Unit 3: Genetics
... Chromosomal Disorders Nondisjunction (failure of homologous chromosomes to separate) occurs during meiosis. The resulting individual has an abnormal number of chromosomes and that results in a disorder! ...
... Chromosomal Disorders Nondisjunction (failure of homologous chromosomes to separate) occurs during meiosis. The resulting individual has an abnormal number of chromosomes and that results in a disorder! ...
Chromosome 21 Scan in Down Syndrome Reveals DSCAM as a
... International Hirschsprung Disease Consortium in which the proband had both HSCR and Down syndrome. Among them, 12 were recruited in France, 8 in the USA, 4 in Spain, one in The Netherlands and one in Italy. The validation sample consisted of DNA from 220 Caucasian cases with isolated HSCR and their ...
... International Hirschsprung Disease Consortium in which the proband had both HSCR and Down syndrome. Among them, 12 were recruited in France, 8 in the USA, 4 in Spain, one in The Netherlands and one in Italy. The validation sample consisted of DNA from 220 Caucasian cases with isolated HSCR and their ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... dominant and recessive “factors” to describe the results of his experiments. He did not know where these “factors” were located in cells. Hypothesized that only one copy of a factor went into each sperm or ovum, i.e. if a parent were truebreeding for round seeds, for example, all its gametes wou ...
... dominant and recessive “factors” to describe the results of his experiments. He did not know where these “factors” were located in cells. Hypothesized that only one copy of a factor went into each sperm or ovum, i.e. if a parent were truebreeding for round seeds, for example, all its gametes wou ...
Dihybrid cross are explained by Mendel`s 3rd law: Law of Assortment
... equatorial plate . So for the two traits YyRr (Round yellow seeds) of one parent, there are four possible ways for chromosome traits to divide for gametes: ...
... equatorial plate . So for the two traits YyRr (Round yellow seeds) of one parent, there are four possible ways for chromosome traits to divide for gametes: ...
artificial yeast chromosomes
... without SUP11, the yeast turn red; with one copy, they are pink, and with two or more copies they are white. The yeast you will be working with are homozygous for ade2-101, so two copies of the SUP11 gene are necessary to fully suppress the mutation. The strains that you will be working with have ha ...
... without SUP11, the yeast turn red; with one copy, they are pink, and with two or more copies they are white. The yeast you will be working with are homozygous for ade2-101, so two copies of the SUP11 gene are necessary to fully suppress the mutation. The strains that you will be working with have ha ...
Genetic Analyses of Agronomic Traits Controlled by Wheat
... determined by heading date; however, none of the previous research was designed to determine the number of loci affecting the trait. A unimodal normal distribution was observed for grain yield, kernel number per spike, kernel weight, spike number per square meter, grain volume weight, and plant heig ...
... determined by heading date; however, none of the previous research was designed to determine the number of loci affecting the trait. A unimodal normal distribution was observed for grain yield, kernel number per spike, kernel weight, spike number per square meter, grain volume weight, and plant heig ...
Genetics
... • Cell: Building blocks of the human body, approximately 50 trillion of them • Cell nucleus: brain of the cell, it makes amino acids that form proteins • Chromosome: strands of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid contained in the nucleus of every cell, a map of how to make amino acids ...
... • Cell: Building blocks of the human body, approximately 50 trillion of them • Cell nucleus: brain of the cell, it makes amino acids that form proteins • Chromosome: strands of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid contained in the nucleus of every cell, a map of how to make amino acids ...
Recombination - CCGB | index
... molecules to produce new DNA molecules • Reciprocal recombination: new DNA molecules carry genetic information from both parental molecules. • Gene conversion: one way transfer of information, resulting in an allele on one parental chromosome being changed to the allele from the other homologous chr ...
... molecules to produce new DNA molecules • Reciprocal recombination: new DNA molecules carry genetic information from both parental molecules. • Gene conversion: one way transfer of information, resulting in an allele on one parental chromosome being changed to the allele from the other homologous chr ...
Chapter 15 ppt
... Recombination of Unlinked Genes: Independent Assortment of Chromosomes • Mendel observed that combinations of traits in some offspring differ from either parent • Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotypes are called parental types • Offspring with nonparental phenotypes (ne ...
... Recombination of Unlinked Genes: Independent Assortment of Chromosomes • Mendel observed that combinations of traits in some offspring differ from either parent • Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotypes are called parental types • Offspring with nonparental phenotypes (ne ...
FREE Sample Here
... the kits sold by scientific supply companies are even better than drawings. Have the students identify such features as a centromere, a short arm of a chromatid, a pair of chromosomes, two non-sister chromatids, etc. Students commonly report that such exercises help them greatly to visualize and und ...
... the kits sold by scientific supply companies are even better than drawings. Have the students identify such features as a centromere, a short arm of a chromatid, a pair of chromosomes, two non-sister chromatids, etc. Students commonly report that such exercises help them greatly to visualize and und ...
EWORP Alien Genetics
... Introduction: Background: Have you ever wondered why so many people can look different from each other, even when they are closely related? Our particular combination of features makes us unique. Just like in real life, the different combinations are created by the union of egg and sperm cells durin ...
... Introduction: Background: Have you ever wondered why so many people can look different from each other, even when they are closely related? Our particular combination of features makes us unique. Just like in real life, the different combinations are created by the union of egg and sperm cells durin ...
