic electrodes on the electromotive force (emf) of a voltaic cell (1). In the copper-zinc Daniell cell he had found that sheet, electrodeposited, and other types of copper, combined with various types of zinc, produced essentially t ...
File
... 1. What is the oxidation number of carbon in methane (CH4)? Hydrogen has an oxidation number of There are 4 hydrogens, so the total oxidation number for the hydrogen in this molecule is. The molecule is electrically neutral (it does not have a net charge), so therefore the carbon must have an oxidat ...
... 1. What is the oxidation number of carbon in methane (CH4)? Hydrogen has an oxidation number of There are 4 hydrogens, so the total oxidation number for the hydrogen in this molecule is. The molecule is electrically neutral (it does not have a net charge), so therefore the carbon must have an oxidat ...
Theory of solar cells

The theory of solar cells explains the physical and chemical processes by which photons are converted into electric current when striking a suitable semiconductor device. The theoretical studies are of practical use because they predict the fundamental limits of solar cell, and give guidance on the phenomena that contribute to losses and solar cell efficiency.