Worked out problems
... Sample Exercise 20.4 Describing a Voltaic Cell The oxidation-reduction reaction is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with ei ...
... Sample Exercise 20.4 Describing a Voltaic Cell The oxidation-reduction reaction is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with ei ...
pulsed laser atom probe characterization of silicon carbide
... In these high resistivity materials, reliable voltage-pulsed field evaporation proved to b e unattainable even with pulse fractions of over 100%. Therefore, chemical analysis was performed in a pulsed laser atom probe. Specimens prepared from the ,%Sic whiskers grown by the VLS process were used. T ...
... In these high resistivity materials, reliable voltage-pulsed field evaporation proved to b e unattainable even with pulse fractions of over 100%. Therefore, chemical analysis was performed in a pulsed laser atom probe. Specimens prepared from the ,%Sic whiskers grown by the VLS process were used. T ...
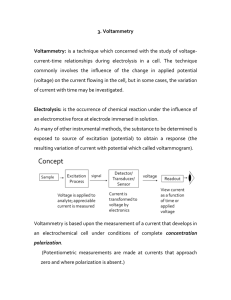
Oxygen Reduction Reaction with the Rotating Ring Disk Electrode
... given potential value can be elucidated based on the presence of H2O2 detected at the ring (WE2). The data presented in Figure 1 indicates that ORR proceeds via a mixture of the four-electron and two-electron pathways at potential values within the mass transfer limited plateau. At potential values ...
... given potential value can be elucidated based on the presence of H2O2 detected at the ring (WE2). The data presented in Figure 1 indicates that ORR proceeds via a mixture of the four-electron and two-electron pathways at potential values within the mass transfer limited plateau. At potential values ...
electrochemistry
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
Chap 9 Redox Review Q`s
... Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity but molten sodium chloride does. Explain this difference, and outline what happens in an electrolytic cell during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using carbon electrodes. ...
... Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity but molten sodium chloride does. Explain this difference, and outline what happens in an electrolytic cell during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using carbon electrodes. ...
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... The formation of the electric double layer causes a potential difference between the surface of the metal and the liquid; this is called the electrode potential. The further to the left the above equilibrium lies, the greater the potential difference will be. For a given metal, the position of the e ...
... The formation of the electric double layer causes a potential difference between the surface of the metal and the liquid; this is called the electrode potential. The further to the left the above equilibrium lies, the greater the potential difference will be. For a given metal, the position of the e ...
Diffusion current - Prof Dr Hisham E Abdellatef
... In this method, a Hanging Mercury Drop Electrode (HMDE) is used, the potentiostat is set a fixed value (0.2-0.4 V) more negative than the highest reduction potential encountered among the reducible ions, then electrolysis will occur, deposition of metals will take place on the HMDE cathode and amalg ...
... In this method, a Hanging Mercury Drop Electrode (HMDE) is used, the potentiostat is set a fixed value (0.2-0.4 V) more negative than the highest reduction potential encountered among the reducible ions, then electrolysis will occur, deposition of metals will take place on the HMDE cathode and amalg ...
Building the sense of math in physics activities
... the object and v is its velocity through the fluid. (This is actually correct up to a dimensionless factor. For this problem take Re to be the ratio of these two forces.) B.1 Write an equation for the Reynolds number for this example, simplifying the equation as much as possible (e.g., cancelling fa ...
... the object and v is its velocity through the fluid. (This is actually correct up to a dimensionless factor. For this problem take Re to be the ratio of these two forces.) B.1 Write an equation for the Reynolds number for this example, simplifying the equation as much as possible (e.g., cancelling fa ...
MT 3 Practice
... precipitate was then dissolved by the addition of HCl. Sodium sulfate was then added and a precipitate formed. What is the identity of the cation. [A] Co2+ [B] Ca2+ [C] Ba2+ [D] Ni2+ 2. 1M NH3 was added to to a solution of one of the ions from the list of ions at the start of the flow chart A precip ...
... precipitate was then dissolved by the addition of HCl. Sodium sulfate was then added and a precipitate formed. What is the identity of the cation. [A] Co2+ [B] Ca2+ [C] Ba2+ [D] Ni2+ 2. 1M NH3 was added to to a solution of one of the ions from the list of ions at the start of the flow chart A precip ...
AP Chemistry
... Part 2: Measure the change in mass of the zinc electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas produced during electrolysis, calculate the molar mass of zinc and compare the value to the periodic table. Fill a 150 mL beaker ¾ full with conducting solution. Fill the 50 mL volumetric flask with the conductin ...
... Part 2: Measure the change in mass of the zinc electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas produced during electrolysis, calculate the molar mass of zinc and compare the value to the periodic table. Fill a 150 mL beaker ¾ full with conducting solution. Fill the 50 mL volumetric flask with the conductin ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
Batteries are all over the place -- in our cars, our
... If you now stick a carbon rod in the acid, the acid does nothing to it. But if you connect a wire between the zinc rod and the carbon rod, two things change: The electrons flow through the wire and combine with hydrogen on the carbon ...
... If you now stick a carbon rod in the acid, the acid does nothing to it. But if you connect a wire between the zinc rod and the carbon rod, two things change: The electrons flow through the wire and combine with hydrogen on the carbon ...
Electrochemistry
... reduce the Cu2+ ions, thus effectively stopping the reaction after only a minute amount has taken place. In order to sustain the cell reaction, the charge carried by the electrons through the external circuit must be accompanied by a compensating transport of ions between the two cells. This means t ...
... reduce the Cu2+ ions, thus effectively stopping the reaction after only a minute amount has taken place. In order to sustain the cell reaction, the charge carried by the electrons through the external circuit must be accompanied by a compensating transport of ions between the two cells. This means t ...