Genetics - Biology Junction
... 1. Two genetic disorders resulting from faulty genes are Huntington disease and cystic fibrosis. 2 Researchers are tests that can detect particular DNA base sequencing that may be able to identify individuals who may either have a genetic disease or if they are carriers to a particular genetic disea ...
... 1. Two genetic disorders resulting from faulty genes are Huntington disease and cystic fibrosis. 2 Researchers are tests that can detect particular DNA base sequencing that may be able to identify individuals who may either have a genetic disease or if they are carriers to a particular genetic disea ...
Chapter 8
... Fertilization after nondisjunction yields zygotes with altered numbers of chromosomes ...
... Fertilization after nondisjunction yields zygotes with altered numbers of chromosomes ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... different tissues or organs. Autosomal dominant traits are commonly pleiotropic. The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome is made based a triad of cardiovascular (aortic aneurysm, aortic insufficiency), skeletal (long limbs, fingers and toes, loose-jointedness), and eye (dislocated lens) findings. Although ...
... different tissues or organs. Autosomal dominant traits are commonly pleiotropic. The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome is made based a triad of cardiovascular (aortic aneurysm, aortic insufficiency), skeletal (long limbs, fingers and toes, loose-jointedness), and eye (dislocated lens) findings. Although ...
Class Notes On Heredity
... Chromatin condenses into ziti like chromosomes (DNA wrapped around histone proteins) Therefore genes are located on chromosomes A duplicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids(each chromatid is one half of the X) ...
... Chromatin condenses into ziti like chromosomes (DNA wrapped around histone proteins) Therefore genes are located on chromosomes A duplicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids(each chromatid is one half of the X) ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... B) The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II. C) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distri ...
... B) The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II. C) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distri ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... B) The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II. C) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distri ...
... B) The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II. C) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distri ...
lecture 11, part 1, beyond mendel, 042809c
... The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is often used in genetics research because it can be inexpensively grown, and can produce several generations within a few months. In fruit flies, the results of crossing-over patterns can be used to map the location of genes on chromosomes. The farther apart ...
... The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is often used in genetics research because it can be inexpensively grown, and can produce several generations within a few months. In fruit flies, the results of crossing-over patterns can be used to map the location of genes on chromosomes. The farther apart ...
Beckwith-Wiedemann and Russel
... EGL is an academic, not-for-profit organization and a global leader in genetic testing. Associated with the prestigious Emory University School of Medicine, EGL has fully integrated biochemical, cytogenetics, and molecular laboratories, employing the latest technologies for one of the most comprehen ...
... EGL is an academic, not-for-profit organization and a global leader in genetic testing. Associated with the prestigious Emory University School of Medicine, EGL has fully integrated biochemical, cytogenetics, and molecular laboratories, employing the latest technologies for one of the most comprehen ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... a. This genetic blood disorder results from a defective copy of a gene found on chromosome 8. b. Symptoms include: spherical shape of red blood cells, and enlarged spleen. c. Hereditary spherocytosis affects 1 in 5,000 people and is one of the most common hereditary blood disorders. H. Testing for G ...
... a. This genetic blood disorder results from a defective copy of a gene found on chromosome 8. b. Symptoms include: spherical shape of red blood cells, and enlarged spleen. c. Hereditary spherocytosis affects 1 in 5,000 people and is one of the most common hereditary blood disorders. H. Testing for G ...
ch # 11 review questions
... to form green. (blue and yellow) Then, have them recall an example they have studied in which colors blended and identify the inheritance pattern. (incomplete dominance) Lead students to hypothesize that incomplete dominance could have led to the green color of the parents. To test this idea, have s ...
... to form green. (blue and yellow) Then, have them recall an example they have studied in which colors blended and identify the inheritance pattern. (incomplete dominance) Lead students to hypothesize that incomplete dominance could have led to the green color of the parents. To test this idea, have s ...
Mutations Notes
... 4. Silent Mutations a) mutations that ______ the DNA sequence, but ______ ______ the ______ ____ sequence produced in protein synthesis. – This has NO effect on an organism. Why? ...
... 4. Silent Mutations a) mutations that ______ the DNA sequence, but ______ ______ the ______ ____ sequence produced in protein synthesis. – This has NO effect on an organism. Why? ...
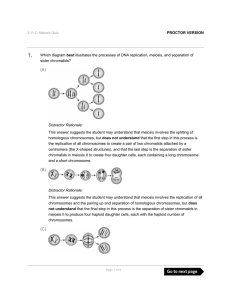
(A) (B) (C)
... This answer suggests the student may understand that there are many more autosomal chromosomes than sex chromosomes in humans, but does not understand that this would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques that can easily locate the marker ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that there are many more autosomal chromosomes than sex chromosomes in humans, but does not understand that this would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques that can easily locate the marker ...
AS 90948 Science 1.9 AS 90948
... 5. Instructions carried on DNA. 6. Genetic variation describes the differences in the DNA of individuals, which give rise to individuals that vary in their structures, life processes and behaviours. Meiosis contributes to genetic variation by mixing DNA when pairs of chromosomes come together, and ...
... 5. Instructions carried on DNA. 6. Genetic variation describes the differences in the DNA of individuals, which give rise to individuals that vary in their structures, life processes and behaviours. Meiosis contributes to genetic variation by mixing DNA when pairs of chromosomes come together, and ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)