Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... which stands for (average, alternating) current, and DC, which stands for (different, direct) current. A good example of a DC voltage source is a (battery, generator), where charges move (one, either) direction. A good example of an AC voltage source is a (battery, generator), where charges (switch, ...
... which stands for (average, alternating) current, and DC, which stands for (different, direct) current. A good example of a DC voltage source is a (battery, generator), where charges move (one, either) direction. A good example of an AC voltage source is a (battery, generator), where charges (switch, ...
Ohm
... Unit = Ohm (Ω) When electrons flow through a resistor, it causes a loss of electric potential (voltage drop) ...
... Unit = Ohm (Ω) When electrons flow through a resistor, it causes a loss of electric potential (voltage drop) ...
Lec #10 ppt
... 3. Be sure to put your discussion section leader’s name on your homework to facilitate its return to you. 4. HW 5 is due at 12:00 noon Tuesday Oct. 4 in 42/100 boxes in 240 Cory. Solutions will be put on top of the boxes at 1 pm that day. 5. Midterm 1 will not include a problem on 2nd-order transien ...
... 3. Be sure to put your discussion section leader’s name on your homework to facilitate its return to you. 4. HW 5 is due at 12:00 noon Tuesday Oct. 4 in 42/100 boxes in 240 Cory. Solutions will be put on top of the boxes at 1 pm that day. 5. Midterm 1 will not include a problem on 2nd-order transien ...
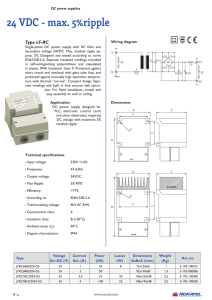
24 VDC - max. 5%ripple
... Single-phase DC power supply with RC filter and secondary voltage 24VDC. Max. residual ripple approx. 5%. Designed and tested according to norm EN61558-2-6. Separate insulated windings moulded in self-extinguishing polyurethane and capsulated in plastic, IP44. Insulation class II. Protected against ...
... Single-phase DC power supply with RC filter and secondary voltage 24VDC. Max. residual ripple approx. 5%. Designed and tested according to norm EN61558-2-6. Separate insulated windings moulded in self-extinguishing polyurethane and capsulated in plastic, IP44. Insulation class II. Protected against ...
Transducer types
... • Bimetallic switch (electro-mechanical) – used in thermostats. Can be “creep” or “snap” action. Creep-action: coil or spiral that unwinds or coils with changing temperature ...
... • Bimetallic switch (electro-mechanical) – used in thermostats. Can be “creep” or “snap” action. Creep-action: coil or spiral that unwinds or coils with changing temperature ...
S3homework 2 - Eyemouth High School
... Help sessions every morning 08.20am-08.50am and Thursday 1.25pm-1.55pm Final Date for Handing in Exercise is 11th December 2015 Notes All diagrams must be labelled and drawn using a ruler The minimum size for diagrams is 8cm by 5cm All questions must be answered in the homework jotter Read t ...
... Help sessions every morning 08.20am-08.50am and Thursday 1.25pm-1.55pm Final Date for Handing in Exercise is 11th December 2015 Notes All diagrams must be labelled and drawn using a ruler The minimum size for diagrams is 8cm by 5cm All questions must be answered in the homework jotter Read t ...
Ohm`s Law
... Practice Problem A lightbulb with resistance of 100 is plugged into a 120 V outlet. What is the current flowing through the bulb? ...
... Practice Problem A lightbulb with resistance of 100 is plugged into a 120 V outlet. What is the current flowing through the bulb? ...
Powerpoint Slides
... each will be the same and will be in phase. This means that the individual voltage drops across each individual element will not be in phase with the current or the total applied voltage. To account for these phase differences we must VL treat the voltages as if they are vectors. Voltage across the ...
... each will be the same and will be in phase. This means that the individual voltage drops across each individual element will not be in phase with the current or the total applied voltage. To account for these phase differences we must VL treat the voltages as if they are vectors. Voltage across the ...
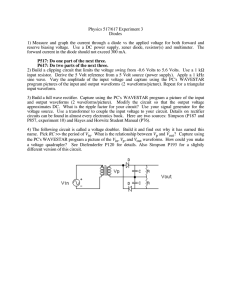
AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
Lecture 14
... An AC voltage in one coil induces a voltage in the other. Ratio of voltages = ratio of turns. (more turns = higher voltage). ...
... An AC voltage in one coil induces a voltage in the other. Ratio of voltages = ratio of turns. (more turns = higher voltage). ...
KIRCHOFF`S VOLTAGE LAW: EXAMPLE 1
... (b) To find IR2, we can use either Loop 2 or Loop 3. Let’s apply KVL to Loop 2. ...
... (b) To find IR2, we can use either Loop 2 or Loop 3. Let’s apply KVL to Loop 2. ...
OSCILLATOR, VERY LOW FREQUENCY - 0.1Hz
... The IEC Very Low Freq. Oscillator is a fixed very low frequency sine wave oscillator which is useful for providing very slow sine wave signals for special experiments. The input is 12V.AC only and the output is 15Volt peak to peak at 5mA max. load. The starting of the oscillation is controlled by a ...
... The IEC Very Low Freq. Oscillator is a fixed very low frequency sine wave oscillator which is useful for providing very slow sine wave signals for special experiments. The input is 12V.AC only and the output is 15Volt peak to peak at 5mA max. load. The starting of the oscillation is controlled by a ...
CR circuit - schoolphysics
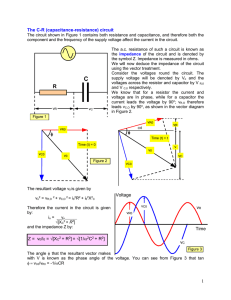
... The C-R (capacitance-resistance) circuit The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit ...
... The C-R (capacitance-resistance) circuit The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit ...
Parallel Circuits Worksheet File
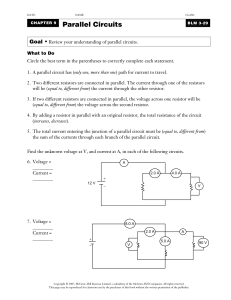
... Goal • Review your understanding of parallel circuits. What to Do Circle the best term in the parentheses to correctly complete each statement. 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through on ...
... Goal • Review your understanding of parallel circuits. What to Do Circle the best term in the parentheses to correctly complete each statement. 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through on ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.