LM383 datasheet
... RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 13.8V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 14.4V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% VS e 16V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% ...
... RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 13.8V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 14.4V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% VS e 16V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% ...
ECE 3144 Lecture 4
... • Circuits with dependent sources – treat the dependent source as though it were an independent source. – write the equations that specifies the relationship of the dependent2 source to the controlling ...
... • Circuits with dependent sources – treat the dependent source as though it were an independent source. – write the equations that specifies the relationship of the dependent2 source to the controlling ...
LM383/LM383A 7W Audio Power Amplifier
... RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 13.8V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 14.4V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% VS e 16V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% ...
... RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 13.8V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% VS e 14.4V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% VS e 16V, f e 1 kHz RL e 4X, THD e 10% RL e 2X, THD e 10% RL e 1.6X, THD e 10% ...
Voltage/current dividers
... right, if RL is attached in parallel with R2, the voltage across R1 doubles. What is the value of RL? From the two expressions for v’R1 ...
... right, if RL is attached in parallel with R2, the voltage across R1 doubles. What is the value of RL? From the two expressions for v’R1 ...
ACBEL POLYTECH INC. Features MPR2700HB Mid Power Rectifier
... adjustable and therefore suitable for any tele- ...
... adjustable and therefore suitable for any tele- ...
Impedance
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
Series and Parallel Circuits 2 - Instructor Outline
... power are reviewed and discussed in further detail. Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule and Junction Rule are reviewed along with a qualitative discussion of Ohm’s Law. The connection is made between the Loop Rule and the conservative nature of the electric force, a concept previously introduced for gravity. The ...
... power are reviewed and discussed in further detail. Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule and Junction Rule are reviewed along with a qualitative discussion of Ohm’s Law. The connection is made between the Loop Rule and the conservative nature of the electric force, a concept previously introduced for gravity. The ...
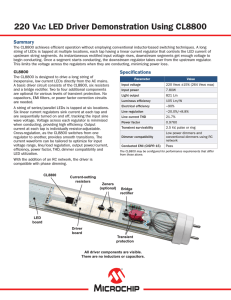
Reverse polarity and overvoltage protection
... It is possible to automatically disconnect a circuit when the input voltage exceeds a predefined level. This is different from parallel transient voltage suppressor and fuse. Blow fuses have the obvious problem of being a one-time devices. PTC resettable fuses tend to be slow and they can conduct si ...
... It is possible to automatically disconnect a circuit when the input voltage exceeds a predefined level. This is different from parallel transient voltage suppressor and fuse. Blow fuses have the obvious problem of being a one-time devices. PTC resettable fuses tend to be slow and they can conduct si ...
Here we`ll find the initial value of capacitor voltage - Rose
... Its current is the time rate of change of its voltage * its capacitance. Rewrite the equation to solve for what we want. This equation is true at t=0, so replace t with 0 in these cases. If we can find ic(0), we’ll know dvc(0) / dt. ic(0) needs to be defined according to passive sign convention. Not ...
... Its current is the time rate of change of its voltage * its capacitance. Rewrite the equation to solve for what we want. This equation is true at t=0, so replace t with 0 in these cases. If we can find ic(0), we’ll know dvc(0) / dt. ic(0) needs to be defined according to passive sign convention. Not ...
Voltage - Madison County Schools
... resulting current is 0.40 amps, what is the resistance of the brake light? ...
... resulting current is 0.40 amps, what is the resistance of the brake light? ...
Test Procedure for the LV5683PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... Refer to Fig1, In initial setting, “USB_EN”, “SWU_EN”, “AUDIO_EN” pins are shorted GND. And USB, AUDIO and SWU-OUT are low potential. 2. Measurement Connect VCC/VCC1 cable and GND cable. Bias VCC/VCC1 voltage. Regarding bias voltage range, refer to Application note. Next step remove 3 “Shorted Ring” ...
... Refer to Fig1, In initial setting, “USB_EN”, “SWU_EN”, “AUDIO_EN” pins are shorted GND. And USB, AUDIO and SWU-OUT are low potential. 2. Measurement Connect VCC/VCC1 cable and GND cable. Bias VCC/VCC1 voltage. Regarding bias voltage range, refer to Application note. Next step remove 3 “Shorted Ring” ...
Physics 184 Exp 2 Ohms
... where V is the voltage in volts, I is the current in am peres, and R is the proportionality constant which is known as the resistance of the conductor whose unit is in ohms. The power dissipated in the conductor is the product of the current in the conductor and the voltage across it: P = I V, where ...
... where V is the voltage in volts, I is the current in am peres, and R is the proportionality constant which is known as the resistance of the conductor whose unit is in ohms. The power dissipated in the conductor is the product of the current in the conductor and the voltage across it: P = I V, where ...
View as Printable PDF
... (V), and for safety purposes, the voltage of most everyday devices we commonly use is relatively low, while industries and transmission lines are relatively high. A simple way to measure voltage is with a voltmeter. [red to positive (+) and black to negative (-)] Some voltmeters can measure a wide r ...
... (V), and for safety purposes, the voltage of most everyday devices we commonly use is relatively low, while industries and transmission lines are relatively high. A simple way to measure voltage is with a voltmeter. [red to positive (+) and black to negative (-)] Some voltmeters can measure a wide r ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.