4. Replace the BJT with one of its small
... Here the operating conditions of the transistor are zero input base current ( IB ), zero output collector current ( IC ) and maximum collector voltage ( VCE ) which results in a large depletion layer and no current flowing through the device. Therefore the transistor is ...
... Here the operating conditions of the transistor are zero input base current ( IB ), zero output collector current ( IC ) and maximum collector voltage ( VCE ) which results in a large depletion layer and no current flowing through the device. Therefore the transistor is ...
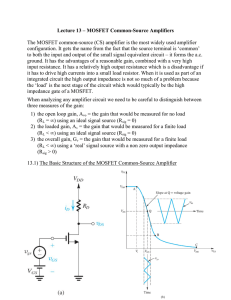
MOSFET Common Source Amplifiers
... input resistance. It has a relatively high output resistance which is a disadvantage if it has to drive high currents into a small load resistor. When it is used as part of an integrated circuit the high output impedance is not so much of a problem because the ‘load’ is the next stage of the circuit ...
... input resistance. It has a relatively high output resistance which is a disadvantage if it has to drive high currents into a small load resistor. When it is used as part of an integrated circuit the high output impedance is not so much of a problem because the ‘load’ is the next stage of the circuit ...
J210 MMBFJ210 MMBFJ211 J211
... N-Channel RF Amplifier This device is designed for HF/VHF mixer/amplifier and applications where Process 50 is not adequate. Sufficient gain and low noise for sensitive receivers. Sourced from Process 90. ...
... N-Channel RF Amplifier This device is designed for HF/VHF mixer/amplifier and applications where Process 50 is not adequate. Sufficient gain and low noise for sensitive receivers. Sourced from Process 90. ...
Introduction
... conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
... conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
Document
... of the two transformers are in series and the secondary windings are in parallel. With optimized dual-phase-shift modulation strategies, zero voltage switching (ZVS) is achieved for both the primary- and secondary-side power MOSFETs in a wide load range. The reverse recovery problem of rectifying di ...
... of the two transformers are in series and the secondary windings are in parallel. With optimized dual-phase-shift modulation strategies, zero voltage switching (ZVS) is achieved for both the primary- and secondary-side power MOSFETs in a wide load range. The reverse recovery problem of rectifying di ...
DN306 - High Performance Op Amps Deliver Precision Waveform Synthesis
... I/Q modulator) or RF transformers. For such applications, the LTC1668 differential current outputs can be amplified with twin transimpedance stages as shown in Figure 2, which offers the opportunity to reduce the DAC current without loss of signal swing. The circuit shown has the DAC full-scale curr ...
... I/Q modulator) or RF transformers. For such applications, the LTC1668 differential current outputs can be amplified with twin transimpedance stages as shown in Figure 2, which offers the opportunity to reduce the DAC current without loss of signal swing. The circuit shown has the DAC full-scale curr ...
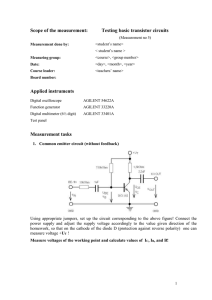
Lab 10 - ece.unm.edu
... 1. Construct the CC amplifier of Figure 10-1. Remember RS is installed in addition to the internal 50 resistance of the function generator. Verify the amplifier operation by measuring the Q-point and midband voltage gain. Monitor the output on the oscilloscope to make sure the waveform is not clippe ...
... 1. Construct the CC amplifier of Figure 10-1. Remember RS is installed in addition to the internal 50 resistance of the function generator. Verify the amplifier operation by measuring the Q-point and midband voltage gain. Monitor the output on the oscilloscope to make sure the waveform is not clippe ...
THE PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
... such as contact potentials of dissimilar metals, that may distort this value. The collector is a circular wire constructed so that a light beam can hit the center of the emitter without also hitting the collector. If light does hit the collector, then the photoelectric effect can also occur at the c ...
... such as contact potentials of dissimilar metals, that may distort this value. The collector is a circular wire constructed so that a light beam can hit the center of the emitter without also hitting the collector. If light does hit the collector, then the photoelectric effect can also occur at the c ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION In this application, the ADL5315 sets the bias voltage on the input PIN photodiode. This voltage is delivered at the INPT pin of the AD8305 and is controlled by the voltage at the VSET pin. VSET is driven by the on-board reference, VSREF, which is equal to VPOS − 1 V. The input c ...
