Output Characteristics (DC)
... output current to be higher than the calibrated setting, and it will actively reduce the output voltage in accordance to the overload. The removal of the overload / short circuit will result in the output voltage being increased to the calibrated value. Regulated auxiliary outputs will also reduce t ...
... output current to be higher than the calibrated setting, and it will actively reduce the output voltage in accordance to the overload. The removal of the overload / short circuit will result in the output voltage being increased to the calibrated value. Regulated auxiliary outputs will also reduce t ...
95MET-2
... 4. (a) Sketch a circuit diagram of an emergency generator power supply system suitable for passenger vessel: including in your diagram the essential services supplied. (b) With reference to an emergency generator state: (i) Its location; (ii) Methods of automatic starting; (iii) The time available f ...
... 4. (a) Sketch a circuit diagram of an emergency generator power supply system suitable for passenger vessel: including in your diagram the essential services supplied. (b) With reference to an emergency generator state: (i) Its location; (ii) Methods of automatic starting; (iii) The time available f ...
Document
... The power input into the primary equals the power output at the secondary. ! I1ΔV1 = I2ΔV2 ! The equivalent resistance of the load resistance when viewed from the primary is given by the square of the turns ratio. ...
... The power input into the primary equals the power output at the secondary. ! I1ΔV1 = I2ΔV2 ! The equivalent resistance of the load resistance when viewed from the primary is given by the square of the turns ratio. ...
Electricity Electric Circuits
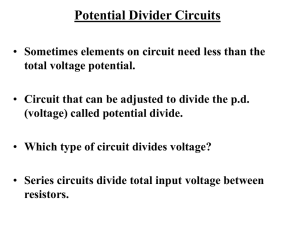
... voltage drop across the potentiometer and voltage drop across the bulb in a circuit. ...
... voltage drop across the potentiometer and voltage drop across the bulb in a circuit. ...
IMPLEMENTATION AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF A
... Electronic systems operate properly as long as the supply voltage stays within a consistent range. There are several types of voltage fluctuations that can cause the systems to malfunction, including surges and spikes, sags, harmonic distortions, and momentary disruptions. Among them, voltage sag is ...
... Electronic systems operate properly as long as the supply voltage stays within a consistent range. There are several types of voltage fluctuations that can cause the systems to malfunction, including surges and spikes, sags, harmonic distortions, and momentary disruptions. Among them, voltage sag is ...
Ohm`s Law Practice Problems (part of 1.2.3) The relationship
... developed by Georg Simon Ohm and is known today as Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that the direct current flowing in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the circuit. In other words, an electric circuit represents the flow of electrons along a conductive pathway betwee ...
... developed by Georg Simon Ohm and is known today as Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that the direct current flowing in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the circuit. In other words, an electric circuit represents the flow of electrons along a conductive pathway betwee ...
1 A circuit consists of three identical lamps connected to a battery
... YEAR 12 PHYSICS Unit 3: Motion in one and two Dimensions ...
... YEAR 12 PHYSICS Unit 3: Motion in one and two Dimensions ...
INVERTERS - SolarEdge
... SE9KUS / SE14.4KUS(1) SE9KUS OUTPUT Rated AC Power Output Maximum AC Power Output AC Output Line Connections AC Output Voltage Minimum-NominalMaximum(2) (L-N) AC Output Voltage Minimum-NominalMaximum(2) (L-L) AC Frequency Min-Nom-Max(2) Max. Continuous Output Current (per Phase) ...
... SE9KUS / SE14.4KUS(1) SE9KUS OUTPUT Rated AC Power Output Maximum AC Power Output AC Output Line Connections AC Output Voltage Minimum-NominalMaximum(2) (L-N) AC Output Voltage Minimum-NominalMaximum(2) (L-L) AC Frequency Min-Nom-Max(2) Max. Continuous Output Current (per Phase) ...
Photoconductivity of CdS
... When a photoconductive material is connected as part of a circuit, it functions as a resistor whose resistance depends on the light intensity. In this context the material is called a photoresistor. Fig.1 depicts the current flow in a Fig.1 Working of a photoresistor photoresistor when exposed to li ...
... When a photoconductive material is connected as part of a circuit, it functions as a resistor whose resistance depends on the light intensity. In this context the material is called a photoresistor. Fig.1 depicts the current flow in a Fig.1 Working of a photoresistor photoresistor when exposed to li ...
Direct current - Sackville School
... In the UK, the frequency of mains electricity is 50 hertz: this alternating current flows backwards and forwards 50 times per second. This frequency is the same at any point in the electricity supply system but the voltage varies in different parts of the national grid. The voltage of mains electric ...
... In the UK, the frequency of mains electricity is 50 hertz: this alternating current flows backwards and forwards 50 times per second. This frequency is the same at any point in the electricity supply system but the voltage varies in different parts of the national grid. The voltage of mains electric ...
Investigation Ohm’s Law
... curved? Which way does the trend go?) 2. Use the cursor keys different currents used. ...
... curved? Which way does the trend go?) 2. Use the cursor keys different currents used. ...
power quality measurement with capacitor voltage
... from a conventional device in terms of a wide bandwidth frequency response is of offered by a resistive-capacitor divider (RCD), which is very expensive, has a very limited output and would not normally be present in a substation environment and does not meet safety requirements for isolation betwee ...
... from a conventional device in terms of a wide bandwidth frequency response is of offered by a resistive-capacitor divider (RCD), which is very expensive, has a very limited output and would not normally be present in a substation environment and does not meet safety requirements for isolation betwee ...
Charging System Fundamentals
... that are stationary As the rotor turns in side the stator ring– current is induced (produced) making current ...
... that are stationary As the rotor turns in side the stator ring– current is induced (produced) making current ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.