Electrode Potentials hw - A
... in the solution at the end of this reaction. State the oxidation state of vanadium in this species and write a half-equation for its formation from V2+(aq). Vanadium species present at end of reaction ............................................................. Oxidation state of vanadium in final ...
... in the solution at the end of this reaction. State the oxidation state of vanadium in this species and write a half-equation for its formation from V2+(aq). Vanadium species present at end of reaction ............................................................. Oxidation state of vanadium in final ...
Chemistry 2008–2012 Written examination – November Examination Specifications
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
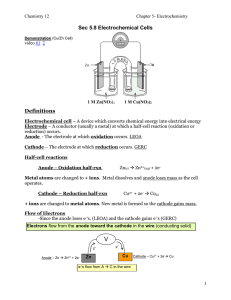
Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
... Summary of Electrochemical Cells (ECC’s) so far… 1) Electrochemical cells convert __________ energy into ___________ energy. 2) ___________ is the electrode where oxidation occurs. 3) Electrons are ________ at the anode. 4) _________ is the electrode where reduction occurs. 5) In the half-rx at the ...
... Summary of Electrochemical Cells (ECC’s) so far… 1) Electrochemical cells convert __________ energy into ___________ energy. 2) ___________ is the electrode where oxidation occurs. 3) Electrons are ________ at the anode. 4) _________ is the electrode where reduction occurs. 5) In the half-rx at the ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... E. Electrochemical Cells The Basics of an Electrochemical Cell Every electrochemical cell (contains two compartments where REDOX reactions can occur) contains 2 electrodes. An electrode is a strip of metal that facilitates the loss or gain of electrons. There are two types of electrodes, known as th ...
... E. Electrochemical Cells The Basics of an Electrochemical Cell Every electrochemical cell (contains two compartments where REDOX reactions can occur) contains 2 electrodes. An electrode is a strip of metal that facilitates the loss or gain of electrons. There are two types of electrodes, known as th ...
A Gas-phase Electrochemical Reactor for Carbon Dioxide
... electrons coming from the anode side and passing through a proton selective membrane (Nafion ) and a wire, respectively (Ampelli et al., 2011a). The design of the PEC reactor takes advantage of fuel cell technology and the electrode materials are assembled together like a MEA (membrane electrode ass ...
... electrons coming from the anode side and passing through a proton selective membrane (Nafion ) and a wire, respectively (Ampelli et al., 2011a). The design of the PEC reactor takes advantage of fuel cell technology and the electrode materials are assembled together like a MEA (membrane electrode ass ...
Oxidation-Reduction and Electrochemistry
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
Practice Exam 3
... b. from He to Ca, stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons. c. isotopes with a low neutron to proton ratio always decay by alpha particle emission. d. the neutron to proton ratio in stable nuclei increases as mass increases. e. beyond calcium, the neutron to proton ratio is a ...
... b. from He to Ca, stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons. c. isotopes with a low neutron to proton ratio always decay by alpha particle emission. d. the neutron to proton ratio in stable nuclei increases as mass increases. e. beyond calcium, the neutron to proton ratio is a ...
Electrochemical Fundamentals
... Hg|Hg2Cl2|KCl (sat’d), Eo = 0.242 V Ag|AgCl|KCl (sat’d), Eo = 0.197 V ...
... Hg|Hg2Cl2|KCl (sat’d), Eo = 0.242 V Ag|AgCl|KCl (sat’d), Eo = 0.197 V ...
Equilibrium Electrochemistry
... E.g. In the Daniel cell (i) two different electrolyte solutions are in contact, (ii) different concentration of hydrochloric acid- At the junction, the mobile H+ ions diffuse into the more dilute solution. The bulkier Cl- ions follow, but initially do so more slowly- results in a potential differe ...
... E.g. In the Daniel cell (i) two different electrolyte solutions are in contact, (ii) different concentration of hydrochloric acid- At the junction, the mobile H+ ions diffuse into the more dilute solution. The bulkier Cl- ions follow, but initially do so more slowly- results in a potential differe ...
Practice problems
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
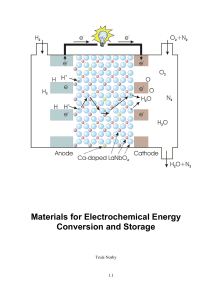
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage
... electrolyte – the ionic conductor that allows ions to pass between fuel and oxidant but denies passage of electrons so that these go through an external path – our electrical circuit. The electrolyte may be as different as an aqueous solution, a molten salt, a solid polymer, or a metal oxide. Their ...
... electrolyte – the ionic conductor that allows ions to pass between fuel and oxidant but denies passage of electrons so that these go through an external path – our electrical circuit. The electrolyte may be as different as an aqueous solution, a molten salt, a solid polymer, or a metal oxide. Their ...
Electro-Kinetics
... root of the rotation rate is obvious from the Levich plot. A linear least squares fit of the data produces an equation for the best straight line passing through the data. The specific experiment shown, the electrode area, A, was 0.1963 cm2, the analyte concentration, C, was 2.55x10–6 mol/cm3, and t ...
... root of the rotation rate is obvious from the Levich plot. A linear least squares fit of the data produces an equation for the best straight line passing through the data. The specific experiment shown, the electrode area, A, was 0.1963 cm2, the analyte concentration, C, was 2.55x10–6 mol/cm3, and t ...
Theory of solar cells

The theory of solar cells explains the physical and chemical processes by which photons are converted into electric current when striking a suitable semiconductor device. The theoretical studies are of practical use because they predict the fundamental limits of solar cell, and give guidance on the phenomena that contribute to losses and solar cell efficiency.