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION In this application, the ADL5315 sets the bias voltage on the input PIN photodiode. This voltage is delivered at the INPT pin of the AD8305 and is controlled by the voltage at the VSET pin. VSET is driven by the on-board reference, VSREF, which is equal to VPOS − 1 V. The input c ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... We can turn off the power supplies then find the equivalent impedance ZTH. To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. ...
... We can turn off the power supplies then find the equivalent impedance ZTH. To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. ...
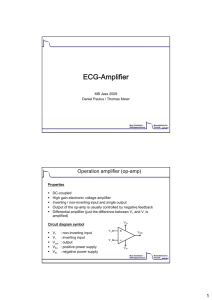
ECG-Amplifier
... Ideal op-amps amplify only the voltage difference in its inputs Real op-amps amplify also voltage that is common to both inputs (common mode gain) Minimizing this common mode gain (i.e. maximizing the common mode rejection ratio, ’CMRR’) is important for most applications ...
... Ideal op-amps amplify only the voltage difference in its inputs Real op-amps amplify also voltage that is common to both inputs (common mode gain) Minimizing this common mode gain (i.e. maximizing the common mode rejection ratio, ’CMRR’) is important for most applications ...
A LED Exercise
... • Remember that in these amplifiers the base-emitter voltage is always close to Vbe = 0.7 V when the transistor is biased for linear amplification. But the voltage across the emitter resistor must be added to the zero line to obtain the actual ‘base voltage’ Vb. • The relation between the collector ...
... • Remember that in these amplifiers the base-emitter voltage is always close to Vbe = 0.7 V when the transistor is biased for linear amplification. But the voltage across the emitter resistor must be added to the zero line to obtain the actual ‘base voltage’ Vb. • The relation between the collector ...
Emf and Terminal Voltage
... Emf = terminal voltage when I = 0 since Ir = 0 Example A battery labeled 12.0 V supplies 1.90 A to a 6.00-ohm. What is the terminal voltage of the battery? What is its internal resistance? Solution: emf = 12.0 V I = 1.90 A R = 6.00 ohm V = emf-Ir = IR ...
... Emf = terminal voltage when I = 0 since Ir = 0 Example A battery labeled 12.0 V supplies 1.90 A to a 6.00-ohm. What is the terminal voltage of the battery? What is its internal resistance? Solution: emf = 12.0 V I = 1.90 A R = 6.00 ohm V = emf-Ir = IR ...
The other night, a full moon emerged over the flat, wet Louisiana
... assumed that the reference resistor behaves as a pure resistor—no inductance or capacitance. Such resistors are available as long as the frequency is not too high (they are called non-inductive resistors, as inductance is the main nonideality for a resistor). It is also assumed—perhaps wrongly!—that ...
... assumed that the reference resistor behaves as a pure resistor—no inductance or capacitance. Such resistors are available as long as the frequency is not too high (they are called non-inductive resistors, as inductance is the main nonideality for a resistor). It is also assumed—perhaps wrongly!—that ...
AC_2014mar10
... • The constant is called the decay constant or damping constant (the inverse of the time constant) with units of inverse time. • Note that the presence of damping makes the oscillating frequency to be less than the resonant frequency 0. • If the friction in the system is higher increases (sys ...
... • The constant is called the decay constant or damping constant (the inverse of the time constant) with units of inverse time. • Note that the presence of damping makes the oscillating frequency to be less than the resonant frequency 0. • If the friction in the system is higher increases (sys ...
meres stilusfajl
... 2.4. Measurement square-wave response of the amplifier After setting jumpers JP7, JP14 ON and JP15 OFF, connect a 1 kHz square-wave signal to the input! 2.4.1 Observe the time function of the output signal and measure its rise time and top-drop! (Which time constant is related to top-drop?) 2.4.2 Co ...
... 2.4. Measurement square-wave response of the amplifier After setting jumpers JP7, JP14 ON and JP15 OFF, connect a 1 kHz square-wave signal to the input! 2.4.1 Observe the time function of the output signal and measure its rise time and top-drop! (Which time constant is related to top-drop?) 2.4.2 Co ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.