Meiosis and Variation Guided Notes
... We need to produce cells with ½ the amount of chromosomes (23). We do that through Meiosis! ...
... We need to produce cells with ½ the amount of chromosomes (23). We do that through Meiosis! ...
Mutations
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
... D. Regulation and Development- especially important in shaping the way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that ...
Use of paper chromosomes: Illustration of meiosis and crossing over
... Use of paper chromosomes: Illustration of meiosis and crossing over. Answer all bold questions IQIA in your journal. Directions for chromosome cut-outs: 1. Observe the chromosomes in set one with the symbols for maternal (from mom) and paternal (from dad) AND color maternal chromosomes red (or pink) ...
... Use of paper chromosomes: Illustration of meiosis and crossing over. Answer all bold questions IQIA in your journal. Directions for chromosome cut-outs: 1. Observe the chromosomes in set one with the symbols for maternal (from mom) and paternal (from dad) AND color maternal chromosomes red (or pink) ...
Complementation
... homologous to X chromosome. Crossing over can occur there during meiosis. Because of this, genes in this location do not behave as sex-linked traits, thus said to be pseudoautosomal because they behave like genes on autosomes rather than sex chromosomes. ...
... homologous to X chromosome. Crossing over can occur there during meiosis. Because of this, genes in this location do not behave as sex-linked traits, thus said to be pseudoautosomal because they behave like genes on autosomes rather than sex chromosomes. ...
File ap notes chapter 15
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
Genetic disorder/testing PPT
... what form of the gene a person has. This testing can be done on embryonic stem cells early in the development or for invitro fertilization OR it can be done on cells in amniotic fluid. • Specific to one gene/protein, but many tests can be run on one sample at the same time. DNA chips are being devel ...
... what form of the gene a person has. This testing can be done on embryonic stem cells early in the development or for invitro fertilization OR it can be done on cells in amniotic fluid. • Specific to one gene/protein, but many tests can be run on one sample at the same time. DNA chips are being devel ...
meiosislab
... 1. Obtain 8 pieces of paper, 4 of each color and 4 paper clips. (in the envelopes on the lab tables) 2. Identify a single gene on each chromosome of the 4 original chromosomes by writing the following letters on each: B = Brown eye, b= blue eyes (on the larger chromosomes), S = dark skin, s= light s ...
... 1. Obtain 8 pieces of paper, 4 of each color and 4 paper clips. (in the envelopes on the lab tables) 2. Identify a single gene on each chromosome of the 4 original chromosomes by writing the following letters on each: B = Brown eye, b= blue eyes (on the larger chromosomes), S = dark skin, s= light s ...
Depat.Anato Genetic/lec 5 Dr.sarab H. 2015 Sex Determination in Man
... In human beings, the presence of Y chromosome determines maleness and its absence determines femaleness. So, males are XY and females are XX in human beings. However, in 1986, certain peculiar cases have been reported which were found to be males with XX chromosomes and females with XY chromosomes. ...
... In human beings, the presence of Y chromosome determines maleness and its absence determines femaleness. So, males are XY and females are XX in human beings. However, in 1986, certain peculiar cases have been reported which were found to be males with XX chromosomes and females with XY chromosomes. ...
Chapter Notes
... Chromosomes within the nucleus are found in pairs. Most humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (so 46 chromosomes) including one pair that determines gender. (XX for female and XY for male) ...
... Chromosomes within the nucleus are found in pairs. Most humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (so 46 chromosomes) including one pair that determines gender. (XX for female and XY for male) ...
1. Changes to the number of chromosomes
... This results in the formation of abnormal gametes. Often these gametes will be unable to form viable embryos because the organism cannot cope with the alteration in genetic material. However, a small number of humans survive for a short time with an extra chromosome 17 or 18. People born with an ext ...
... This results in the formation of abnormal gametes. Often these gametes will be unable to form viable embryos because the organism cannot cope with the alteration in genetic material. However, a small number of humans survive for a short time with an extra chromosome 17 or 18. People born with an ext ...
Sex-determining Region of the Y chromosome
... 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance ...
... 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance ...
Genetics 3 – Aneuploidies and Other Chromosome
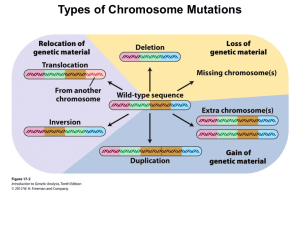
... There are 3 main types of chromosome aberrations: • Structural – translocations, deletions, insertions, inversions, rings • Numerical – aneuploidy, loss or gain • Mosaicism – different cell lines Aberrations cause: - 60% of all early spontaneous miscarriages. - 4.5% of all still births (dead when bo ...
... There are 3 main types of chromosome aberrations: • Structural – translocations, deletions, insertions, inversions, rings • Numerical – aneuploidy, loss or gain • Mosaicism – different cell lines Aberrations cause: - 60% of all early spontaneous miscarriages. - 4.5% of all still births (dead when bo ...
1. Changes to the number of chromosomes
... 2. Changes to the structure of chromosomes These changes affect whole regions of a chromosome and will involve many genes. (There are 30,000 genes in humans shared between the 23 chromosomes which form one chromosome set. Remember we have 2 chromosome sets in all our diploid cells and get one copy o ...
... 2. Changes to the structure of chromosomes These changes affect whole regions of a chromosome and will involve many genes. (There are 30,000 genes in humans shared between the 23 chromosomes which form one chromosome set. Remember we have 2 chromosome sets in all our diploid cells and get one copy o ...
Brooker Chapter 2
... – 3. The nuclei of most eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes that are found in homologous pairs – 4. During the formation of gametes, different types of (nonhomologous) chromosomes segregate independently – 5. Each parent contributes one set of chromosomes to its ...
... – 3. The nuclei of most eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes that are found in homologous pairs – 4. During the formation of gametes, different types of (nonhomologous) chromosomes segregate independently – 5. Each parent contributes one set of chromosomes to its ...
variation
... The genotype of an organism is the alleles it has for a characteristic. A dominant allele will mask the effect of a recessive allele A recessive allele will only be shown in the phenotype if two copies of it are inherited If the two alleles an organism inherits are identical it is said to be ...
... The genotype of an organism is the alleles it has for a characteristic. A dominant allele will mask the effect of a recessive allele A recessive allele will only be shown in the phenotype if two copies of it are inherited If the two alleles an organism inherits are identical it is said to be ...
Chapter 15
... ◦ For a recessive sex-linked trait to be expressed A female needs two copies of the allele A male needs only one copy of the allele ...
... ◦ For a recessive sex-linked trait to be expressed A female needs two copies of the allele A male needs only one copy of the allele ...
DNA Mutations and Disorders 2010
... • Any change in a gene or chromosome. • Most are natural and have no effect on the organism- can promote good genetic diversity • Some are harmful • Some are lethal (cause death in offspring) • Some are good for the organism (ex: some mosquitoes have a gene mutation that makes them resistant to pest ...
... • Any change in a gene or chromosome. • Most are natural and have no effect on the organism- can promote good genetic diversity • Some are harmful • Some are lethal (cause death in offspring) • Some are good for the organism (ex: some mosquitoes have a gene mutation that makes them resistant to pest ...
Genetics 275 Notes
... -in general an organism has the specific chromsome complement which comprises its species specific genome -these chromosomes are characteristically present as homologous pairs -chromosome pairs are qualitively different from each other -the characteristic chromosome number along with their character ...
... -in general an organism has the specific chromsome complement which comprises its species specific genome -these chromosomes are characteristically present as homologous pairs -chromosome pairs are qualitively different from each other -the characteristic chromosome number along with their character ...
Causes of Variation PPT
... What is the difference between a chromosome and a gene? What is the difference between the terms haploid and diploid? How many pairs of chromosomes do we have? What are pair number 23 called? What is the difference between the male and the female karyotype? ...
... What is the difference between a chromosome and a gene? What is the difference between the terms haploid and diploid? How many pairs of chromosomes do we have? What are pair number 23 called? What is the difference between the male and the female karyotype? ...
Chapter 27: Human Genetics Vocabulary
... cY colorblind male 5 Males inherit the gene for color vision from their mother only. Females inherit a gene from both their mother and father. ...
... cY colorblind male 5 Males inherit the gene for color vision from their mother only. Females inherit a gene from both their mother and father. ...
2 Sex chromosomes
... a. Genes located on sex-chromosomes called sex-linked genes b. Many species have specialized sex chromosomes 1). In mammals and some other animals, individuals with XX are female and XY are male 2). X chromosome much larger than Y ...
... a. Genes located on sex-chromosomes called sex-linked genes b. Many species have specialized sex chromosomes 1). In mammals and some other animals, individuals with XX are female and XY are male 2). X chromosome much larger than Y ...
Sex linked Traits
... linkage has to do with the X and Y sex chromosomes. These not only carry the genes that determine male and female traits but also those for some other characteristics as well. Genes that are carried by either sex chromosome are said to be sex linked. ...
... linkage has to do with the X and Y sex chromosomes. These not only carry the genes that determine male and female traits but also those for some other characteristics as well. Genes that are carried by either sex chromosome are said to be sex linked. ...
Genes
... Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome i ...
... Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome i ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)